Addressing Hyperpigmentation: A Comprehensive Look At Bleaching Agents
Addressing Hyperpigmentation: A Comprehensive Look at Bleaching Agents
Related Articles: Addressing Hyperpigmentation: A Comprehensive Look at Bleaching Agents
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Addressing Hyperpigmentation: A Comprehensive Look at Bleaching Agents. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Addressing Hyperpigmentation: A Comprehensive Look at Bleaching Agents

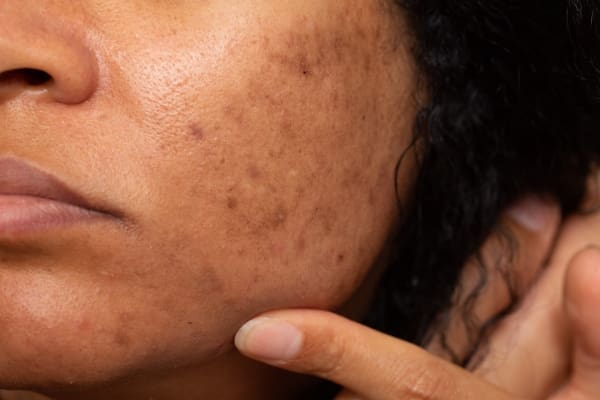
Hyperpigmentation, commonly known as dark spots, is a prevalent skin condition characterized by areas of darkened skin. These spots can arise from various factors, including sun exposure, acne, inflammation, hormonal changes, and certain medications. While they are generally harmless, hyperpigmentation can be a source of cosmetic concern, prompting individuals to seek treatments that can lighten or fade these darkened patches.
One approach frequently employed to address hyperpigmentation is the use of bleaching agents. These topical solutions contain ingredients that work to inhibit the production of melanin, the pigment responsible for skin color. Bleaching agents are available over-the-counter (OTC) and through prescription, with varying strengths and active ingredients.
Understanding the Mechanism of Action
Bleaching agents work by interfering with the production of melanin, the pigment that gives skin its color. Melanin is produced by specialized cells called melanocytes, located in the lower layer of the epidermis. These agents target different stages of the melanin production process, effectively reducing the amount of melanin deposited in the skin.
Common Bleaching Agents and Their Mechanisms
Several active ingredients are commonly found in bleaching agents, each with its unique mechanism of action:
- Hydroquinone: This is a potent ingredient that inhibits the enzyme tyrosinase, which is crucial for the production of melanin. Hydroquinone is available in varying concentrations, with higher concentrations requiring a prescription.
- Kojic Acid: Derived from fungi, kojic acid also inhibits tyrosinase activity, but its efficacy is generally considered weaker than hydroquinone.
- Azelaic Acid: This ingredient acts as a tyrosinase inhibitor and also has anti-inflammatory properties, making it suitable for treating hyperpigmentation associated with acne.
- Retinoids: Retinoids, derivatives of vitamin A, are known to accelerate skin cell turnover, promoting the shedding of pigmented cells and revealing brighter skin underneath.
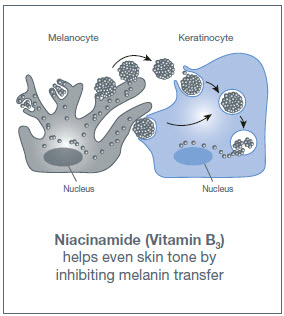
- Niacinamide (Vitamin B3): While not a direct melanin inhibitor, niacinamide reduces inflammation and strengthens the skin barrier, contributing to the overall improvement of hyperpigmentation.
- Alpha Hydroxy Acids (AHAs): These acids, like glycolic acid and lactic acid, exfoliate the skin’s surface, removing dead cells and revealing brighter skin. They also improve skin texture and tone.
- Tranexamic Acid: This ingredient inhibits the production of plasmin, an enzyme involved in melanin production, leading to a reduction in hyperpigmentation.
Considerations for Choosing a Bleaching Agent
Selecting the appropriate bleaching agent depends on several factors, including the severity of hyperpigmentation, skin type, individual sensitivity, and underlying causes.
- Severity of Hyperpigmentation: For mild hyperpigmentation, OTC products containing lower concentrations of bleaching agents may suffice. However, for more severe cases, prescription-strength formulations may be necessary.
- Skin Type: Individuals with sensitive skin may experience irritation or allergic reactions to certain bleaching agents. It is crucial to choose products formulated for sensitive skin or consult a dermatologist for personalized recommendations.
- Individual Sensitivity: Patch testing is recommended before applying any new product to the entire face. This helps identify potential allergies or sensitivities.
- Underlying Causes: Addressing the underlying cause of hyperpigmentation, such as acne or sun exposure, is crucial for long-term success. Sun protection is essential for preventing further pigmentation and maintaining results.
Potential Side Effects and Risks
While bleaching agents can effectively address hyperpigmentation, they are not without potential side effects. Common side effects include:
- Skin Irritation: Redness, dryness, burning, and itching are common side effects, especially with stronger formulations.
- Allergic Reactions: Some individuals may experience allergic reactions to certain ingredients, leading to rash, swelling, or blistering.
- Skin Discoloration: Prolonged use of hydroquinone can lead to ochronosis, a condition characterized by bluish-black skin discoloration.
- Increased Sensitivity to Sun: Bleaching agents can make the skin more sensitive to sun exposure, increasing the risk of sunburn and further hyperpigmentation.
Importance of Sun Protection
Regardless of the bleaching agent chosen, sun protection is paramount. UV radiation is a major contributor to hyperpigmentation, and protecting the skin from the sun is crucial for maintaining results and preventing further pigmentation.
Tips for Using Bleaching Agents Effectively
- Consult a Dermatologist: Before using any bleaching agent, consult a dermatologist to determine the most appropriate treatment plan for your specific needs and skin type.
- Start Slowly: Begin with a lower concentration of the bleaching agent and gradually increase the frequency of application as tolerated.
- Patch Test: Always perform a patch test before applying any new product to the entire face.
- Use Sunscreen: Apply a broad-spectrum sunscreen with an SPF of 30 or higher daily, even on cloudy days.
- Be Patient: Bleaching agents take time to work, and results may not be visible for several weeks or months.
- Avoid Over-Exfoliation: Excessive exfoliation can irritate the skin and hinder the healing process.
- Hydrate: Keep the skin well-hydrated by using a gentle moisturizer.
- Avoid Harsh Scrubs: Avoid harsh scrubs that can irritate the skin and worsen hyperpigmentation.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: How long does it take for bleaching agents to work?
A: The time it takes for bleaching agents to work varies depending on the individual, the severity of hyperpigmentation, and the specific product used. Results may be visible within a few weeks, but it can take several months to see significant improvement.
Q: Are bleaching agents safe for all skin types?
A: Bleaching agents are not safe for all skin types. Individuals with sensitive skin may experience irritation or allergic reactions. It is essential to choose products formulated for sensitive skin or consult a dermatologist for personalized recommendations.
Q: Can bleaching agents cause permanent skin damage?
A: Prolonged use of high-concentration hydroquinone can lead to ochronosis, a condition characterized by bluish-black skin discoloration. However, with proper use and consultation with a dermatologist, bleaching agents are generally safe and do not cause permanent skin damage.
Q: Can I use bleaching agents during pregnancy or breastfeeding?
A: It is generally advised to avoid using bleaching agents during pregnancy or breastfeeding, as there is limited research on their safety during these periods. Consult with a dermatologist for personalized advice.
Q: Can I use bleaching agents on my entire face?
A: Bleaching agents are typically applied only to the affected areas of hyperpigmentation. Applying them to the entire face can lead to irritation and dryness.
Conclusion
Bleaching agents can be effective in addressing hyperpigmentation, but it is crucial to approach their use with caution and awareness. Consulting a dermatologist is essential to determine the most appropriate treatment plan for your individual needs and skin type. Choosing the right product, understanding its mechanism of action, and following proper application techniques can help minimize the risk of side effects and maximize the effectiveness of the treatment. Remember, consistent sun protection is crucial for maintaining results and preventing further pigmentation.




![[PDF] Postinflammatory hyperpigmentation: a review of the epidemiology, clinical features, and](https://d3i71xaburhd42.cloudfront.net/bdaea9452867535c21984b26455af5de8cc84414/3-Figure2-1.png)

Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Addressing Hyperpigmentation: A Comprehensive Look at Bleaching Agents. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!