The Dynamics Of Low Prices: Understanding The Forces Behind Affordable Goods
The Dynamics of Low Prices: Understanding the Forces Behind Affordable Goods
Related Articles: The Dynamics of Low Prices: Understanding the Forces Behind Affordable Goods
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to The Dynamics of Low Prices: Understanding the Forces Behind Affordable Goods. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Dynamics of Low Prices: Understanding the Forces Behind Affordable Goods
The pursuit of affordable goods is a fundamental human desire, driving both individual and societal actions. This pursuit is not merely about acquiring necessities at the lowest cost, but rather reflects a complex interplay of economic, social, and technological factors. Understanding these dynamics is crucial for both consumers and businesses seeking to navigate the ever-evolving landscape of low prices.
Factors Influencing Low Prices:
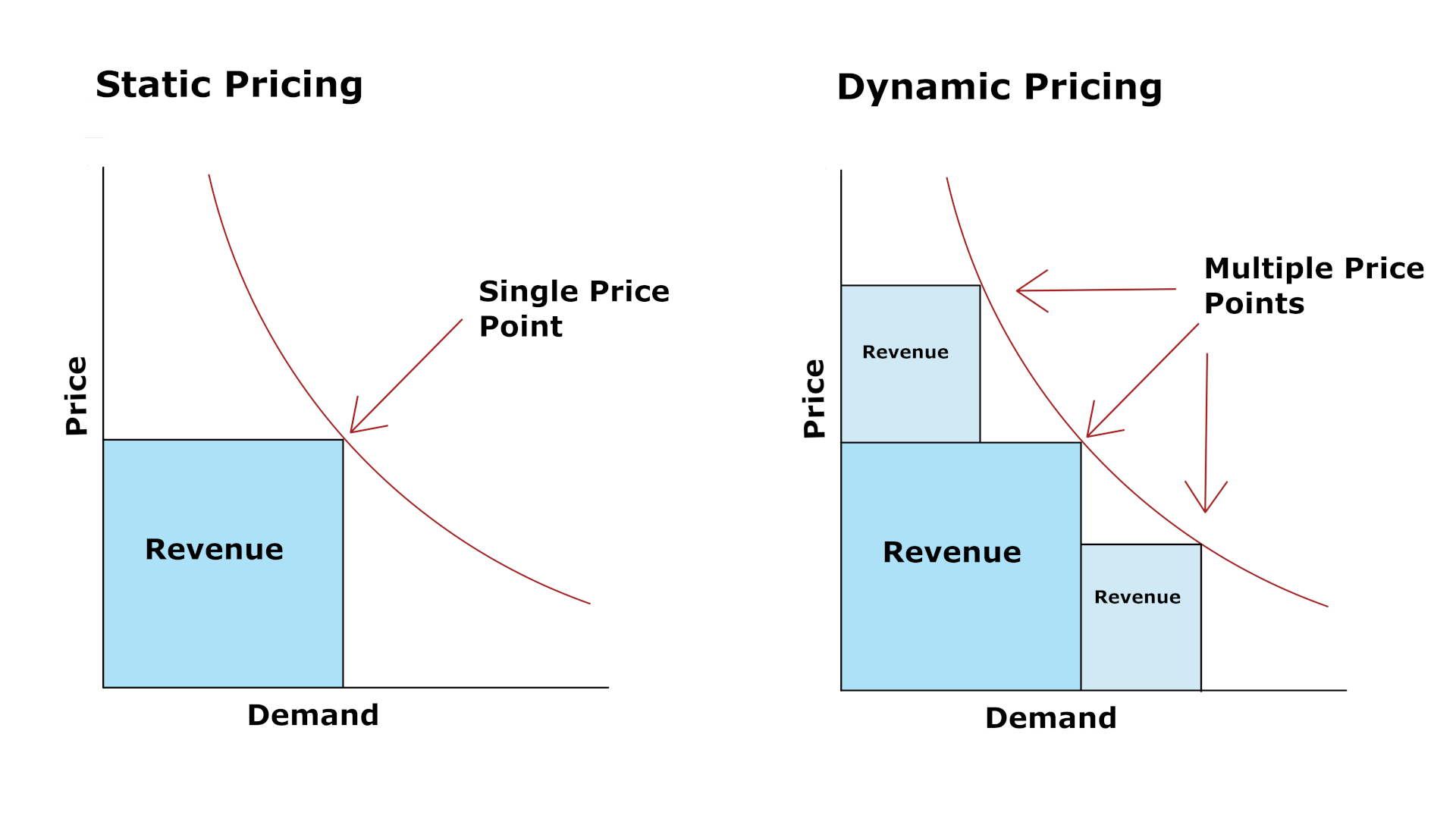
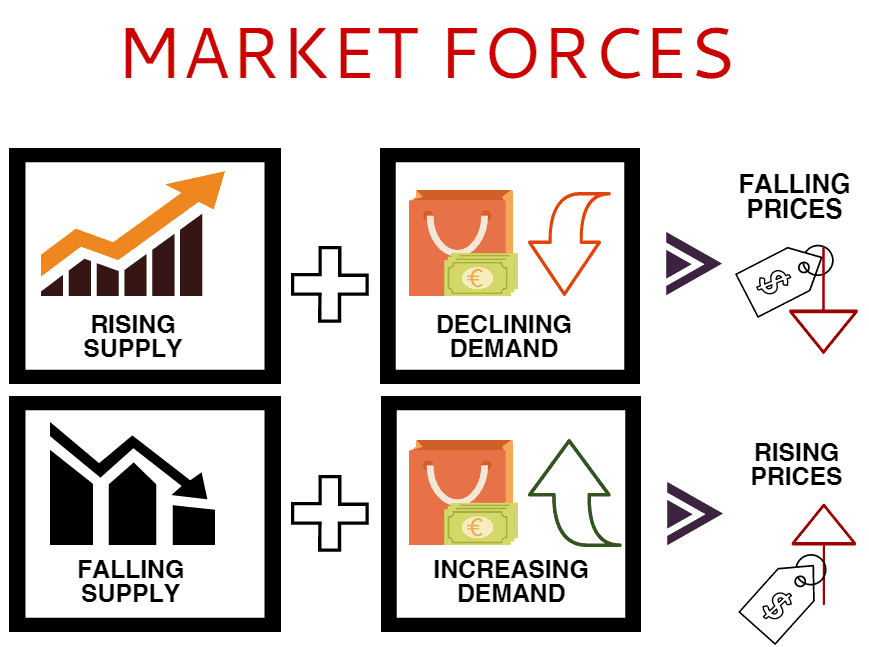
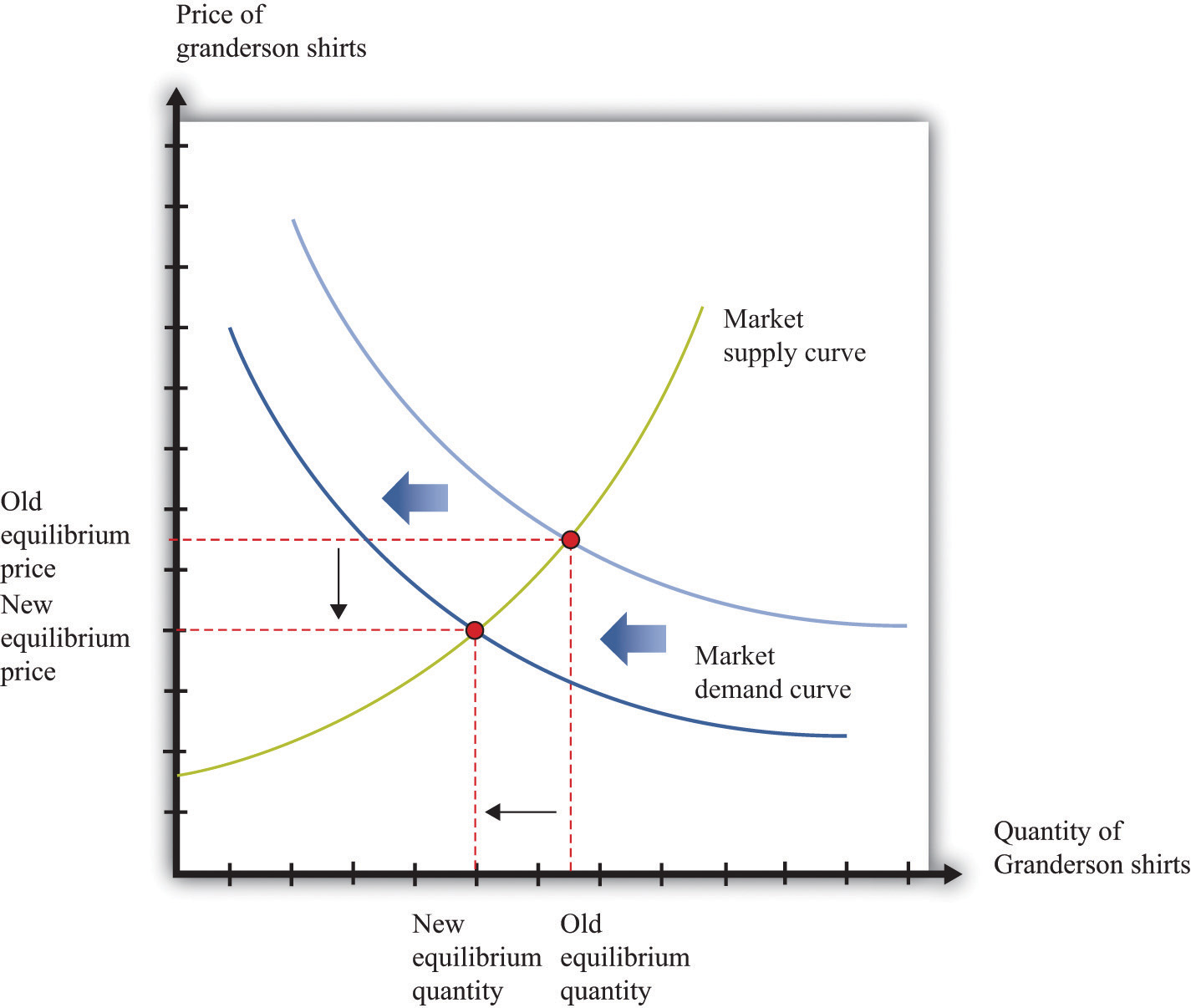
1. Supply and Demand: The bedrock of any market, supply and demand dictate price fluctuations. When supply exceeds demand, prices tend to fall as businesses compete for buyers. Conversely, when demand outstrips supply, prices rise as consumers are willing to pay more for scarce goods.
2. Technological Advancements: Technological innovation plays a significant role in lowering production costs. Automation, robotics, and improved manufacturing processes can lead to increased efficiency, resulting in lower prices for consumers. The rise of e-commerce platforms has also disrupted traditional retail models, fostering competition and driving down prices.
3. Globalization and Trade: The interconnectedness of the global economy allows for sourcing of raw materials and finished goods from various locations with lower production costs. This global competition can lead to lower prices for consumers, although it may also raise concerns about labor practices and environmental sustainability.
4. Competition: The presence of numerous businesses competing for customers within a market can drive prices down. This competition forces businesses to offer attractive prices and promotions to retain and attract customers.
5. Government Policies: Government policies, such as subsidies, tax breaks, and trade agreements, can influence the cost of goods. For example, subsidies for agricultural production can lower the cost of food, while tariffs on imported goods can raise prices for consumers.
The Benefits of Low Prices:
1. Increased Purchasing Power: Low prices allow consumers to stretch their budgets further, enabling them to acquire more goods and services with the same amount of money. This can improve living standards and foster economic growth by stimulating consumer spending.
2. Access to Essential Goods: Low prices on essential goods, such as food, healthcare, and education, ensure that a larger segment of the population can afford these necessities. This can contribute to a more equitable society and reduce poverty.
3. Economic Growth: Low prices can fuel economic growth by encouraging businesses to invest and expand, leading to job creation and increased production. This cycle of growth can further benefit consumers through lower prices and more choices.
4. Innovation and Efficiency: The pursuit of low prices often drives businesses to seek innovative ways to reduce costs and improve efficiency. This can lead to technological advancements and improvements in production processes, benefiting both consumers and businesses.
Challenges Associated with Low Prices:
1. Quality Concerns: Low prices can sometimes be associated with lower quality products, as businesses may cut corners to maintain affordability. This can lead to consumer dissatisfaction and a decline in trust.
2. Labor Exploitation: The pursuit of low prices can incentivize businesses to seek out low-wage labor markets, potentially leading to exploitation of workers and unfair labor practices.
3. Environmental Impact: Low prices can encourage excessive consumption and production, leading to increased environmental impact through resource depletion, pollution, and waste generation.
4. Economic Instability: In some cases, low prices can lead to economic instability, particularly in industries with low profit margins. This can result in business closures, job losses, and economic downturns.
FAQs on Low Prices:
Q: How can consumers benefit from low prices?
A: Consumers benefit from low prices by having greater purchasing power, enabling them to buy more goods and services with the same amount of money. This can improve their living standards and access to essential goods.
Q: What are the potential drawbacks of low prices?
A: Potential drawbacks of low prices include concerns about product quality, labor exploitation, environmental impact, and economic instability.
Q: How can businesses ensure they offer low prices without compromising quality?
A: Businesses can offer low prices without compromising quality by focusing on efficiency, streamlining processes, and sourcing materials strategically. They can also invest in technology and automation to reduce production costs.
Q: What role does government policy play in influencing low prices?
A: Government policies, such as subsidies, tax breaks, and trade agreements, can influence the cost of goods by either lowering or raising prices for consumers.
Tips for Consumers Seeking Low Prices:
1. Shop Around: Compare prices from different retailers and online platforms to find the best deals.
2. Utilize Coupons and Discounts: Take advantage of coupons, discounts, and loyalty programs to reduce the cost of goods.
3. Consider Generic Brands: Generic brands often offer similar quality at lower prices compared to name-brand products.
4. Buy in Bulk: Purchasing items in bulk can lead to significant cost savings, especially for frequently used products.
5. Look for Sales and Promotions: Pay attention to sales and promotional periods to capitalize on discounted prices.
Conclusion:
Low prices are a complex and multifaceted phenomenon driven by various economic, social, and technological factors. While they offer significant benefits to consumers, businesses, and economies, it is important to consider the potential drawbacks and challenges associated with the pursuit of low prices. By understanding the dynamics of low prices and navigating these complexities responsibly, individuals and societies can harness the benefits of affordability while mitigating potential risks.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/g367-5c79c858c9e77c0001d19d1d.jpg)

![[DIAGRAM] Diagram Of Price Elasticity Of Demand - MYDIAGRAM.ONLINE](https://www.doffitt.com/wp-content/uploads/2019/12/What-is-Price-Elasticity-of-Demand.jpg)


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Dynamics of Low Prices: Understanding the Forces Behind Affordable Goods. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!