The Act Of Discarding Technology: Exploring The Reasons And Ramifications Of Computer Disposal
The Act of Discarding Technology: Exploring the Reasons and Ramifications of Computer Disposal
Related Articles: The Act of Discarding Technology: Exploring the Reasons and Ramifications of Computer Disposal
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to The Act of Discarding Technology: Exploring the Reasons and Ramifications of Computer Disposal. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Act of Discarding Technology: Exploring the Reasons and Ramifications of Computer Disposal
The act of discarding a computer, often referred to as "throwing it out the window," represents a complex intersection of technological obsolescence, environmental concerns, and societal attitudes towards electronic waste. While the phrase itself is a dramatic and hyperbolic depiction of a physical act, it serves as a potent metaphor for the broader issue of responsible technology disposal. This article delves into the various facets of this issue, examining the motivations behind discarding computers, the potential consequences of improper disposal, and the evolving landscape of responsible technology management.
Motivations for Discarding Computers:
The decision to discard a computer is rarely a straightforward one. It stems from a confluence of factors, including:
-
Technological Obsolescence: Rapid technological advancements lead to a constant cycle of new and improved devices. Older computers, while functional, may struggle to meet the demands of modern software and applications. The allure of faster processors, larger storage capacities, and enhanced features often drives individuals and businesses to replace their existing computers.
-
Hardware Malfunctions: Computers, like any complex machine, are susceptible to breakdowns and malfunctions. When repairs become costly or unfeasible, the decision to discard the device may become the most practical option.
-
Software Compatibility Issues: Outdated operating systems and software can create compatibility issues with newer applications and updates. This can significantly hinder productivity and necessitate a replacement.
-
Security Concerns: Security vulnerabilities in older computers can expose sensitive data to cyberattacks. The need to safeguard personal and professional information may necessitate the disposal of an outdated device.
-
Upgrade Cycles: Businesses often adhere to strict upgrade cycles to maintain a consistent level of technological performance and security within their IT infrastructure. This can lead to the discarding of perfectly functional computers.
Consequences of Improper Disposal:
The act of discarding a computer without proper handling carries significant environmental and societal implications:
-
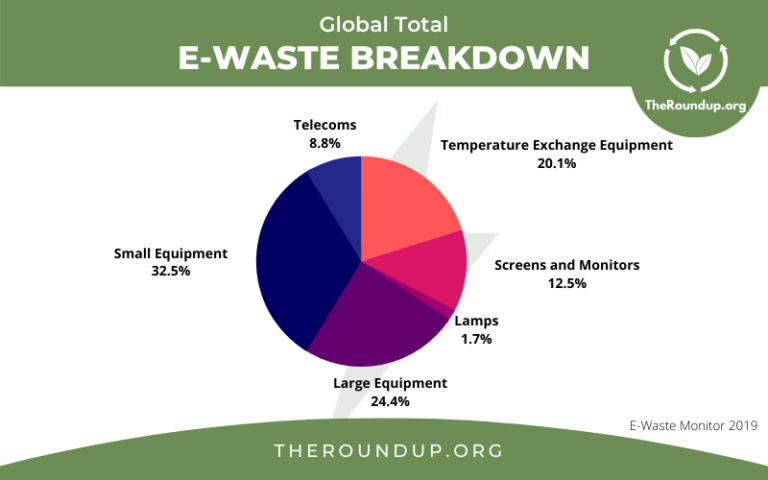
E-Waste and Environmental Contamination: Computers contain a wide array of hazardous materials, including lead, mercury, cadmium, and arsenic. Improper disposal, such as landfilling or burning, releases these toxins into the environment, polluting soil, water sources, and the air.
-
Resource Depletion: The production of new computers requires the extraction of precious metals and other raw materials. Discarding computers without proper recycling perpetuates the cycle of resource depletion and contributes to environmental damage.
-
Security Risks: Discarding computers without properly erasing data leaves sensitive information vulnerable to theft and misuse. This can have severe consequences for individuals and organizations, compromising privacy and financial security.
Responsible Technology Management:
In light of the environmental and societal ramifications of improper computer disposal, responsible technology management has become increasingly crucial:
-
Recycling and Reuse: Recycling programs and e-waste collection initiatives offer a safe and environmentally sound method for disposing of old computers. These programs extract valuable materials and prevent hazardous substances from entering the environment.
-
Data Erasure and Security: Prior to disposal, it is essential to erase all sensitive data from computers to prevent unauthorized access and information theft. Secure data erasure methods ensure that data is permanently removed and cannot be retrieved.
-
Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR): This principle holds manufacturers accountable for the environmental impact of their products throughout their lifecycle. EPR programs encourage manufacturers to design products for easy recycling and to take responsibility for the collection and proper disposal of their products.
-
Sustainable Practices: Businesses and individuals can adopt sustainable practices by opting for energy-efficient computers, minimizing printing, and promoting digital alternatives to paper-based processes.
FAQs
Q: What are the legal implications of improper computer disposal?
A: Many jurisdictions have implemented regulations and laws governing the disposal of electronic waste. Improper disposal can result in fines and penalties for individuals and businesses.
Q: What is the best way to dispose of an old computer?
A: The most responsible option is to recycle the computer through certified e-waste recycling programs or authorized collection centers.
Q: Can I sell or donate an old computer?
A: While selling or donating old computers can be a viable option, it is crucial to ensure that all sensitive data is properly erased and that the recipient is aware of the device’s condition and limitations.
Q: What are some tips for extending the lifespan of a computer?
A: Regular maintenance, such as cleaning, software updates, and virus scans, can help prolong the lifespan of a computer.
Conclusion:
The act of discarding a computer is not merely a physical act of disposal but a complex issue with far-reaching consequences. Responsible technology management, encompassing proper recycling, data security, and sustainable practices, is essential for mitigating the environmental and societal impacts of computer disposal. By embracing responsible technology management practices, individuals and organizations can contribute to a more sustainable future, minimizing the environmental footprint of technology while ensuring the secure and responsible disposal of outdated devices.







Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Act of Discarding Technology: Exploring the Reasons and Ramifications of Computer Disposal. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!