The Arsenal Against Microbes: A Comprehensive Look At Antibacterial Agents
The Arsenal Against Microbes: A Comprehensive Look at Antibacterial Agents
Related Articles: The Arsenal Against Microbes: A Comprehensive Look at Antibacterial Agents
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to The Arsenal Against Microbes: A Comprehensive Look at Antibacterial Agents. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Arsenal Against Microbes: A Comprehensive Look at Antibacterial Agents

Bacteria, ubiquitous and diverse, play crucial roles in our environment. However, some bacterial strains pose significant threats to human health, causing infections ranging from mild skin irritations to life-threatening illnesses. To combat these microbial adversaries, scientists have developed a formidable arsenal of antibacterial agents, collectively known as antibiotics. These compounds, often derived from natural sources or synthesized in laboratories, target specific bacterial processes, disrupting their ability to survive and multiply.
Understanding the Battlefield: A Glimpse into Bacterial Physiology
To appreciate the effectiveness of antibacterial agents, it is crucial to understand the fundamental workings of bacterial cells. These single-celled organisms, unlike eukaryotic cells, lack membrane-bound organelles such as nuclei and mitochondria. Their genetic material, in the form of a single circular DNA molecule, resides in the cytoplasm. This simpler structure, while efficient for bacterial survival, presents unique targets for antimicrobial intervention.
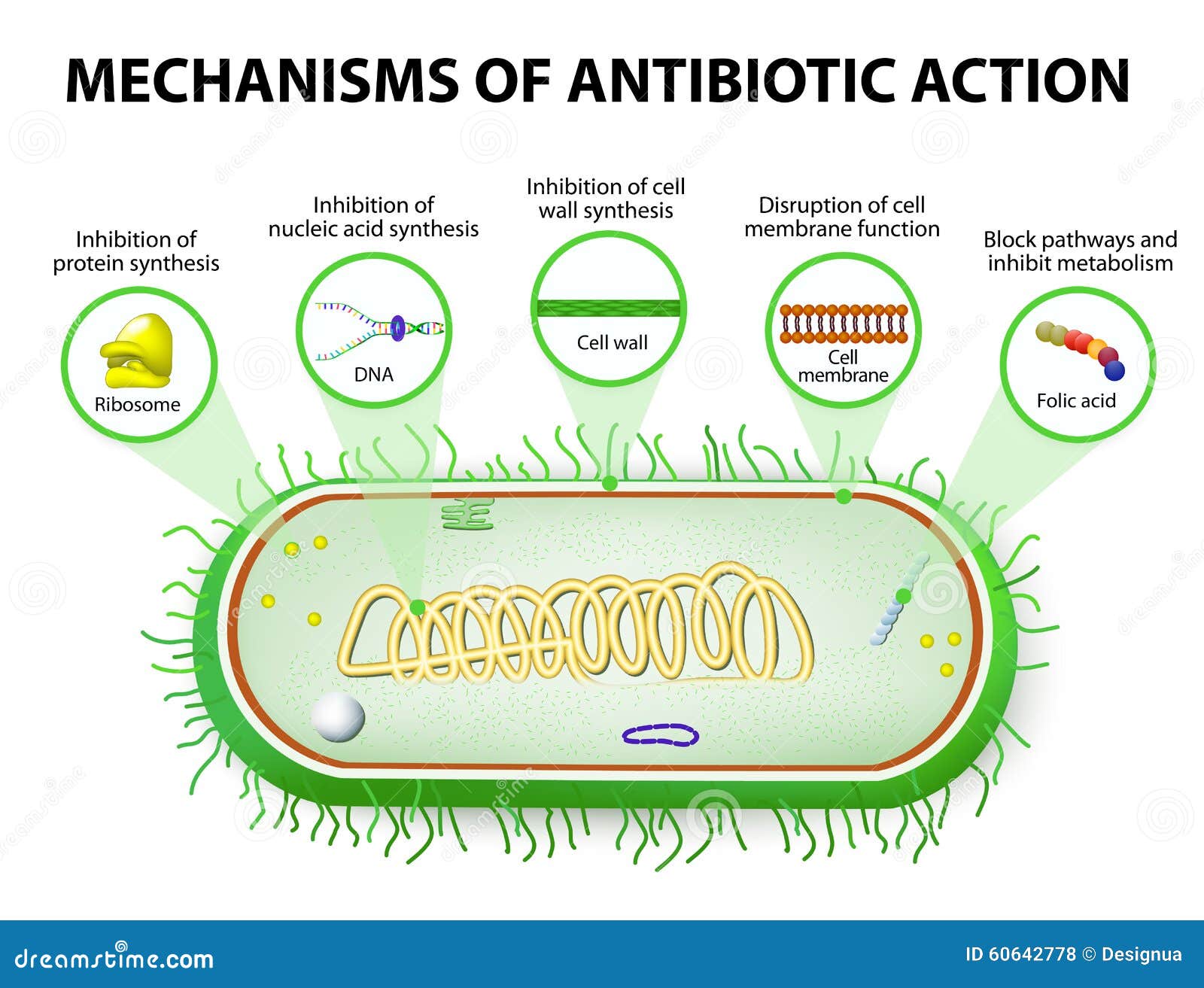
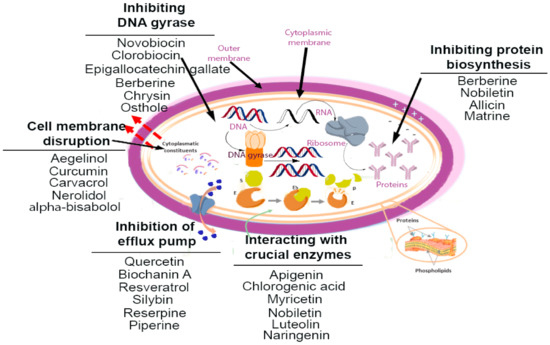
Targeting the Enemy: Mechanisms of Antibacterial Action
Antibacterial agents exert their effects by interfering with essential bacterial processes. These mechanisms can be broadly categorized as follows:
-
Inhibition of Cell Wall Synthesis: The bacterial cell wall, a rigid outer layer, provides structural integrity and protects the cell from osmotic stress. Antibacterial agents like penicillin and its derivatives disrupt the synthesis of peptidoglycan, a key component of the cell wall, leading to weakened cell walls and eventual lysis (bursting). This strategy is particularly effective against Gram-positive bacteria, which have a thicker peptidoglycan layer.
-
Disruption of Protein Synthesis: Bacteria, like all living organisms, rely on protein synthesis for growth and survival. Antibacterial agents like aminoglycosides and macrolides bind to ribosomes, the cellular machinery responsible for protein synthesis, interfering with the process and preventing the production of essential proteins. This inhibition ultimately leads to bacterial death.
-
Interference with DNA Replication and Transcription: DNA replication and transcription are fundamental processes for bacterial growth and division. Antibacterial agents like quinolones target DNA gyrase, an enzyme essential for DNA replication, while rifampicin inhibits RNA polymerase, responsible for transcription. By disrupting these processes, these agents effectively halt bacterial growth and proliferation.
-
Inhibition of Metabolic Pathways: Bacteria, like all living organisms, rely on specific metabolic pathways for energy production and essential building blocks. Antibacterial agents like sulfa drugs and trimethoprim interfere with the synthesis of folic acid, a vital coenzyme in metabolic pathways. By depleting folic acid levels, these agents inhibit bacterial growth and survival.
The Importance of Antibacterial Agents: A Lifeline in a Microbial World
Antibacterial agents have revolutionized healthcare, dramatically reducing the incidence and severity of bacterial infections. They have played a critical role in treating a wide range of infections, from pneumonia and urinary tract infections to life-threatening sepsis. Their effectiveness has enabled complex surgical procedures, organ transplantation, and the management of chronic illnesses, improving the quality of life for countless individuals.
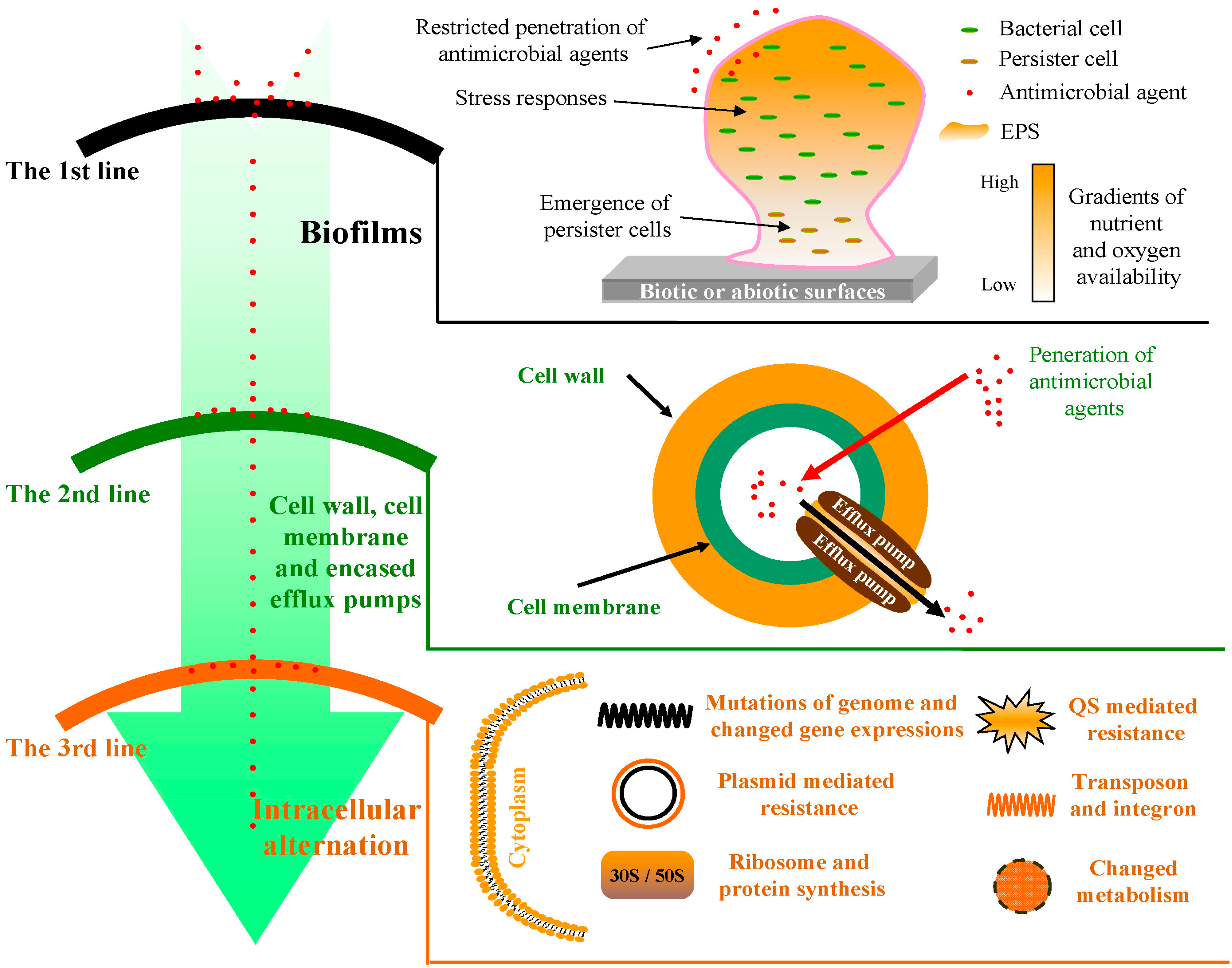
The Growing Challenge of Antibiotic Resistance
Despite their immense benefits, the widespread use of antibacterial agents has inadvertently fueled the emergence of antibiotic resistance. Bacteria, through evolutionary adaptation, can develop mechanisms to circumvent the effects of these drugs. This resistance, a growing public health concern, threatens the effectiveness of many antibiotics and necessitates the development of new strategies to combat resistant strains.
Exploring New Avenues: The Search for Effective Antibacterial Agents
To combat the challenge of antibiotic resistance, researchers are actively exploring new avenues for antibacterial development. These include:
-
Developing Novel Antibacterial Targets: Identifying and targeting unique bacterial processes that are not essential in human cells offers a promising strategy for developing new antibacterial agents with fewer side effects.
-
Exploiting Natural Sources: Nature provides a rich source of antimicrobial compounds, including those produced by bacteria, fungi, and plants. Researchers are actively investigating these natural sources for new antibacterial agents with unique mechanisms of action.
-
Targeting Bacterial Virulence Factors: Instead of targeting essential bacterial processes, some researchers are focusing on developing agents that disrupt bacterial virulence factors, the molecules responsible for causing disease. This approach aims to reduce the severity of infections without directly killing bacteria.
FAQs: Addressing Common Concerns
Q1: How do I know if an infection is bacterial?
A: A diagnosis of a bacterial infection typically involves a combination of clinical symptoms, physical examination, and laboratory tests. Blood cultures, urine cultures, and swabs from infected areas can help identify the causative bacteria and guide treatment.
Q2: Can I take antibiotics for a viral infection?
A: Antibiotics are ineffective against viral infections. Taking antibiotics for a viral infection will not improve your condition and can contribute to antibiotic resistance.
Q3: What are the potential side effects of antibiotics?
A: Antibiotics can cause side effects, ranging from mild gastrointestinal disturbances to more serious allergic reactions. The specific side effects vary depending on the antibiotic used. Consult with a healthcare professional to discuss potential side effects and appropriate treatment options.
Q4: How can I prevent antibiotic resistance?
A: You can contribute to preventing antibiotic resistance by:
* Taking antibiotics only when prescribed by a healthcare professional.
* Completing the full course of antibiotics as directed, even if you start feeling better.
* Practicing good hygiene, such as washing hands frequently and avoiding close contact with sick individuals.Q5: What are some natural ways to fight bacterial infections?
A: While natural remedies may offer some relief, they are not a substitute for appropriate medical treatment. Some natural remedies that may have antibacterial properties include:
* Garlic: Contains compounds with antimicrobial activity.
* Honey: Possesses antibacterial and wound-healing properties.
* Echinacea: May boost the immune system.Tips for Using Antibacterial Agents Safely and Effectively
- Always consult with a healthcare professional before taking any antibacterial agent. They can assess your condition, prescribe the appropriate medication, and monitor your progress.
- Take antibiotics exactly as prescribed. Completing the full course of antibiotics, even if you start feeling better, is essential to ensure the infection is completely eradicated and prevent the development of antibiotic resistance.
- Avoid sharing antibiotics with others. Antibiotics are specifically prescribed for individual infections and may not be appropriate for other conditions.
- Be aware of potential side effects. If you experience any unusual symptoms while taking antibiotics, contact your healthcare provider immediately.
- Practice good hygiene to prevent the spread of bacteria. Wash your hands frequently, especially before eating and after using the restroom.
Conclusion: A Constant Battle for Microbial Control
Antibacterial agents remain a cornerstone of modern medicine, providing a powerful defense against bacterial infections. However, the challenge of antibiotic resistance necessitates a multifaceted approach, including responsible antibiotic use, the development of new antibacterial agents, and alternative strategies to combat resistant strains. By understanding the mechanisms of antibacterial action and practicing responsible antibiotic use, we can contribute to the fight against bacterial infections and safeguard the effectiveness of these essential therapies.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Arsenal Against Microbes: A Comprehensive Look at Antibacterial Agents. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!