Navigating The Plate: Dietary Strategies For Rheumatoid Arthritis Management
Navigating the Plate: Dietary Strategies for Rheumatoid Arthritis Management
Related Articles: Navigating the Plate: Dietary Strategies for Rheumatoid Arthritis Management
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Plate: Dietary Strategies for Rheumatoid Arthritis Management. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Plate: Dietary Strategies for Rheumatoid Arthritis Management

Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic autoimmune disease that affects the joints, causing pain, stiffness, and inflammation. While there is no cure for RA, dietary interventions can play a significant role in managing symptoms and improving overall well-being. This article delves into the complex relationship between diet and RA, exploring the best food choices and dietary strategies for those living with the condition.
Understanding the Connection Between Diet and Rheumatoid Arthritis
The exact cause of RA remains elusive, but research suggests a combination of genetic predisposition and environmental factors, including diet, contribute to its development. While the link between diet and RA is complex, emerging evidence points towards the potential impact of certain dietary components on inflammation and immune system function.
Anti-Inflammatory Foods: A Cornerstone of the RA Diet
Inflammation is a key characteristic of RA, and reducing inflammation through dietary choices can significantly impact symptom management. Foods rich in antioxidants, omega-3 fatty acids, and certain vitamins and minerals have been shown to possess anti-inflammatory properties.
1. Omega-3 Fatty Acids: A Natural Anti-Inflammatory
Omega-3 fatty acids, found primarily in fatty fish like salmon, mackerel, and tuna, have demonstrated anti-inflammatory effects. They help reduce the production of inflammatory chemicals in the body, potentially easing joint pain and stiffness.
2. Antioxidants: Fighting Free Radicals
Antioxidants, found in fruits, vegetables, and certain spices, combat free radicals, unstable molecules that can damage cells and contribute to inflammation. Foods rich in antioxidants include berries, leafy green vegetables, tomatoes, turmeric, and ginger.
3. Vitamin D: Supporting Immune Function
Vitamin D plays a crucial role in immune system regulation. Sunlight exposure is the primary source of vitamin D, but dietary sources like fatty fish, fortified milk, and eggs can also contribute. Adequate vitamin D levels may help modulate the immune response in RA.
4. Cruciferous Vegetables: Potential for RA Management
Cruciferous vegetables like broccoli, cauliflower, and Brussels sprouts contain compounds that may help reduce inflammation. Studies suggest these vegetables may have a role in modulating the immune response in RA.
5. Fiber: Promoting Gut Health
A diet rich in fiber, found in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, promotes a healthy gut microbiome. Research suggests a link between gut health and immune function, highlighting the importance of fiber in managing RA.
Foods to Limit or Avoid: A Focus on Reducing Inflammation
While certain foods can help manage RA symptoms, others may contribute to inflammation and worsen the condition.
1. Saturated and Trans Fats: Avoiding Inflammatory Triggers
Saturated and trans fats, found in red meat, butter, and processed foods, can increase inflammation. Limiting these fats can help reduce inflammation and improve overall health.
2. Sugar: A Potential Inflammatory Agent
Excessive sugar consumption can contribute to inflammation and may worsen RA symptoms. Limiting added sugars in processed foods, sugary drinks, and desserts is essential.
3. Processed Foods: A Source of Inflammatory Compounds
Processed foods, often high in saturated fat, sugar, and salt, contain inflammatory compounds that can exacerbate RA symptoms. Opting for whole, unprocessed foods is crucial.
4. Alcohol: A Potential Trigger for Inflammation
Alcohol consumption can increase inflammation and may worsen RA symptoms. Limiting alcohol intake or abstaining entirely is recommended.
5. Nightshade Vegetables: A Potential Trigger for Some
Nightshade vegetables, including tomatoes, potatoes, and peppers, contain a compound called solanine, which some individuals with RA find triggers their symptoms. While research is inconclusive, individuals may benefit from limiting or eliminating these vegetables from their diet.
Dietary Strategies for Rheumatoid Arthritis Management
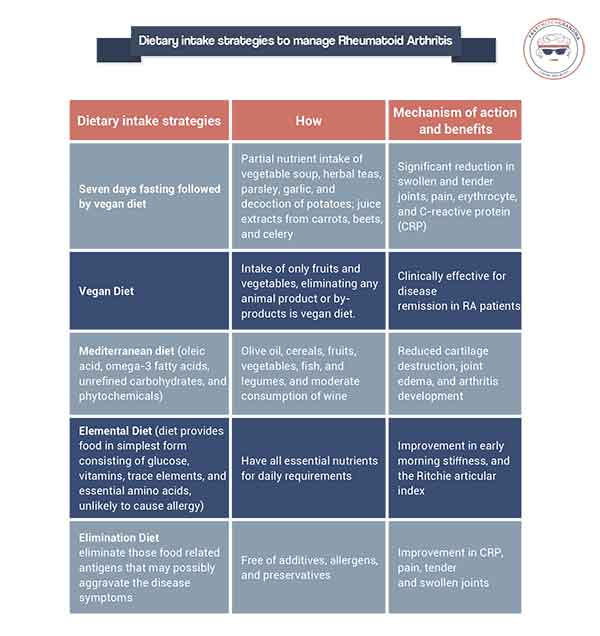
1. The Mediterranean Diet: A Model for Anti-Inflammatory Eating
The Mediterranean diet, characterized by a high intake of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, legumes, and healthy fats, has been linked to reduced inflammation and improved cardiovascular health. It provides a framework for creating a balanced and anti-inflammatory diet for RA management.
2. The DASH Diet: Focusing on Blood Pressure Control
The Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension (DASH) diet emphasizes fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and low-fat dairy, while limiting saturated fat, cholesterol, and sodium. This diet can help manage blood pressure, a common issue for individuals with RA, and contribute to overall health.
3. Personalized Nutrition: Tailoring the Diet to Individual Needs
No single diet fits all. Individual dietary needs and preferences should be considered when developing an RA-friendly eating plan. Working with a registered dietitian can provide personalized guidance and support.
4. Food Sensitivity Testing: Identifying Potential Triggers
Food sensitivities can contribute to inflammation and worsen RA symptoms. Consider food sensitivity testing to identify potential triggers and adjust the diet accordingly.
5. Supplementation: Addressing Potential Deficiencies
Individuals with RA may experience deficiencies in certain nutrients, such as vitamin D, omega-3 fatty acids, or antioxidants. Supplementation, under the guidance of a healthcare professional, can help address these deficiencies.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: Can diet cure rheumatoid arthritis?
A: While diet cannot cure RA, it can significantly impact symptom management and overall health.
Q: Are there specific foods that trigger RA symptoms?
A: While research is ongoing, some individuals report symptom flare-ups after consuming nightshade vegetables, processed foods, or excessive sugar.
Q: Can I still enjoy my favorite foods if I have RA?
A: Yes, you can still enjoy your favorite foods, but moderation and mindful choices are key. Focus on incorporating anti-inflammatory foods into your diet while limiting those that may contribute to inflammation.
Q: How can I make sure I’m getting enough nutrients on an RA-friendly diet?
A: Consult with a registered dietitian to create a personalized meal plan that meets your individual nutritional needs.
Tips for Incorporating an RA-Friendly Diet
1. Start with Small Changes: Instead of completely overhauling your diet, focus on making gradual changes. Replace one sugary drink with water, add more vegetables to your meals, or choose whole grains over refined grains.
2. Cook More Meals at Home: This allows you to control ingredients and portion sizes.
3. Read Food Labels: Pay attention to added sugars, saturated fats, and sodium content.
4. Experiment with New Recipes: Find recipes that incorporate anti-inflammatory foods and satisfy your taste buds.
5. Stay Hydrated: Drink plenty of water throughout the day to support overall health.
Conclusion
Dietary interventions play a crucial role in managing rheumatoid arthritis. By focusing on anti-inflammatory foods, limiting potential triggers, and adopting healthy eating strategies, individuals with RA can improve their symptoms, enhance their quality of life, and support their overall well-being. Collaboration with a healthcare professional, including a registered dietitian, is essential for developing a personalized and effective dietary plan.



:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/rheumatoid-arthritis-diet-and-exercise-5094998_final-30997c03f3e94927898ceb065d0ee512.jpg)



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Plate: Dietary Strategies for Rheumatoid Arthritis Management. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!