The Invisible Symphony: Electromagnetic Waves And Their Impact On Our World
The Invisible Symphony: Electromagnetic Waves and Their Impact on Our World
Related Articles: The Invisible Symphony: Electromagnetic Waves and Their Impact on Our World
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to The Invisible Symphony: Electromagnetic Waves and Their Impact on Our World. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Invisible Symphony: Electromagnetic Waves and Their Impact on Our World

Electromagnetic waves, an invisible force that permeates our universe, play a crucial role in shaping our modern world. From the light that illuminates our homes to the radio waves that connect us across continents, these waves are fundamental to countless technologies and aspects of our daily lives. Understanding the nature and applications of electromagnetic waves is essential for appreciating their profound impact on society.
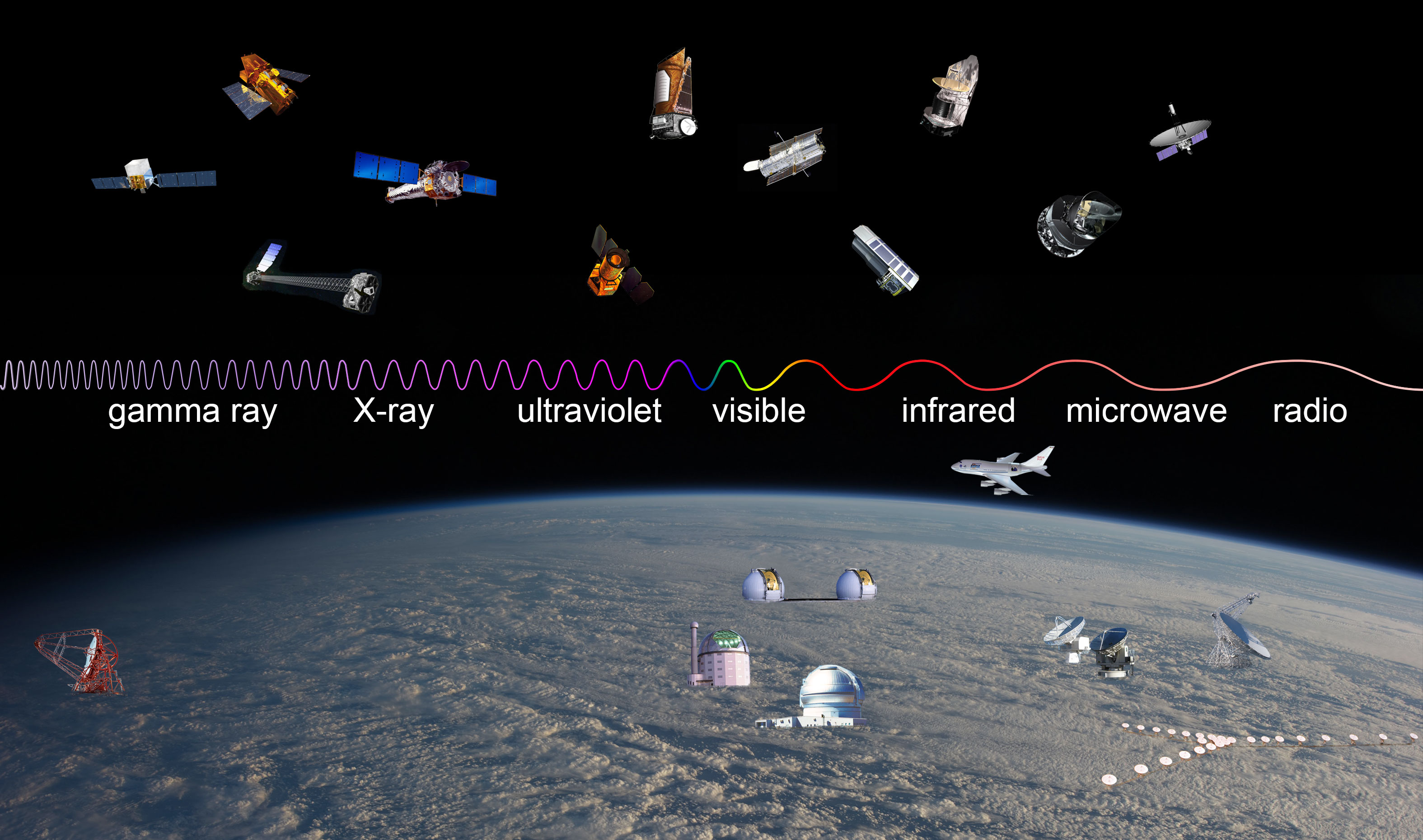
A Glimpse into the Electromagnetic Spectrum:
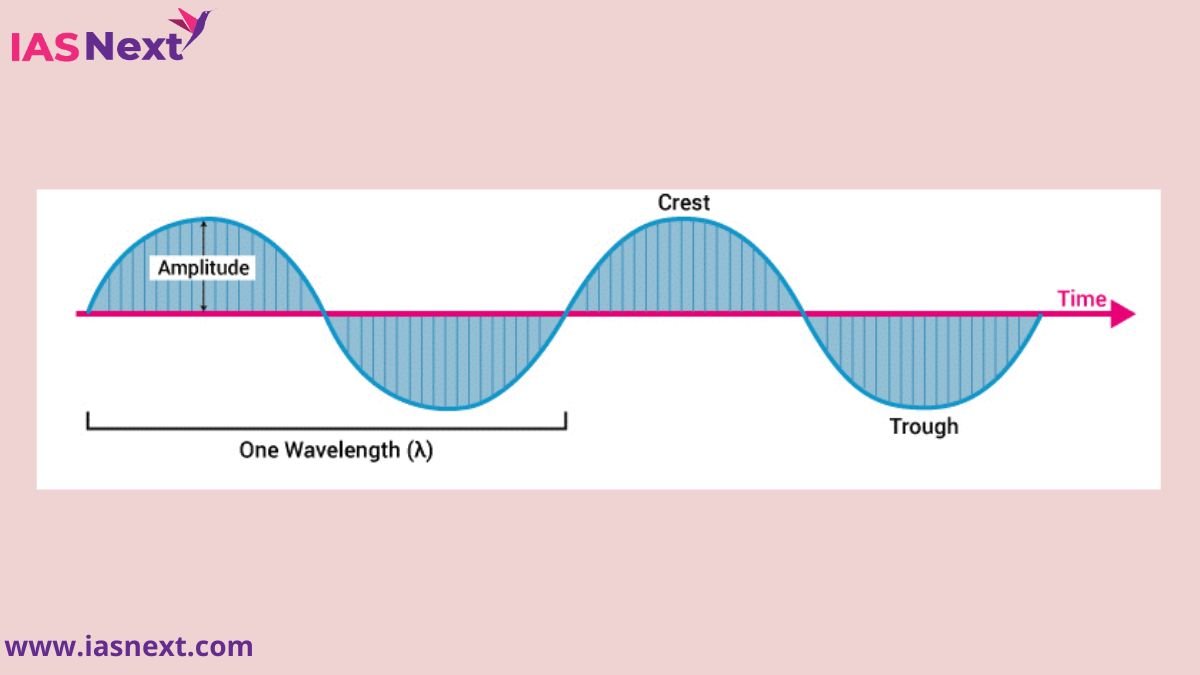
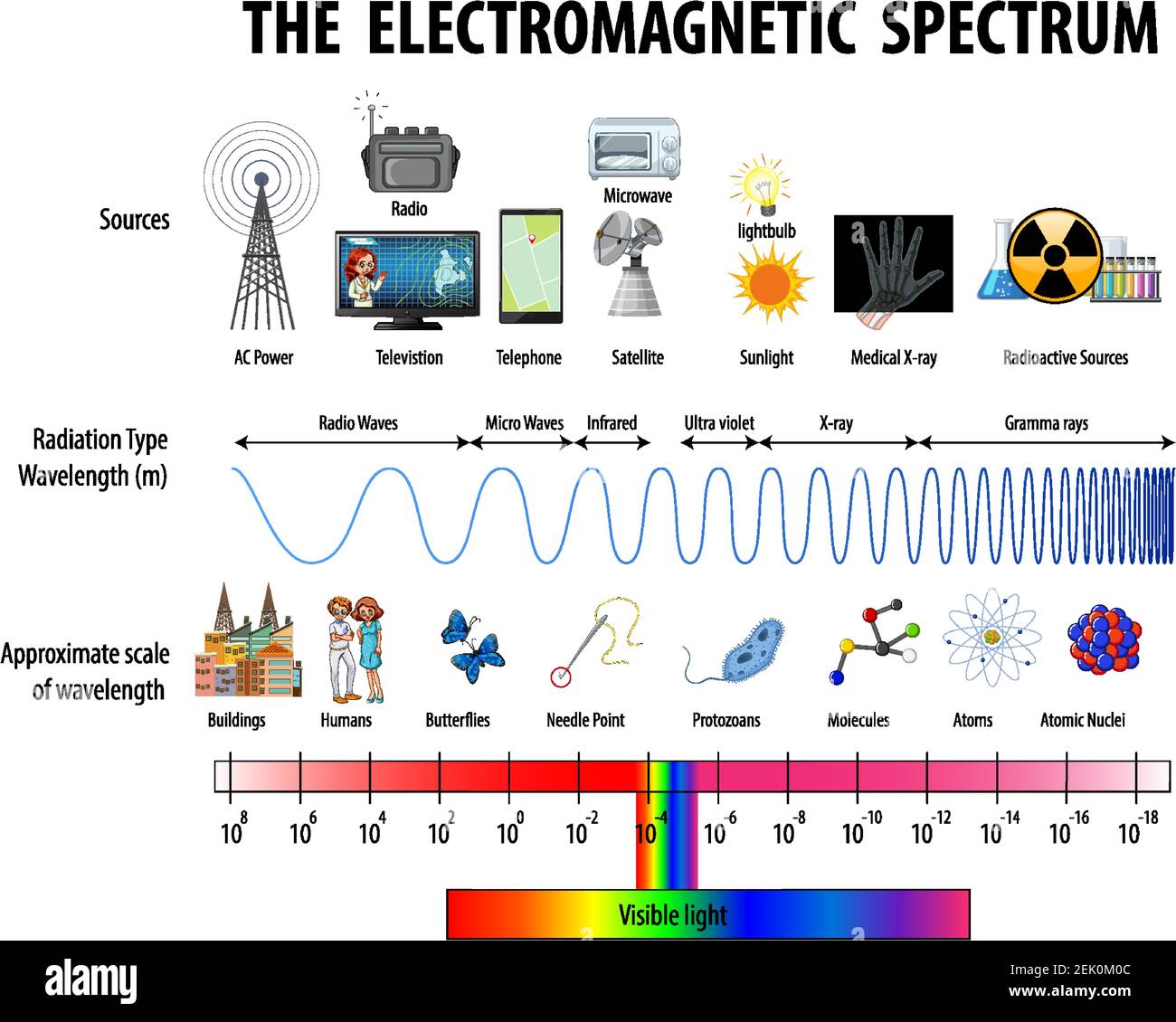
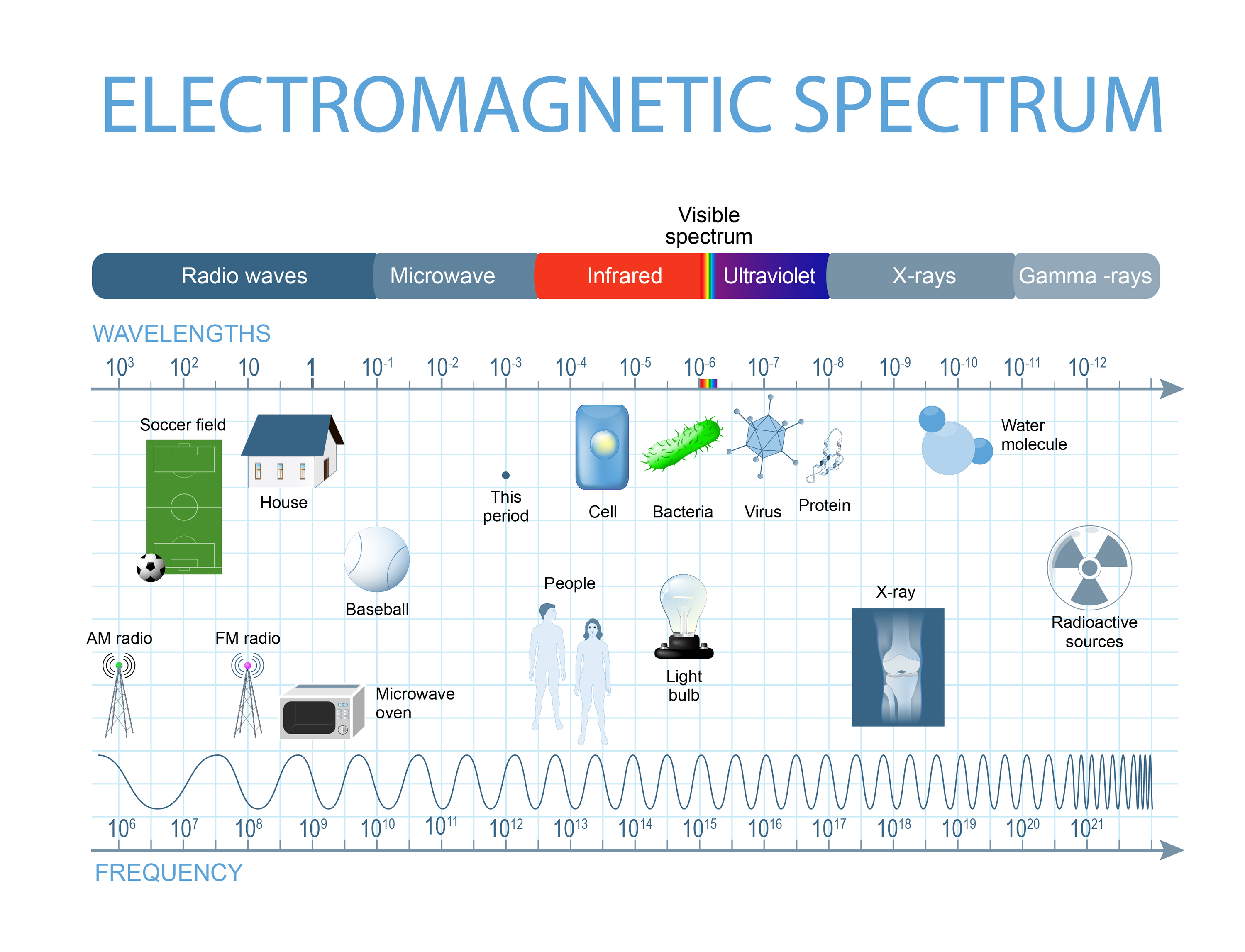
Electromagnetic waves are disturbances in electric and magnetic fields that propagate at the speed of light. They are characterized by their frequency, wavelength, and energy. The electromagnetic spectrum encompasses a vast range of frequencies, from extremely low-frequency radio waves to high-energy gamma rays. This spectrum is often divided into different regions based on the characteristics and applications of the waves:
- Radio Waves: The longest wavelength region, used for communication, broadcasting, and radar.
- Microwaves: Used for communication, radar, and heating.
- Infrared Radiation: Used for thermal imaging, remote sensing, and communication.
- Visible Light: The only portion of the electromagnetic spectrum visible to the human eye, responsible for our perception of colors.
- Ultraviolet Radiation: Used for sterilization, medical treatments, and tanning.
- X-rays: Used for medical imaging, industrial inspection, and security screening.
- Gamma Rays: Used in medical treatments, industrial processes, and nuclear research.
Illuminating Our Lives: The Role of Light
Visible light, a crucial part of the electromagnetic spectrum, is essential for our vision and plays a vital role in our daily lives. It allows us to perceive the world around us, navigate our surroundings, and engage in various activities. Artificial light sources, such as incandescent bulbs, fluorescent lamps, and LED lights, have revolutionized our ability to extend the day and improve our living conditions.
Beyond illumination, light has numerous applications in various fields:
- Photography: Capturing images using the interaction of light with a photosensitive material.
- Optical Microscopy: Visualizing microscopic objects using light waves.
- Spectroscopy: Analyzing the interaction of light with matter to identify its composition and properties.
- Fiber Optics: Transmitting information over long distances using light pulses traveling through optical fibers.
Communication Revolution: The Power of Radio Waves
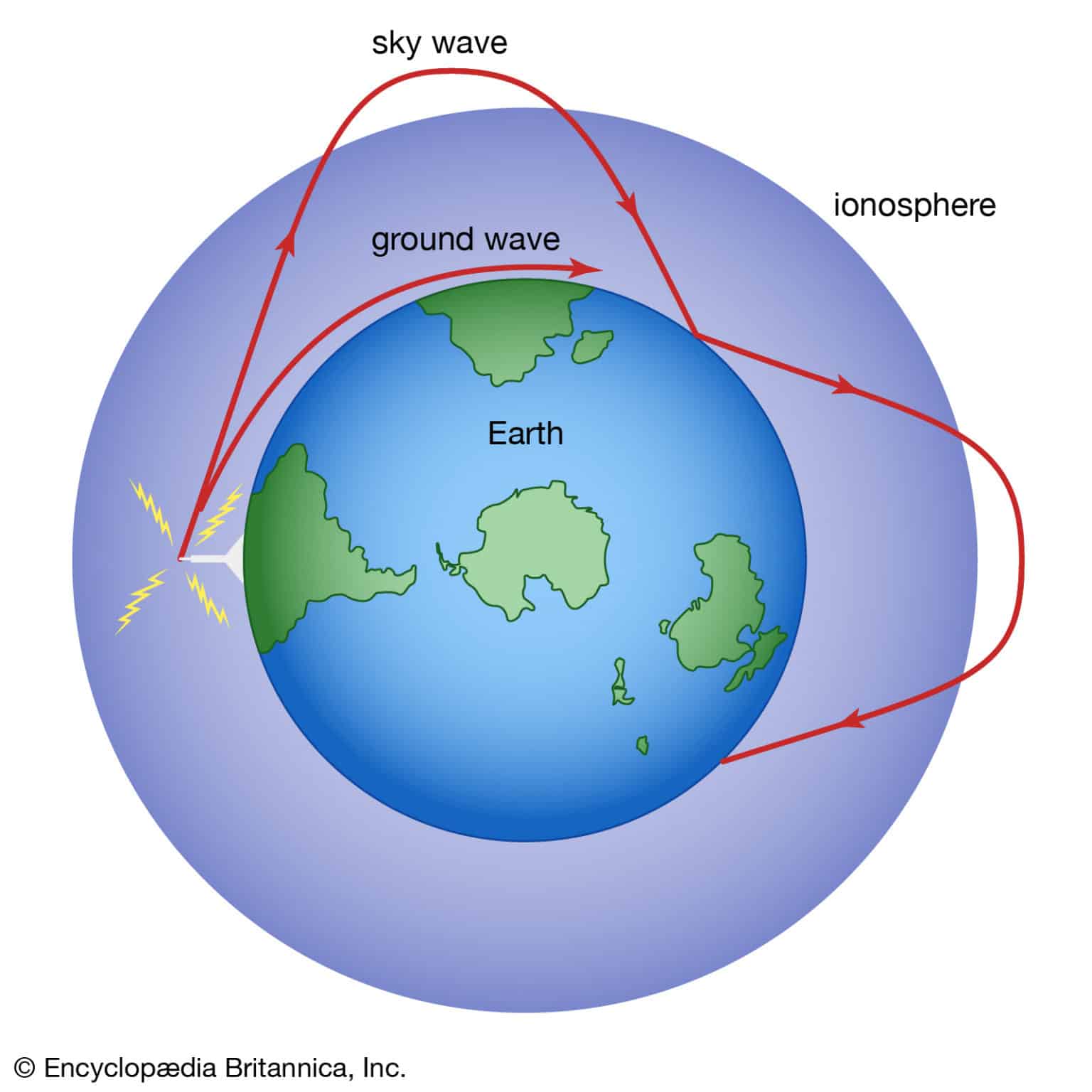
Radio waves, the longest wavelength portion of the electromagnetic spectrum, have revolutionized communication. Their ability to travel long distances through air and other mediums makes them ideal for broadcasting information. Radio waves are used in:
- Broadcasting: Transmitting audio and video content over vast distances through radio and television stations.
- Telecommunications: Enabling mobile phone communication, wireless internet access, and satellite communication.
- Navigation: Guiding ships, aircraft, and vehicles using Global Positioning System (GPS) signals.
- Radar: Detecting objects and measuring their distance, speed, and direction using radio wave reflections.
Medical Advancements: The Healing Power of Electromagnetic Waves
Electromagnetic waves are not only essential for communication and information transfer but also play a crucial role in healthcare. Their unique properties are harnessed for various medical applications:
- X-rays: Used for medical imaging to diagnose and treat various conditions.
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI): Using strong magnetic fields and radio waves to create detailed images of internal organs and tissues.
- Ultrasound: Using high-frequency sound waves to create images of internal organs and tissues.
- Laser Surgery: Using highly focused beams of light to perform precise surgical procedures.
- Photodynamic Therapy: Using light-sensitive drugs to treat cancer and other diseases.
Beyond Our Senses: The Applications of Other Electromagnetic Waves
While visible light and radio waves are the most familiar applications of electromagnetic waves, other regions of the spectrum also have significant uses:
- Microwaves: Used for heating food in microwave ovens, communication in satellite links, and radar systems.
- Infrared Radiation: Used in thermal imaging for night vision, remote sensing for environmental monitoring, and communication in infrared remote controls.
- Ultraviolet Radiation: Used for sterilization, medical treatments, and tanning.
- Gamma Rays: Used in medical treatments for cancer, industrial processes for sterilizing medical equipment, and nuclear research.
FAQs on Electromagnetic Waves
1. How are electromagnetic waves produced?
Electromagnetic waves are produced when charged particles accelerate. This acceleration can be caused by various mechanisms, including the movement of electrons in an antenna, the vibration of atoms in a heated object, or the decay of radioactive nuclei.
2. How do electromagnetic waves travel through space?
Electromagnetic waves travel through space by oscillating electric and magnetic fields that are perpendicular to each other and to the direction of propagation. These fields regenerate each other as they travel, creating a self-sustaining wave.
3. What are the dangers of electromagnetic radiation?
High-energy electromagnetic radiation, such as ultraviolet radiation, X-rays, and gamma rays, can be harmful to living organisms. These forms of radiation can damage DNA, cause cancer, and lead to other health problems. However, lower-energy forms of electromagnetic radiation, such as radio waves and visible light, are generally considered safe.
4. How do electromagnetic waves interact with matter?
Electromagnetic waves interact with matter in various ways, depending on the frequency of the wave and the properties of the material. Some materials absorb electromagnetic waves, while others reflect or transmit them. These interactions are responsible for phenomena such as heating, reflection, refraction, and diffraction.
5. How are electromagnetic waves used in technology?
Electromagnetic waves are used in a wide range of technologies, including communication, navigation, medical imaging, industrial processes, and scientific research. The specific application of a particular electromagnetic wave depends on its frequency and the properties of the material it interacts with.
Tips for Understanding Electromagnetic Waves
- Visualize the electromagnetic spectrum: Imagine a spectrum with different colors representing the various types of electromagnetic waves, from low-energy radio waves to high-energy gamma rays.
- Focus on the key properties: Understand the concepts of frequency, wavelength, and energy, and how they relate to each other.
- Explore real-world applications: Learn about how electromagnetic waves are used in everyday technologies, such as your mobile phone, microwave oven, and medical imaging equipment.
- Consider the potential risks: Be aware of the dangers of high-energy electromagnetic radiation and take precautions to minimize exposure.
Conclusion:
Electromagnetic waves are an integral part of our world, shaping our lives in countless ways. From the light that illuminates our homes to the radio waves that connect us across continents, these invisible forces have revolutionized communication, healthcare, and countless other aspects of modern society. Understanding the nature and applications of electromagnetic waves is essential for appreciating their profound impact on our world and for harnessing their potential for future advancements.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Invisible Symphony: Electromagnetic Waves and Their Impact on Our World. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!