The Chemistry Of Our Homes: Understanding Acids In Everyday Life
The Chemistry of Our Homes: Understanding Acids in Everyday Life
Related Articles: The Chemistry of Our Homes: Understanding Acids in Everyday Life
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to The Chemistry of Our Homes: Understanding Acids in Everyday Life. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Chemistry of Our Homes: Understanding Acids in Everyday Life

Acids are ubiquitous in our homes, playing a vital role in cleaning, cooking, and even personal care. While often associated with corrosive properties, most household acids are diluted and safe for everyday use when handled appropriately. Understanding their properties and applications allows us to harness their benefits while minimizing potential risks.
The Nature of Acids
Acids are chemical compounds that release hydrogen ions (H+) when dissolved in water. This release of hydrogen ions is what gives acids their characteristic sour taste and corrosive properties. The strength of an acid is determined by its ability to donate hydrogen ions. Strong acids, such as hydrochloric acid (HCl), readily donate hydrogen ions, while weak acids, such as citric acid, donate fewer ions.
Common Household Acids
Numerous acidic substances are commonly found in our homes, each serving a specific purpose:
1. Vinegar (Acetic Acid): Vinegar is a dilute solution of acetic acid, a weak organic acid. Its versatility makes it a staple in kitchens and cleaning supplies.
- Culinary Applications: Vinegar adds a tangy flavor to dishes, marinades, and dressings. It is also used in pickling and preserving food.
- Cleaning: Vinegar’s acidic nature effectively cuts through grease, grime, and mineral deposits, making it an excellent natural cleaner for surfaces, appliances, and windows.
- Other Uses: Vinegar can be used as a fabric softener, a weed killer, and a deodorizer.
2. Citric Acid: Citric acid, a weak organic acid found in citrus fruits, is a popular ingredient in food and beverages.
- Food and Beverages: Citric acid is used as a flavoring agent, an antioxidant, and a preservative in a wide range of products, from juices and candies to jams and jellies.
- Cleaning: Citric acid is effective in removing mineral deposits, rust, and limescale from various surfaces.
- Other Uses: Citric acid is used in cosmetics, pharmaceuticals, and as a pH adjuster in various industrial applications.
3. Carbonic Acid: Carbonic acid is a weak inorganic acid formed when carbon dioxide dissolves in water. It is present in carbonated beverages and plays a crucial role in the natural carbon cycle.
- Carbonated Beverages: The fizz in sodas and sparkling water is due to the presence of carbonic acid.
- Natural Carbon Cycle: Carbonic acid forms in rainwater, contributing to the weathering of rocks and the formation of caves.
4. Lactic Acid: Lactic acid is a weak organic acid produced naturally in our bodies during exercise and fermentation. It is commonly found in dairy products, such as yogurt and sour cream.
- Dairy Products: Lactic acid contributes to the tangy flavor and creamy texture of fermented dairy products.
- Other Uses: Lactic acid is used in skincare products, as a food preservative, and in the textile industry.
5. Ascorbic Acid (Vitamin C): Ascorbic acid is a vital nutrient that acts as an antioxidant in our bodies. It is found in fruits and vegetables, particularly citrus fruits.
- Health Benefits: Ascorbic acid plays a crucial role in immune function, collagen synthesis, and wound healing.
- Other Uses: Ascorbic acid is used as a food additive, a preservative, and a supplement.
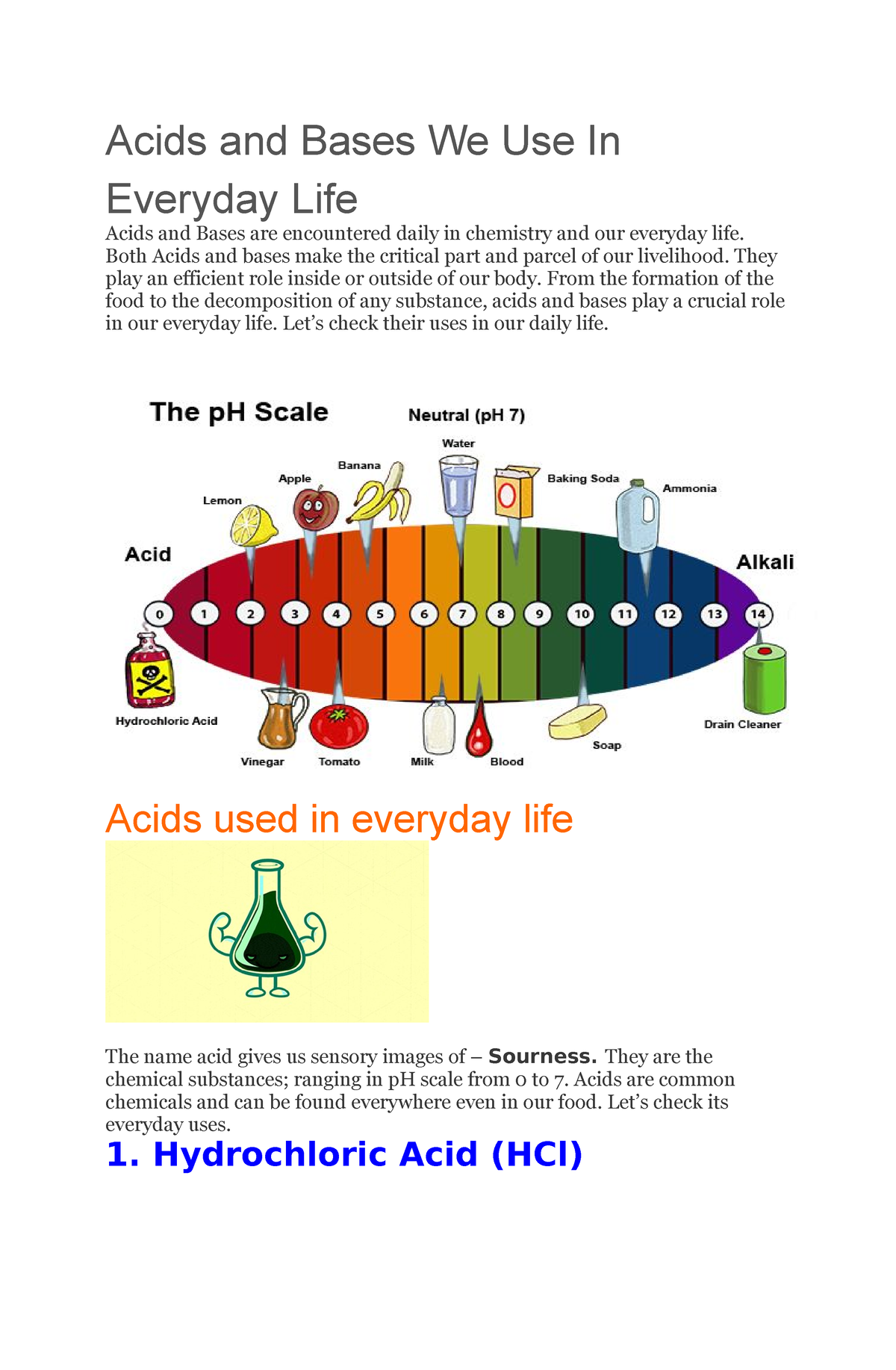
6. Hydrochloric Acid (HCl): Hydrochloric acid is a strong inorganic acid found in the stomach, where it aids in digestion. It is also used in various industrial processes.
- Digestion: Hydrochloric acid helps break down food, activate digestive enzymes, and kill bacteria in the stomach.
- Industrial Applications: Hydrochloric acid is used in the production of fertilizers, plastics, and other chemicals.
7. Sulfuric Acid: Sulfuric acid is a strong inorganic acid used in various industrial applications, including the production of fertilizers, batteries, and detergents. It is not typically found in household settings.
8. Phosphoric Acid: Phosphoric acid is a weak inorganic acid found in soft drinks, fertilizers, and some cleaning products.
- Food and Beverages: Phosphoric acid is used as a flavoring agent, an acidity regulator, and a preservative in soft drinks and other beverages.
- Fertilizers: Phosphoric acid is a key ingredient in fertilizers, providing phosphorus to plants.
9. Boric Acid: Boric acid is a weak inorganic acid found in some cleaning products and insecticides. It is also used as an antiseptic and a fire retardant.
- Cleaning: Boric acid is effective in killing mold and mildew, making it a useful ingredient in some cleaning products.
- Other Uses: Boric acid is used in insecticides, as an antiseptic, and as a fire retardant.
Safety Considerations
While most household acids are diluted and safe for everyday use, it is essential to handle them with care.
- Avoid Contact with Skin and Eyes: Acids can cause irritation, burns, and other skin and eye damage. Always wear gloves and eye protection when handling acidic substances.
- Store Acids Safely: Store acids in their original containers, away from heat and direct sunlight. Keep them out of reach of children and pets.
- Mix Acids with Caution: Never mix different acids together without proper knowledge and safety precautions. Mixing acids can create dangerous reactions.
- Dilute Acids Properly: When diluting acids, always add acid to water, never water to acid. This prevents the formation of dangerous heat and splatter.
- Ventilate Properly: When using acids, ensure adequate ventilation to avoid inhaling fumes.
Benefits of Acids in Our Homes
Acids play a vital role in our everyday lives, offering numerous benefits:
- Cleaning and Disinfecting: Acids are effective cleaning agents, breaking down grease, grime, and mineral deposits. They also have disinfecting properties, killing bacteria and viruses.
- Food Preservation and Flavoring: Acids are used to preserve food, enhance flavor, and improve texture.
- Personal Care: Acids are found in many skincare products, helping to exfoliate, brighten skin, and reduce blemishes.
- Industrial Applications: Acids are essential for numerous industrial processes, from fertilizer production to battery manufacturing.
FAQs About Household Acids
Q: What happens if I accidentally mix different acids?
A: Mixing different acids can create dangerous reactions, potentially releasing harmful fumes or generating heat. It is crucial to avoid mixing acids unless you have proper knowledge and safety precautions.
Q: How do I safely dispose of acidic substances?
A: Never pour acidic substances down the drain. Instead, consult your local waste disposal guidelines for proper disposal methods.
Q: How can I tell if a substance is acidic?
A: You can use pH paper to test the acidity of a substance. Acidic substances will turn pH paper red, while neutral substances will turn it green, and alkaline substances will turn it blue.
Q: What are the symptoms of acid exposure?
A: Symptoms of acid exposure can include skin irritation, burning, redness, itching, and swelling. If you suspect acid exposure, immediately flush the affected area with plenty of water and seek medical attention.
Tips for Using Acids Safely at Home
- Always read and follow the manufacturer’s instructions before using any acidic substance.
- Wear appropriate protective gear, including gloves and eye protection, when handling acids.
- Store acids in their original containers, away from heat and direct sunlight.
- Keep acids out of reach of children and pets.
- Never mix different acids together without proper knowledge and safety precautions.
- Dilute acids properly, always adding acid to water, never water to acid.
- Ensure adequate ventilation when using acids.
- Dispose of acids properly according to local waste disposal guidelines.
Conclusion
Acids are essential components of our homes, serving a wide range of purposes. By understanding their properties, applications, and safety precautions, we can harness their benefits while minimizing potential risks. From cleaning and cooking to personal care and industrial applications, acids play a vital role in our modern lives. By using them responsibly and safely, we can enjoy the advantages they offer while ensuring the well-being of ourselves and our families.







Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Chemistry of Our Homes: Understanding Acids in Everyday Life. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!