The Chemistry Of Our Homes: Exploring Acidic And Basic Household Items
The Chemistry of Our Homes: Exploring Acidic and Basic Household Items
Related Articles: The Chemistry of Our Homes: Exploring Acidic and Basic Household Items
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to The Chemistry of Our Homes: Exploring Acidic and Basic Household Items. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Chemistry of Our Homes: Exploring Acidic and Basic Household Items

The world around us, including our homes, is a tapestry of chemical interactions. Understanding the nature of these interactions, particularly the distinction between acids and bases, can enhance our understanding of everyday products and practices. Acids and bases are ubiquitous in our homes, playing critical roles in cleaning, cooking, and even personal care.
Understanding Acids and Bases
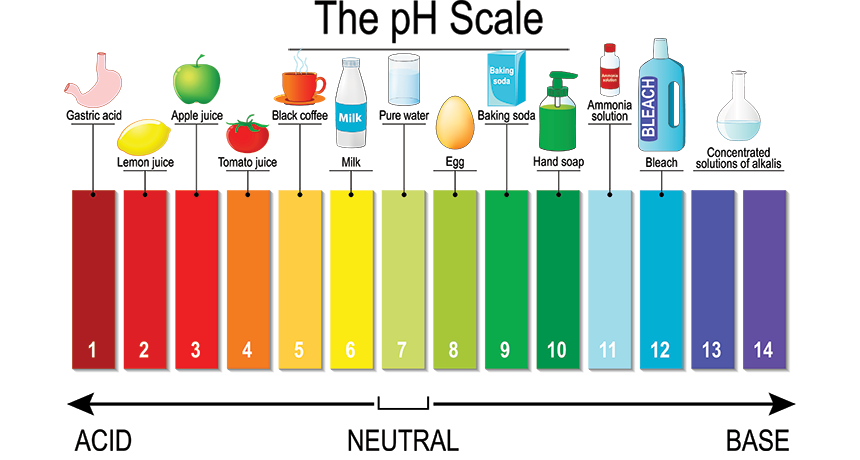
Acids and bases are defined by their chemical properties, specifically their ability to donate or accept hydrogen ions (H+). Acids are substances that donate hydrogen ions in solution, while bases accept these ions. This fundamental difference leads to distinct chemical behaviors and applications.
Key Characteristics of Acids
- Sour taste: Acids are typically characterized by a sour taste, as exemplified by lemon juice and vinegar.
- pH below 7: The pH scale measures the acidity or alkalinity of a solution. Acids have a pH value below 7, with lower values indicating stronger acidity.
- React with bases to form salts and water: This neutralization reaction is a fundamental principle in chemistry and is often used in practical applications.
- Corrosive properties: Many acids can be corrosive, meaning they can damage materials like metals and fabrics.
Key Characteristics of Bases
- Bitter taste and slippery feel: Bases have a bitter taste and feel slippery to the touch, like soap.
- pH above 7: Bases have a pH value above 7, with higher values indicating stronger alkalinity.
- React with acids to form salts and water: This neutralization reaction is the opposite of the reaction with acids.
- Can be corrosive: Strong bases can also be corrosive to materials, though their effects may differ from those of acids.
Common Acidic Household Items
- Vinegar: A dilute solution of acetic acid, vinegar is a staple in many kitchens. It is used for salad dressings, pickling, and cleaning.
- Lemon juice: Rich in citric acid, lemon juice is used for flavoring drinks, baking, and cleaning.
- Fruit juices: Many fruit juices contain citric acid or other organic acids, contributing to their tangy flavor.
- Carbonated beverages: These drinks contain carbonic acid, which gives them their fizz.
- Battery acid: Car batteries use sulfuric acid as their electrolyte, which is highly corrosive.
- Toilet bowl cleaner: Many toilet bowl cleaners contain hydrochloric acid, which is used to remove stains and mineral deposits.
Common Basic Household Items
- Baking soda: Sodium bicarbonate is a common baking ingredient and is also used for cleaning and deodorizing.
- Ammonia: A colorless gas that dissolves in water to form a basic solution, ammonia is a powerful cleaning agent.
- Soap: Soaps are made from fats or oils combined with a strong base, typically sodium hydroxide or potassium hydroxide.
- Lye (sodium hydroxide): A strong base used in soap making, drain cleaners, and other industrial applications.
- Dishwasher detergent: Many dishwasher detergents contain sodium hydroxide or other strong bases to remove grease and food particles.
- Antacids: These medications contain bases like calcium carbonate or magnesium hydroxide to neutralize stomach acid.
Importance and Benefits of Acidic and Basic Household Items
The diverse applications of acids and bases highlight their importance in our daily lives. They are essential for:
- Cleaning: Acids and bases are widely used in cleaning products. Acids can remove mineral deposits and stains, while bases are effective for removing grease and grime.
- Cooking: Acids like vinegar and lemon juice are used for flavoring, tenderizing meat, and preserving food. Bases like baking soda are used for leavening, neutralizing acids, and creating fluffy textures in baked goods.
- Personal care: Acids are used in skin care products to exfoliate and brighten the skin, while bases are present in soaps and shampoos to cleanse and remove dirt.
- Industrial applications: Acids and bases play critical roles in various industries, including manufacturing, agriculture, and pharmaceuticals.
FAQs about Acidic and Basic Household Items
Q: Can I mix acidic and basic household items?
A: It is generally not recommended to mix acidic and basic household items, especially strong acids and bases. Mixing these substances can result in a rapid chemical reaction, generating heat, fumes, and potentially dangerous substances.
Q: How do I safely handle acidic and basic household items?
A: Always read and follow the instructions on product labels. Wear appropriate protective gear, such as gloves and goggles, when handling concentrated acids and bases. Avoid contact with skin, eyes, and clothing. Store these items separately in well-ventilated areas.
Q: What are the safety precautions when using acidic and basic cleaning products?
A: Always dilute acidic and basic cleaners according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Never mix different cleaning products unless explicitly stated as safe. Avoid mixing bleach with acids, as this can produce toxic chlorine gas. Ensure adequate ventilation when using cleaning products, and wear gloves and protective eyewear.
Q: How can I neutralize a spill of an acidic or basic substance?
A: For acidic spills, use a mild base like baking soda. For basic spills, use a mild acid like vinegar. Neutralize the spill slowly and carefully, ensuring proper ventilation. If the spill is significant or involves a strong acid or base, seek professional assistance.
Tips for Using Acidic and Basic Household Items
- Vinegar: Use vinegar to clean windows, mirrors, and countertops. It can also be used to remove mineral deposits from coffee makers and tea kettles.
- Lemon juice: Use lemon juice to brighten whites, remove stains from fruits and vegetables, and add a fresh scent to cleaning solutions.
- Baking soda: Use baking soda to deodorize refrigerators, clean ovens, and neutralize acidic spills.
- Ammonia: Use ammonia for cleaning floors, windows, and bathrooms. It is effective for removing grease and grime.
- Soap: Use soap to wash dishes, clothes, and your body. It is also effective for removing grease and grime from surfaces.
Conclusion
The presence of acids and bases in our homes underscores their importance in our daily lives. By understanding their properties and safe handling, we can utilize these substances effectively for cleaning, cooking, and personal care. Furthermore, recognizing the potential hazards associated with their misuse enables us to practice responsible stewardship of these powerful chemical agents. By embracing a balanced and informed approach, we can harness the benefits of acids and bases while minimizing potential risks, ensuring a safer and more efficient household environment.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Chemistry of Our Homes: Exploring Acidic and Basic Household Items. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!