Demystifying Appliance Wattage: A Guide To Understanding Your Energy Consumption
Demystifying Appliance Wattage: A Guide to Understanding Your Energy Consumption
Related Articles: Demystifying Appliance Wattage: A Guide to Understanding Your Energy Consumption
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Demystifying Appliance Wattage: A Guide to Understanding Your Energy Consumption. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Demystifying Appliance Wattage: A Guide to Understanding Your Energy Consumption
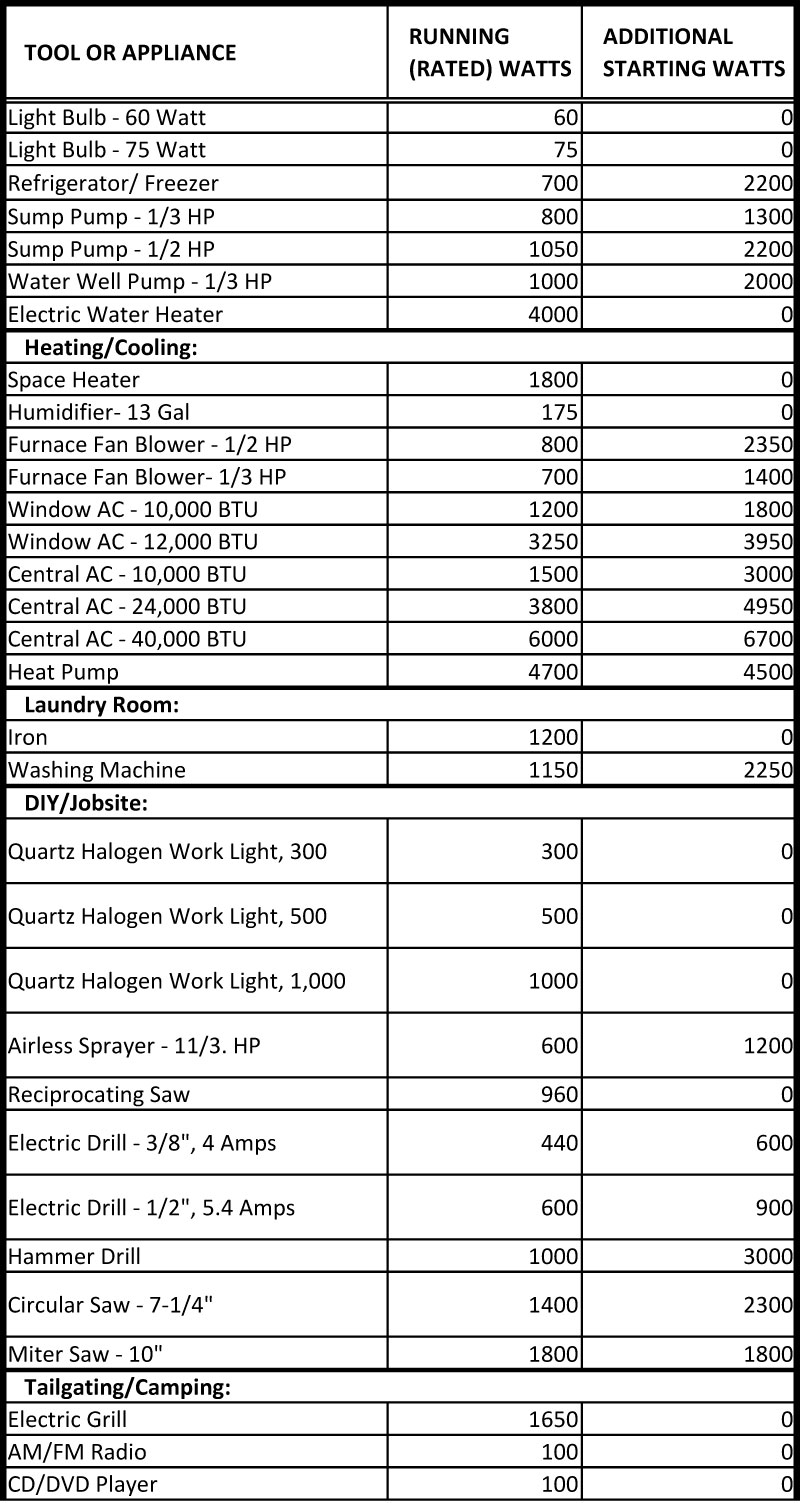
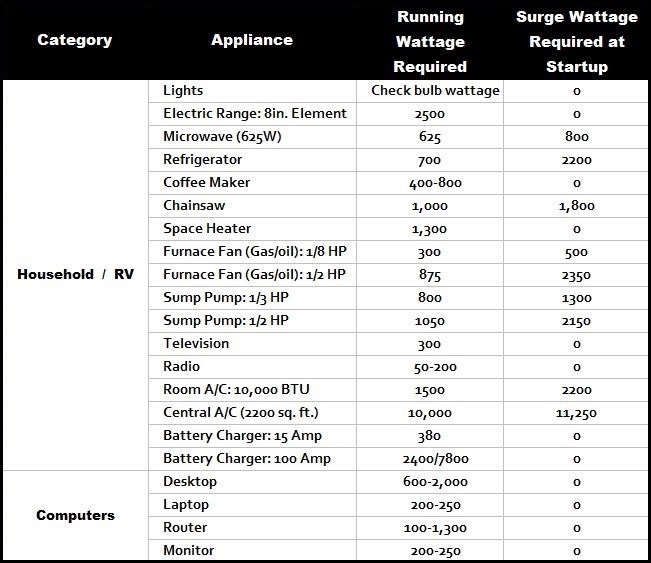
In today’s world, where environmental consciousness is paramount and energy costs are a significant household expense, understanding appliance wattage becomes crucial. This information provides valuable insights into energy consumption patterns, allowing individuals to make informed decisions regarding appliance usage and potentially reduce their environmental footprint and energy bills.
Understanding Wattage and Its Significance
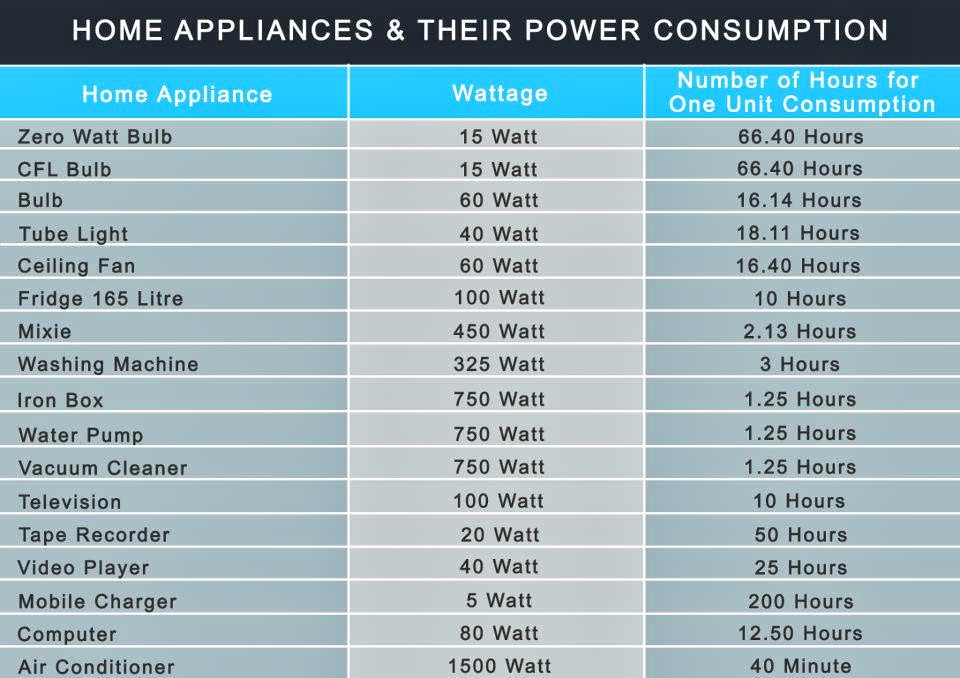
Wattage, measured in watts (W), represents the power an appliance consumes. The higher the wattage, the more electricity the appliance uses. This information is typically found on the appliance’s label or in its user manual.
The Importance of Appliance Wattage Charts
Appliance wattage charts are invaluable tools for understanding the energy consumption of various household appliances. These charts compile data on the wattage of common appliances, providing a comprehensive overview of their energy usage. This information empowers consumers to:
- Identify energy-hungry appliances: By comparing wattage ratings, individuals can pinpoint appliances that consume a significant amount of electricity. This knowledge can guide them towards more energy-efficient alternatives or adopting more mindful usage habits.
- Estimate energy costs: With the wattage information, consumers can calculate the cost of running specific appliances, allowing them to make informed decisions regarding usage frequency and potentially identify areas for cost savings.
- Optimize energy efficiency: Understanding appliance wattage enables consumers to make conscious choices about their energy usage. For example, they can opt for appliances with lower wattage ratings or utilize energy-saving features available in many modern appliances.
- Reduce environmental impact: By minimizing energy consumption through informed appliance usage, individuals contribute to a more sustainable future by reducing their carbon footprint.
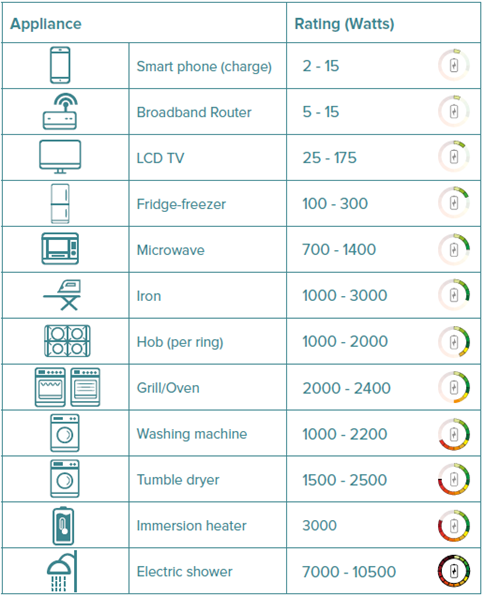
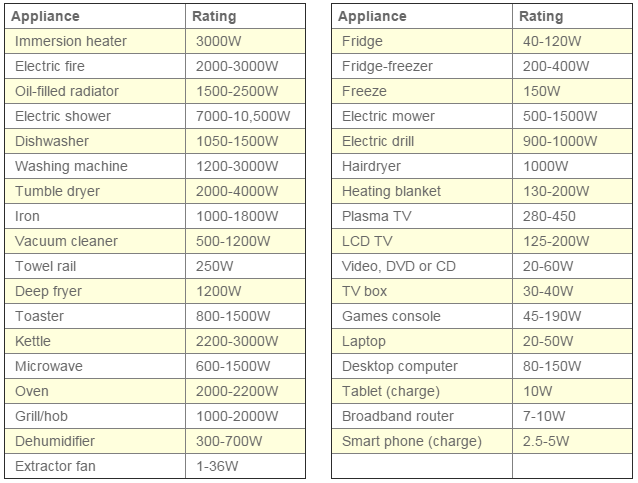
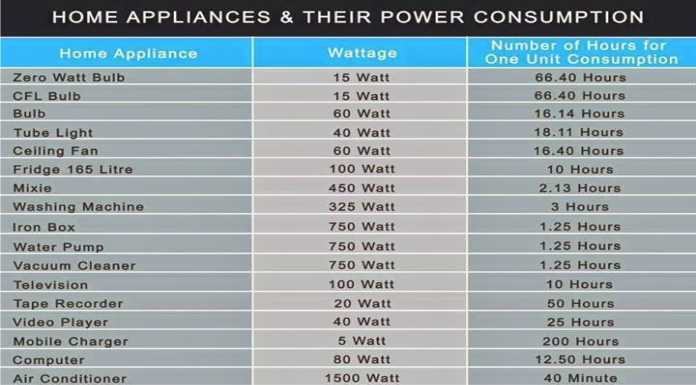
A Comprehensive Guide to Appliance Wattage
The following section provides a detailed breakdown of common household appliances and their typical wattage consumption, offering a comprehensive guide to understanding energy usage in the home:
1. Kitchen Appliances
-
Refrigerator:
- Average wattage: 100-200W
- Energy consumption varies significantly based on size, model, and features.
- Modern refrigerators with energy-efficient technology can significantly reduce energy consumption.
-
Freezer:
- Average wattage: 100-250W
- Similar to refrigerators, energy consumption depends on size and model.
- Consider using a chest freezer for optimal energy efficiency.
-
Oven:
- Average wattage: 2,000-3,000W
- Electric ovens generally consume more power than gas ovens.
- Utilize the oven’s self-cleaning feature sparingly as it consumes significant energy.
-
Microwave:
- Average wattage: 700-1,200W
- Microwave ovens are generally more energy-efficient than traditional ovens.
- Choosing a model with a lower wattage can save energy.
-
Dishwasher:
- Average wattage: 1,200-1,800W
- Energy consumption depends on the model and the selected cycle.
- Opt for energy-efficient dishwashers and use the appropriate cycle based on the level of soiling.
-
Coffee Maker:
- Average wattage: 800-1,200W
- Energy consumption varies based on the size and type of coffee maker.
- Consider using a programmable coffee maker to reduce energy waste.
-
Toaster:
- Average wattage: 800-1,200W
- Energy consumption depends on the number of slices and the heating elements.
- Opt for toasters with multiple settings to adjust power consumption based on the desired level of toast.
2. Laundry Appliances
-
Washing Machine:
- Average wattage: 500-1,500W
- Energy consumption depends on the model, load size, and water temperature.
- Utilize cold water washes whenever possible and select the appropriate load size.
-
Clothes Dryer:
- Average wattage: 3,000-5,000W
- Energy consumption is significantly higher than washing machines.
- Consider using a clothesline or a dryer with an energy-efficient heat pump to reduce energy consumption.
3. Heating and Cooling Systems
-
Air Conditioner:
- Average wattage: 1,000-1,500W
- Energy consumption varies based on the size and type of air conditioner.
- Utilize fans, window blinds, and other energy-saving techniques to minimize air conditioning usage.
-
Heating System:
- Average wattage: Varies significantly based on type and size.
- Gas heating systems generally consume less energy than electric heating systems.
- Ensure proper insulation and sealing of windows and doors to minimize heat loss.
4. Entertainment Systems
-
Television:
- Average wattage: 50-200W
- Energy consumption varies based on screen size and technology.
- Opt for energy-efficient televisions with LED or OLED technology.
-
Computer:
- Average wattage: 100-250W
- Energy consumption depends on the type and configuration of the computer.
- Consider using a power management setting to reduce energy consumption when not in use.
-
Gaming Console:
- Average wattage: 100-200W
- Energy consumption varies based on the console and the game being played.
- Ensure the console is turned off when not in use.
5. Lighting
-
Incandescent Light Bulb:
- Average wattage: 40-100W
- Incandescent bulbs are the least energy-efficient type of lighting.
- Opt for LED or CFL bulbs for significant energy savings.
-
LED Light Bulb:
- Average wattage: 5-15W
- LED bulbs are highly energy-efficient and have a longer lifespan.
-
CFL Light Bulb:
- Average wattage: 10-25W
- CFL bulbs are more energy-efficient than incandescent bulbs but have a shorter lifespan than LEDs.
Understanding Appliance Wattage: FAQs
1. What factors influence appliance wattage?
Appliance wattage can be influenced by various factors, including:
- Size: Larger appliances generally consume more power.
- Model: Different models of the same appliance can have varying wattage ratings.
- Features: Appliances with advanced features, such as self-cleaning ovens or energy-saving modes, may have higher wattage requirements.
- Usage: The frequency and duration of appliance use directly impact energy consumption.
2. How can I determine the wattage of my appliances?
The wattage of an appliance can usually be found:
- On the appliance’s label: Most appliances have a label that includes the wattage rating.
- In the user manual: The user manual often provides detailed specifications, including wattage.
- Online resources: Websites of appliance manufacturers or energy efficiency organizations may provide wattage information for specific models.
3. How can I reduce my energy consumption from appliances?
Several strategies can help reduce energy consumption from appliances:
- Choose energy-efficient appliances: Opt for models with Energy Star certification or other energy-efficiency ratings.
- Utilize energy-saving features: Many appliances offer energy-saving modes or settings.
- Practice mindful usage: Avoid unnecessary appliance usage and utilize them efficiently.
- Maintain appliances regularly: Ensure appliances are functioning optimally to prevent energy waste.
Tips for Reducing Appliance Energy Consumption
- Unplug unused appliances: Even when turned off, some appliances continue to draw power.
- Use power strips: Power strips allow you to easily disconnect multiple appliances from the power source.
- Wash clothes in cold water: Most laundry detergents are effective in cold water, reducing energy consumption.
- Air dry clothes: Consider air drying clothes instead of using a dryer to save energy.
- Use a programmable thermostat: Set your thermostat to adjust automatically based on your schedule.
- Install a smart meter: A smart meter provides real-time energy usage data, allowing you to monitor and adjust your consumption.
Conclusion
Understanding appliance wattage is crucial for making informed decisions about energy consumption and reducing environmental impact. By using appliance wattage charts, individuals can identify energy-hungry appliances, estimate energy costs, optimize energy efficiency, and contribute to a more sustainable future. By implementing energy-saving strategies and making conscious choices regarding appliance usage, consumers can effectively manage their energy consumption and minimize their environmental footprint.


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Demystifying Appliance Wattage: A Guide to Understanding Your Energy Consumption. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!