Navigating Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia: A Comprehensive Guide To Treatment Options
Navigating Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia: A Comprehensive Guide to Treatment Options
Related Articles: Navigating Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia: A Comprehensive Guide to Treatment Options
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Navigating Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia: A Comprehensive Guide to Treatment Options. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia: A Comprehensive Guide to Treatment Options
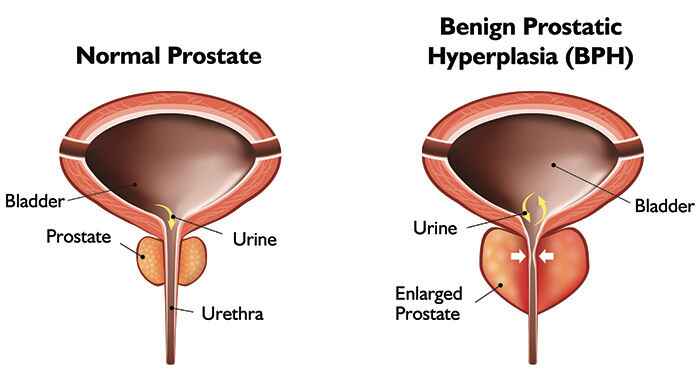
Benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH), commonly referred to as an enlarged prostate, affects millions of men globally. This condition occurs when the prostate gland, located just below the bladder, grows larger than normal, obstructing the flow of urine. While not cancerous, BPH can significantly impact quality of life, causing discomfort, frequent urination, and other urinary issues.
Fortunately, a range of treatment options are available to address BPH, from lifestyle modifications to surgical interventions. This comprehensive guide explores various approaches, including medications, minimally invasive procedures, and surgical options, providing a detailed understanding of their effectiveness, potential risks, and suitability for different individuals.
Understanding the Underlying Mechanisms
Before delving into treatment options, it is crucial to grasp the physiological processes driving BPH. The prostate gland, responsible for producing seminal fluid, undergoes a natural growth process as men age. In some individuals, this growth becomes excessive, leading to BPH. The exact cause of this enlargement remains unclear, but hormonal changes, particularly an increase in dihydrotestosterone (DHT), are believed to play a significant role.
Treatment Options: A Spectrum of Approaches
Treatment for BPH aims to alleviate symptoms and improve urinary flow, ultimately enhancing quality of life. The optimal approach depends on the severity of symptoms, individual preferences, and overall health status.
1. Lifestyle Modifications:
- Fluid Management: Limiting fluid intake, particularly in the evenings, can reduce nighttime urination.
- Dietary Adjustments: A balanced diet, low in saturated fat and cholesterol, may contribute to prostate health.
- Weight Management: Obesity can exacerbate BPH symptoms, making weight loss beneficial.
- Regular Exercise: Physical activity can improve overall health and potentially reduce BPH symptoms.
2. Medications:
- Alpha-blockers: These medications relax the muscles surrounding the prostate and bladder neck, facilitating urine flow. Common examples include tamsulosin (Flomax), terazosin (Hytrin), and doxazosin (Cardura).
- 5-alpha reductase inhibitors: These medications shrink the prostate gland by blocking the conversion of testosterone to DHT. Finasteride (Proscar) and dutasteride (Avodart) are commonly prescribed.
- Combination Therapy: Combining alpha-blockers and 5-alpha reductase inhibitors can provide synergistic effects, leading to greater symptom relief.
- Other Medications: Certain medications, such as anticholinergics, can help manage urinary frequency and urgency, but their effectiveness in BPH is limited.
3. Minimally Invasive Procedures:
- Transurethral Needle Ablation (TUNA): This procedure uses radiofrequency energy to heat and destroy prostate tissue.
- Transurethral Microwave Thermotherapy (TUMT): This technique employs microwave energy to shrink the prostate.
- Transurethral Electrovaporization (TUVP): This method utilizes an electric current to vaporize excess prostate tissue.
- High-Intensity Focused Ultrasound (HIFU): This non-invasive procedure uses focused ultrasound waves to destroy prostate tissue.
4. Surgical Interventions:
- Transurethral Resection of the Prostate (TURP): This procedure involves removing excess prostate tissue using a resectoscope inserted through the urethra. It is considered the gold standard for BPH surgery.
- Open Prostatectomy: This procedure involves surgically removing the enlarged prostate through an incision in the abdomen. It is typically reserved for very large prostates or when other treatments have failed.
- Laser Prostatectomy: This minimally invasive procedure uses laser energy to remove prostate tissue.
Choosing the Right Treatment:
Selecting the most appropriate treatment requires careful consideration of individual factors, including:
- Severity of symptoms: Mild symptoms may be effectively managed with lifestyle changes or medication. Severe symptoms may necessitate more invasive procedures.
- Age and overall health: Younger and healthier individuals may be better candidates for more aggressive treatments.
- Individual preferences: Some individuals prefer non-invasive options, while others may opt for surgery for faster relief.
- Potential risks and benefits: Each treatment option carries specific risks and benefits that must be carefully weighed.
FAQs: Addressing Common Concerns
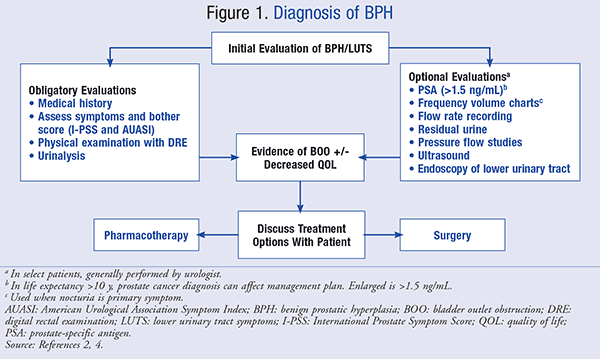
Q: How is BPH diagnosed?
A: Diagnosis typically involves a combination of physical examination, medical history, and diagnostic tests, including:
- Digital rectal examination (DRE): A doctor inserts a gloved finger into the rectum to feel the size and texture of the prostate.
- Urinalysis: A urine sample is analyzed for signs of infection or other abnormalities.
- Uroflowmetry: This test measures the rate and volume of urine flow.
- Post-void residual volume (PVR): This test measures the amount of urine remaining in the bladder after urination.
- Prostate-specific antigen (PSA) test: This blood test measures the level of PSA, a protein produced by the prostate. Elevated PSA levels may indicate BPH, prostate cancer, or other conditions.
Q: What are the potential risks of BPH treatment?
A: Risks vary depending on the chosen treatment. Potential complications include:
- Medication side effects: Alpha-blockers can cause dizziness, low blood pressure, and retrograde ejaculation. 5-alpha reductase inhibitors can reduce libido and cause erectile dysfunction.
- Procedural complications: Minimally invasive procedures and surgeries can lead to bleeding, infection, urinary incontinence, and erectile dysfunction.
Q: Can BPH be prevented?
A: While there is no guaranteed way to prevent BPH, certain lifestyle modifications may reduce the risk, including:
- Maintaining a healthy weight: Obesity is linked to an increased risk of BPH.
- Eating a balanced diet: A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains may be protective.
- Regular exercise: Physical activity can promote overall health and may reduce BPH risk.
Tips for Managing BPH:
- Consult a healthcare professional: Early diagnosis and treatment can help prevent complications.
- Follow treatment recommendations: Adhere to prescribed medications and lifestyle changes.
- Attend regular checkups: Monitoring BPH progression and managing potential complications.
- Seek information and support: Connect with support groups or online resources for guidance and emotional support.
Conclusion: Empowering Men to Take Control of Their Health
BPH is a common condition that can significantly impact quality of life. However, with effective treatment options and proactive management, men can navigate BPH successfully. Understanding the available approaches, their benefits, and potential risks empowers individuals to make informed decisions about their healthcare. By working closely with healthcare professionals and adopting healthy lifestyle habits, men can effectively manage BPH and maintain a fulfilling life.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia: A Comprehensive Guide to Treatment Options. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!