Shielding Against The Invisible: A Guide To Radiation Protection
Shielding Against the Invisible: A Guide to Radiation Protection
Related Articles: Shielding Against the Invisible: A Guide to Radiation Protection
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Shielding Against the Invisible: A Guide to Radiation Protection. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Shielding Against the Invisible: A Guide to Radiation Protection

Radiation, a ubiquitous force in our universe, can be both beneficial and harmful. While it plays a crucial role in medical imaging, power generation, and scientific research, excessive exposure can pose significant health risks. Understanding the nature of radiation and the various methods for mitigating its impact is essential for safeguarding well-being. This article explores the best ways to protect ourselves from the potentially damaging effects of radiation, providing a comprehensive overview of the science behind shielding and practical strategies for minimizing exposure.
Understanding the Nature of Radiation
Radiation encompasses a spectrum of energy, from the low-energy radio waves used in communication to the high-energy gamma rays emitted by radioactive materials. The key factor determining the potential harm of radiation is its ionizing ability. Ionizing radiation, such as X-rays and gamma rays, carries enough energy to knock electrons out of atoms, creating ions and potentially damaging biological molecules.
Sources of Radiation Exposure
Humans are constantly exposed to low levels of background radiation from natural sources like cosmic rays, radon gas, and radioactive elements in the Earth’s crust. However, there are also numerous man-made sources of radiation, including:
- Medical Procedures: X-rays, CT scans, and nuclear medicine treatments are significant contributors to medical radiation exposure.
- Nuclear Power Plants: While tightly regulated, nuclear power plants release small amounts of radiation into the environment.
- Industrial Applications: Industrial processes like welding and metalworking can involve exposure to X-rays and other forms of radiation.
- Consumer Products: Some consumer products, such as smoke detectors and certain types of watches, contain small amounts of radioactive materials.
The Importance of Radiation Protection
Exposure to ionizing radiation can lead to a range of health problems, including:
- Cancer: Excessive radiation exposure is a known carcinogen, increasing the risk of developing various types of cancer.
- Genetic Damage: Radiation can damage DNA, potentially leading to genetic mutations and birth defects.
- Tissue Damage: High doses of radiation can cause immediate damage to tissues, leading to radiation burns and other acute health effects.
Strategies for Radiation Protection
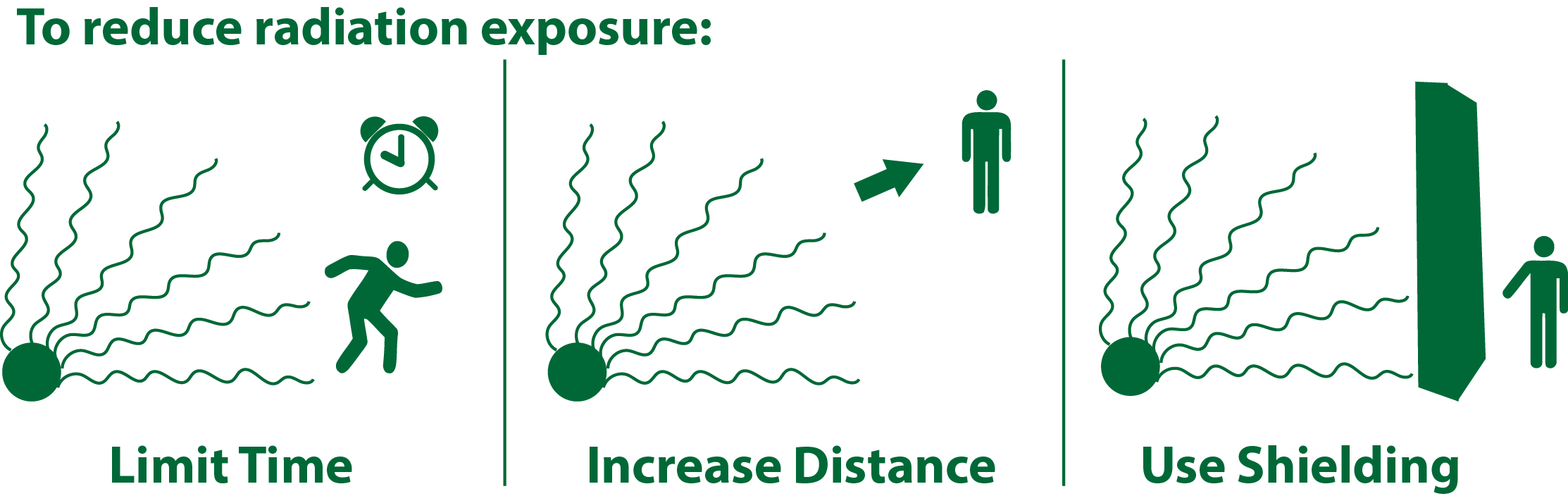
Minimizing radiation exposure is crucial for safeguarding health. The following strategies can be employed to reduce the risk:
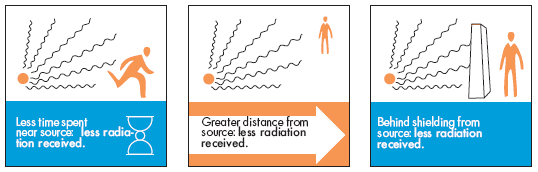
1. Time: Reducing the duration of exposure is a fundamental principle of radiation protection. The longer the exposure time, the greater the cumulative dose.
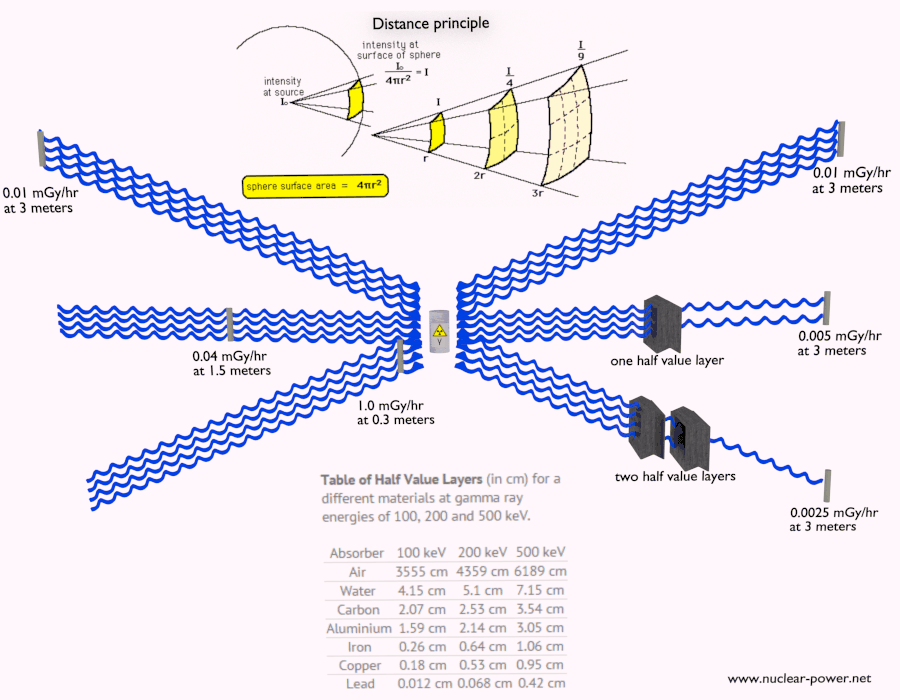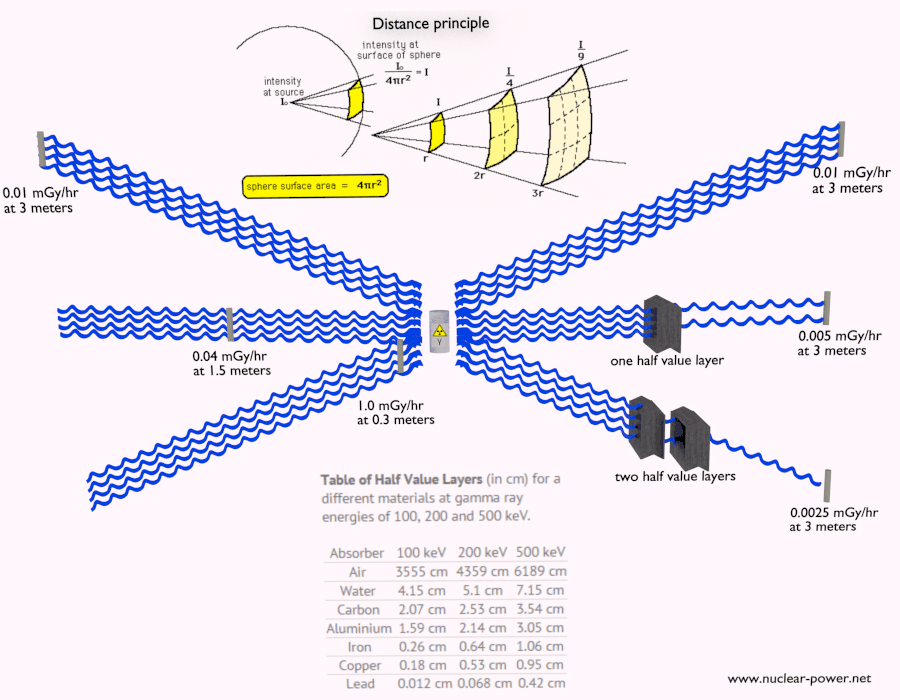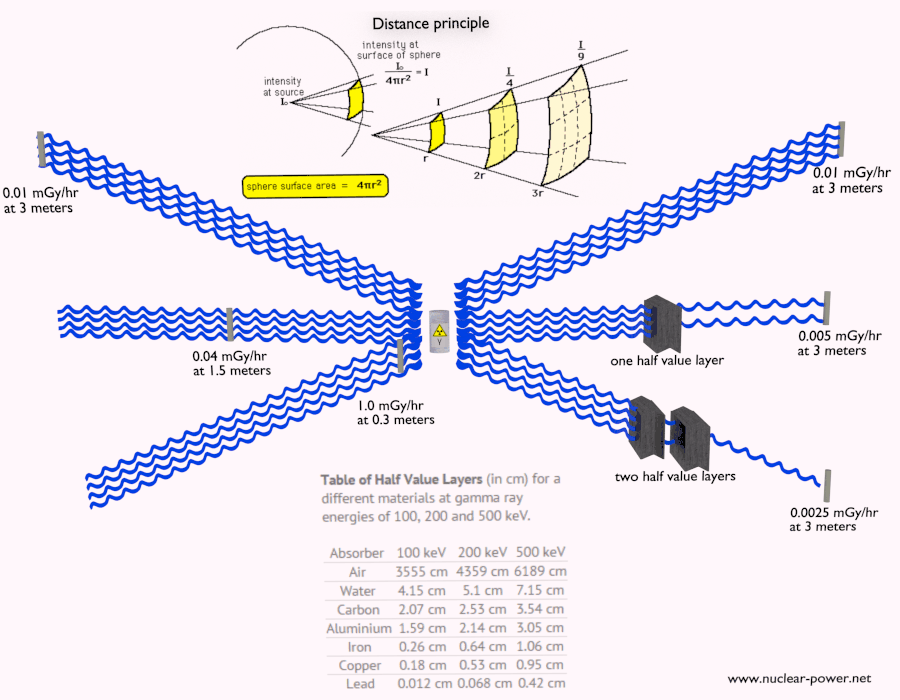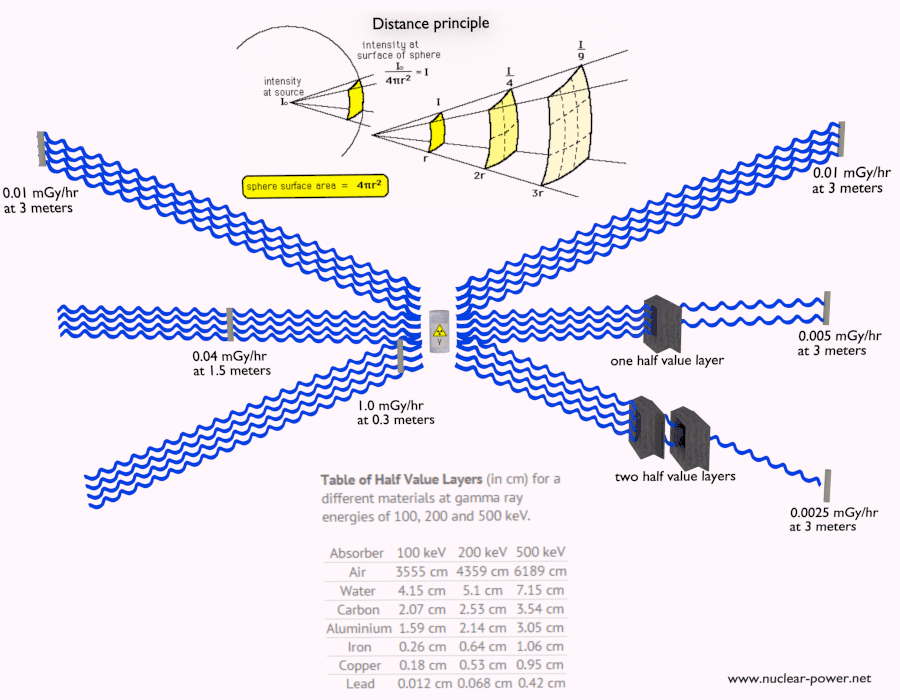
2. Distance: Radiation intensity decreases rapidly with distance from the source. Maintaining a safe distance from radioactive sources can significantly reduce exposure.
3. Shielding: Using appropriate materials to absorb or deflect radiation is the most effective way to reduce exposure. The effectiveness of a shield depends on the type of radiation and the material used.
Shielding Materials and Their Effectiveness
- Lead: Lead is a dense material that effectively absorbs X-rays and gamma rays. It is commonly used in medical imaging equipment, nuclear power plants, and radiation therapy.
- Concrete: Concrete is a readily available and cost-effective shielding material. Its density provides good protection against gamma rays and neutrons.
- Water: Water is an excellent absorber of neutrons and can be used in combination with other shielding materials.
- Steel: Steel is often used in combination with other materials to provide structural support and shielding.
- Plastic: Certain types of plastic, such as polyethylene, can be effective in absorbing beta radiation.
Practical Applications of Radiation Shielding
- Medical Imaging: Lead aprons and shields are used to protect patients and medical personnel during X-ray procedures.
- Nuclear Power Plants: Concrete and steel are used extensively in nuclear power plants to shield workers and the public from radiation.
- Industrial Applications: Lead-lined containers and shielding enclosures are used to protect workers from radiation sources in industrial settings.
- Radiation Therapy: Lead and concrete are used to direct and control radiation beams in cancer treatment.
FAQs on Radiation Protection
Q: Is it safe to use mobile phones?
A: While mobile phones emit low-frequency electromagnetic radiation, there is no conclusive scientific evidence linking their use to health risks. However, it is advisable to minimize exposure, especially for children.
Q: How can I protect myself from radon gas?
A: Radon gas is a naturally occurring radioactive element that can accumulate in homes. Testing for radon levels and implementing mitigation measures, such as sealing cracks and installing ventilation systems, can help reduce exposure.
Q: What should I do if I am exposed to radiation?
A: In the event of a radiation emergency, it is crucial to follow the instructions of local authorities. Seek immediate medical attention and provide information about the exposure event.
Tips for Minimizing Radiation Exposure
- Avoid unnecessary medical imaging. Discuss the risks and benefits of medical procedures with your doctor.
- Limit exposure to sunlight. Ultraviolet radiation from the sun can be harmful to the skin.
- Be mindful of consumer products. Choose products that emit low levels of radiation.
- Stay informed about environmental radiation. Consult local authorities and environmental agencies for information on radiation levels in your area.
Conclusion
Radiation protection is an essential aspect of safeguarding health. By understanding the nature of radiation, its sources, and the methods for minimizing exposure, individuals can take proactive steps to protect themselves from its potentially harmful effects. The strategies outlined in this article, including time, distance, and shielding, provide a comprehensive framework for mitigating radiation risk and ensuring a safe and healthy environment.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Shielding Against the Invisible: A Guide to Radiation Protection. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!