Powering Our Homes: Understanding The Biggest Electricity Consumers
Powering Our Homes: Understanding the Biggest Electricity Consumers
Related Articles: Powering Our Homes: Understanding the Biggest Electricity Consumers
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Powering Our Homes: Understanding the Biggest Electricity Consumers. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Powering Our Homes: Understanding the Biggest Electricity Consumers

Electricity is the lifeblood of modern homes, powering everything from lighting and heating to entertainment and communication. While the convenience it brings is undeniable, understanding the major electricity consumers within our homes is crucial for responsible energy consumption and cost management. This article delves into the significant uses of electricity in a typical household, exploring their importance, benefits, and potential for optimization.
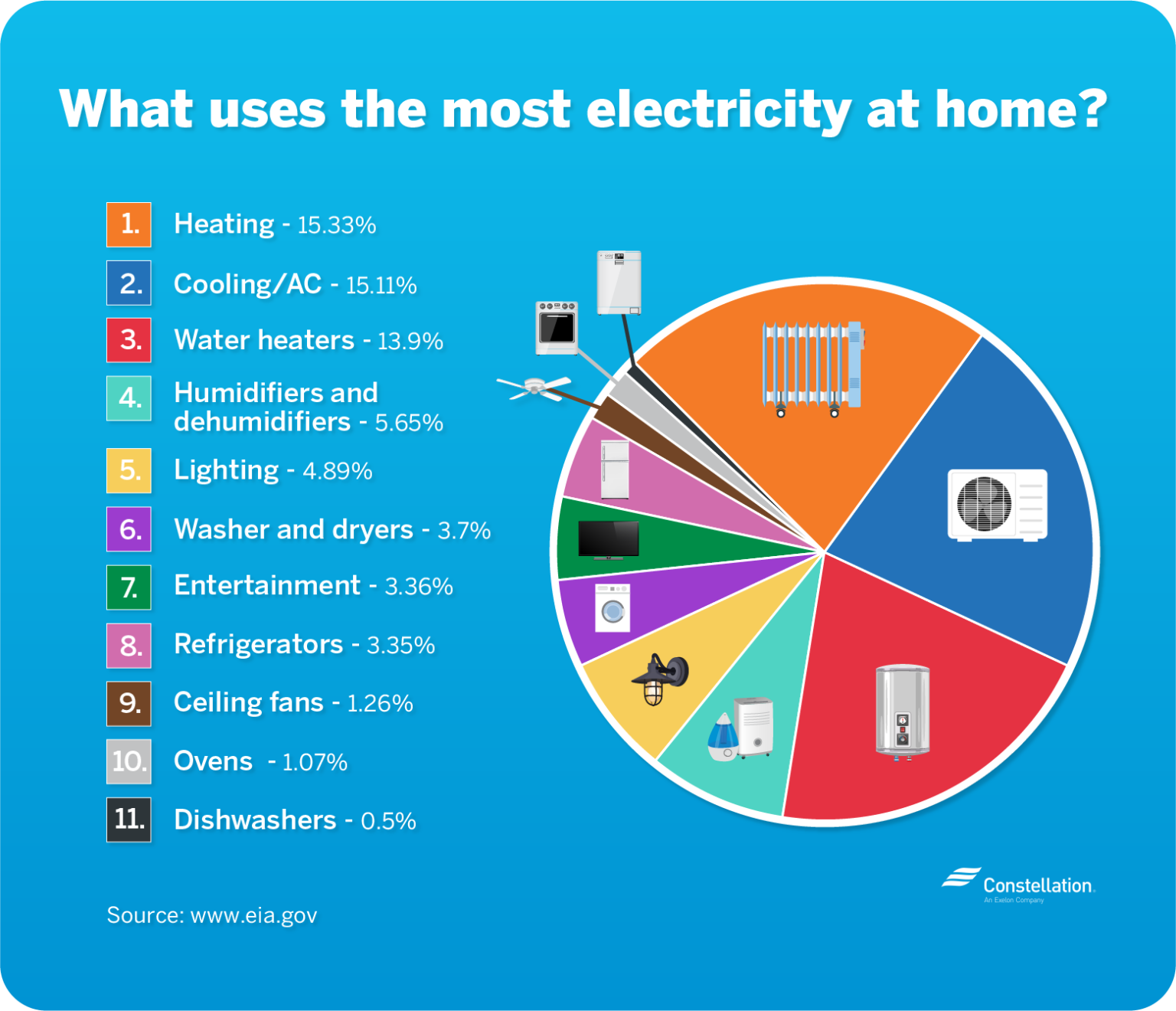
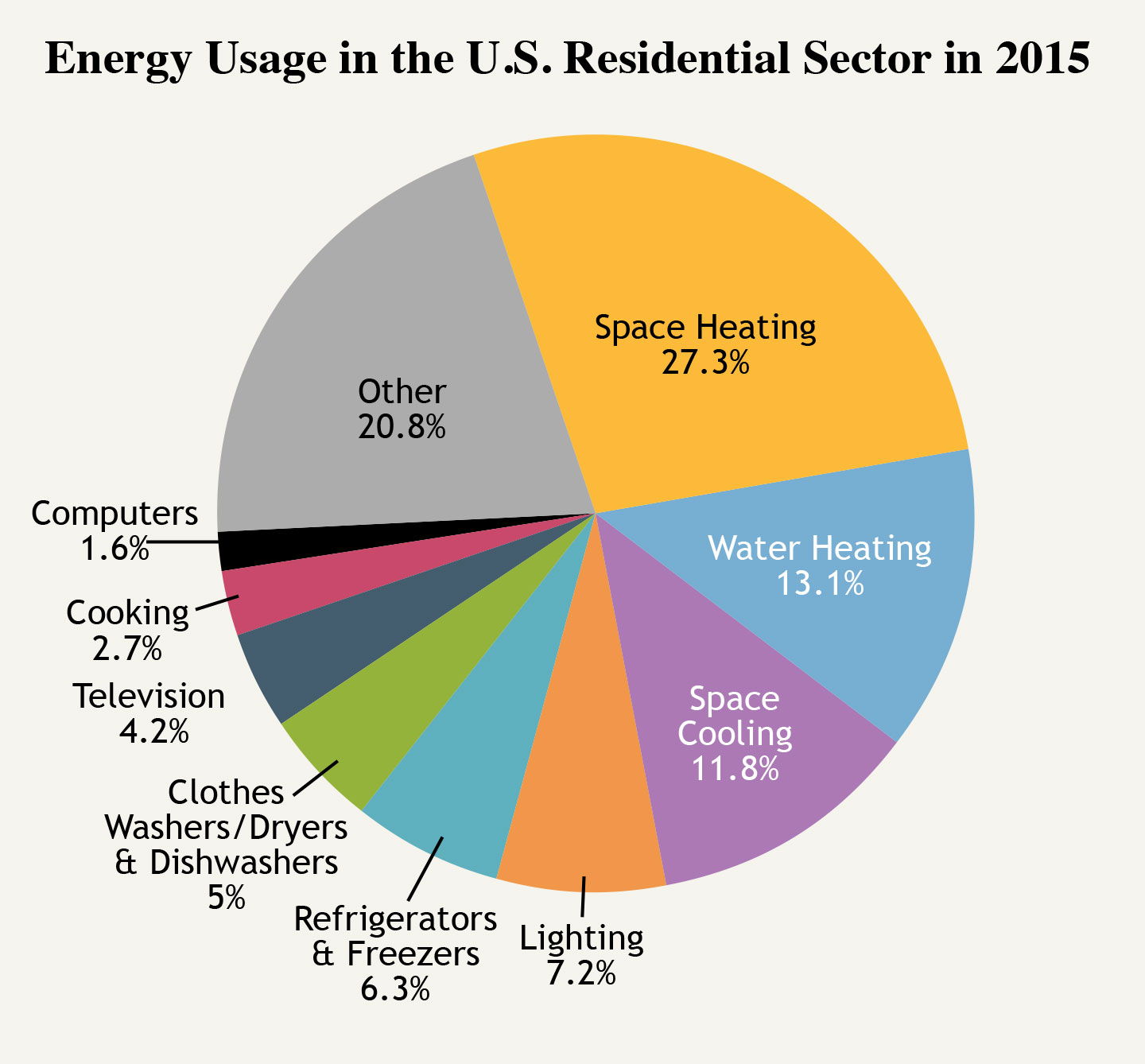
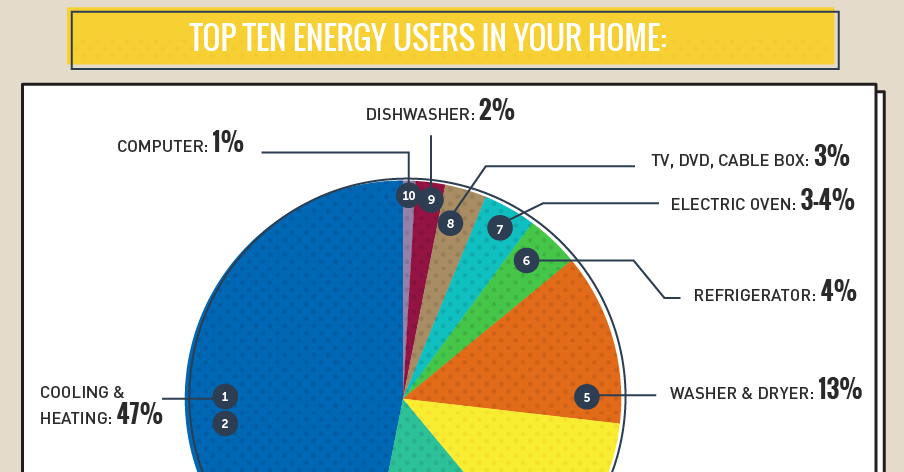
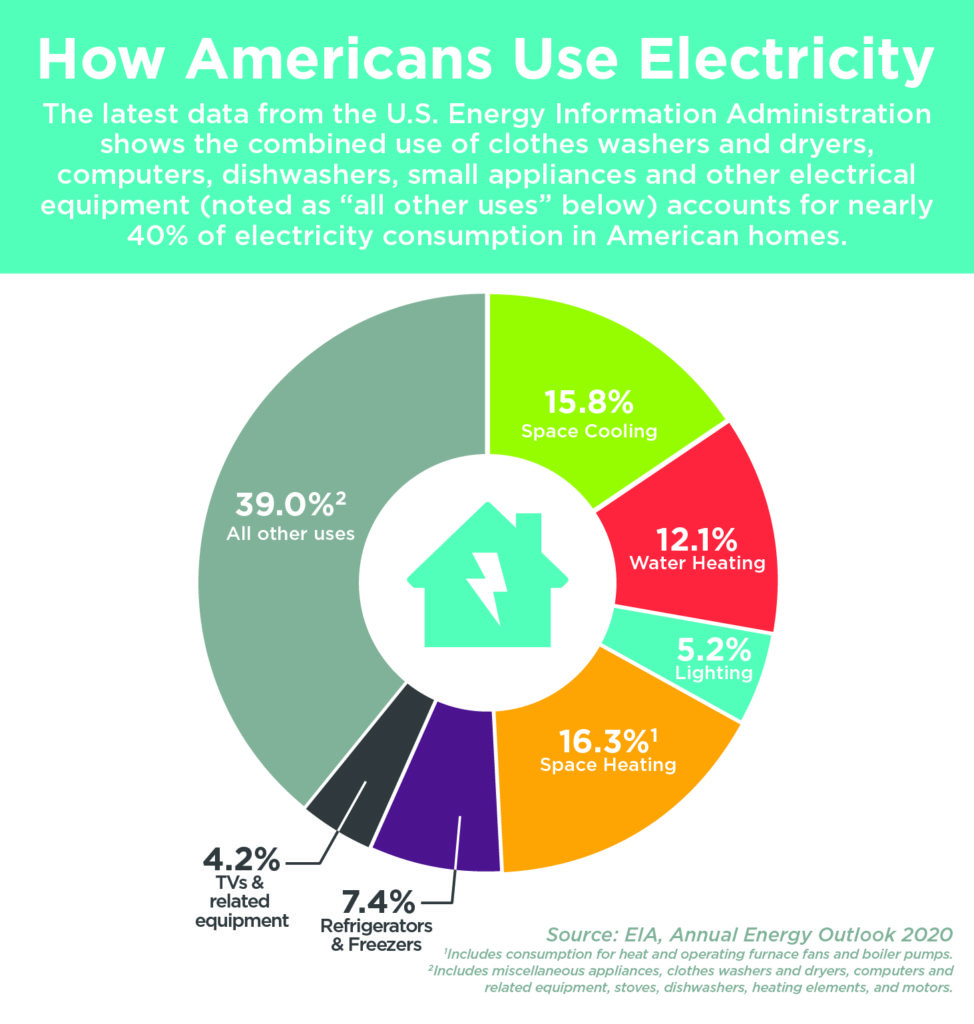
1. Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning (HVAC)
HVAC systems, encompassing heating, ventilation, and air conditioning, are often the biggest electricity consumers in a home, accounting for a significant portion of the energy bill.
Importance: HVAC systems are essential for maintaining a comfortable and healthy indoor environment. They provide warmth during cold weather, cooling during hot weather, and ensure proper ventilation for fresh air circulation.
Benefits:
- Comfort: HVAC systems create a comfortable indoor temperature, regardless of external weather conditions.
- Health: Proper ventilation removes pollutants and allergens, improving indoor air quality and overall health.
- Safety: Heating systems prevent freezing pipes and potential damage during winter, while air conditioning offers relief from extreme heat.
Optimization:
- Energy-efficient models: Investing in energy-efficient HVAC systems with higher SEER (Seasonal Energy Efficiency Ratio) ratings can significantly reduce energy consumption.
- Regular maintenance: Scheduled maintenance ensures optimal performance and prevents breakdowns, minimizing energy waste.
- Smart thermostats: Programmable or smart thermostats allow for customized temperature settings, automatically adjusting the system based on occupancy and weather conditions.
- Proper insulation: Adequate insulation in walls, ceilings, and attics minimizes heat loss or gain, reducing the workload on the HVAC system.
2. Water Heating
Heating water for showers, baths, dishwashing, and laundry accounts for a significant portion of household energy consumption.
Importance: Hot water is essential for daily hygiene, cleaning, and cooking.
Benefits:
- Hygiene: Hot water is crucial for personal hygiene, ensuring cleanliness and health.
- Cooking: Hot water is essential for cooking, cleaning dishes, and various food preparation tasks.
- Laundry: Hot water is required for effective laundry cleaning, removing stains and sanitizing clothes.
Optimization:
- Tankless water heaters: Tankless water heaters heat water on demand, eliminating standby losses and potentially reducing energy consumption.
- Insulating hot water pipes: Insulating pipes prevents heat loss during water transport, improving efficiency.
- Low-flow showerheads and faucets: Reducing water flow minimizes the amount of water that needs to be heated, saving energy.
- Washing clothes in cold water: Many laundry cycles can be completed effectively using cold water, significantly reducing energy usage.
3. Lighting
Lighting plays a crucial role in home safety and comfort, but it can also contribute significantly to electricity consumption.
Importance: Lighting provides visibility, enhancing safety and security within the home. It also creates ambiance and supports various activities.
Benefits:
- Safety: Adequate lighting improves visibility, reducing the risk of accidents and enhancing security.
- Comfort: Proper lighting creates a comfortable and inviting atmosphere, enhancing mood and well-being.
- Functionality: Different types of lighting serve specific purposes, supporting various activities like reading, cooking, or working.
Optimization:
- LED bulbs: LED bulbs are significantly more energy-efficient than traditional incandescent bulbs, consuming less energy while providing equivalent brightness.
- Smart lighting: Smart lighting systems allow for automated control, dimming, and scheduling, optimizing lighting usage and reducing energy waste.
- Natural light: Maximizing natural light through windows and skylights reduces reliance on artificial lighting during daylight hours.
4. Appliances
Household appliances, ranging from refrigerators and ovens to washing machines and dryers, are significant electricity consumers.
Importance: Appliances provide convenience and support various household tasks, simplifying daily life.
Benefits:
- Convenience: Appliances automate tasks, saving time and effort, and making daily life easier.
- Functionality: Different appliances serve specific purposes, supporting cooking, cleaning, entertainment, and communication.
- Safety: Certain appliances, like refrigerators and freezers, preserve food, minimizing spoilage and ensuring food safety.
Optimization:
- Energy-efficient models: Choosing appliances with Energy Star ratings ensures they are energy-efficient and consume less electricity.
- Proper usage: Using appliances efficiently, like running full loads in dishwashers and washing machines, minimizes energy consumption.
- Unplugging unused appliances: Unplugging appliances when not in use prevents phantom load, where devices continue to consume electricity even when turned off.
5. Electronics
Electronics, including televisions, computers, and gaming consoles, contribute to household electricity consumption.
Importance: Electronics provide entertainment, information, and communication, enriching our lives.
Benefits:
- Entertainment: Electronics provide access to a wide range of entertainment options, including movies, music, and gaming.
- Information: Computers and mobile devices offer access to vast amounts of information and online resources.
- Communication: Electronics facilitate communication, allowing us to stay connected with family, friends, and colleagues.
Optimization:
- Energy-saving modes: Utilizing energy-saving modes on televisions and computers reduces energy consumption while maintaining functionality.
- Unplugging devices when not in use: Unplugging chargers and other electronics when not in use minimizes phantom load.
- Choosing energy-efficient models: Selecting televisions and computers with energy-efficient ratings reduces electricity consumption.
FAQs
Q: What are the most energy-intensive appliances in a home?
A: The most energy-intensive appliances typically include refrigerators, water heaters, ovens, and air conditioners.
Q: How can I reduce my electricity bill?
A: Implementing energy-saving strategies like using energy-efficient appliances, optimizing HVAC systems, and minimizing phantom load can significantly reduce electricity consumption and lower your bill.
Q: What is phantom load, and how can I reduce it?
A: Phantom load refers to the energy consumed by devices even when they are turned off but plugged in. Unplugging devices when not in use can effectively minimize phantom load.
Q: How can I make my home more energy-efficient?
A: Implementing energy-efficient practices like using LED bulbs, optimizing HVAC systems, and choosing energy-efficient appliances can make your home more energy-efficient and reduce your environmental footprint.
Tips
- Regularly monitor your energy consumption: Tracking your energy usage allows you to identify areas for improvement and implement targeted energy-saving measures.
- Consider solar energy: Installing solar panels can significantly reduce your reliance on the grid and lower your electricity bill.
- Educate yourself about energy-saving programs: Many utility companies offer programs and rebates for energy-efficient upgrades, providing financial incentives for reducing energy consumption.
- Promote energy conservation in your household: Encourage family members to adopt energy-saving habits, like turning off lights when leaving a room and unplugging devices when not in use.
Conclusion
Understanding the major electricity consumers in our homes is crucial for responsible energy consumption and cost management. By implementing energy-saving strategies, optimizing appliance usage, and adopting energy-efficient technologies, we can minimize our environmental impact and reduce our electricity bills. Making informed choices about our energy usage empowers us to live sustainably and contribute to a greener future.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Powering Our Homes: Understanding the Biggest Electricity Consumers. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!