The Powerhouse Within: Exploring The Significance Of Mitochondria-Rich Cells
The Powerhouse Within: Exploring the Significance of Mitochondria-Rich Cells
Related Articles: The Powerhouse Within: Exploring the Significance of Mitochondria-Rich Cells
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to The Powerhouse Within: Exploring the Significance of Mitochondria-Rich Cells. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Powerhouse Within: Exploring the Significance of Mitochondria-Rich Cells
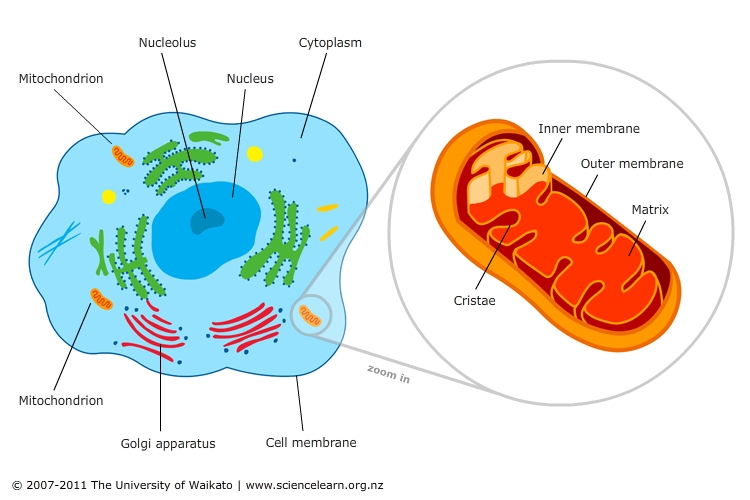
The human body is a marvel of complex machinery, with each cell performing specific functions that contribute to the overall well-being of the organism. Within these cells, a vital organelle, the mitochondrion, plays a central role in energy production, a process essential for life. While all cells contain mitochondria, certain cells require a greater number of these organelles to meet their high energy demands. This article delves into the significance of cells with abundant mitochondria, exploring their unique functions, the benefits they offer, and their implications for health and disease.
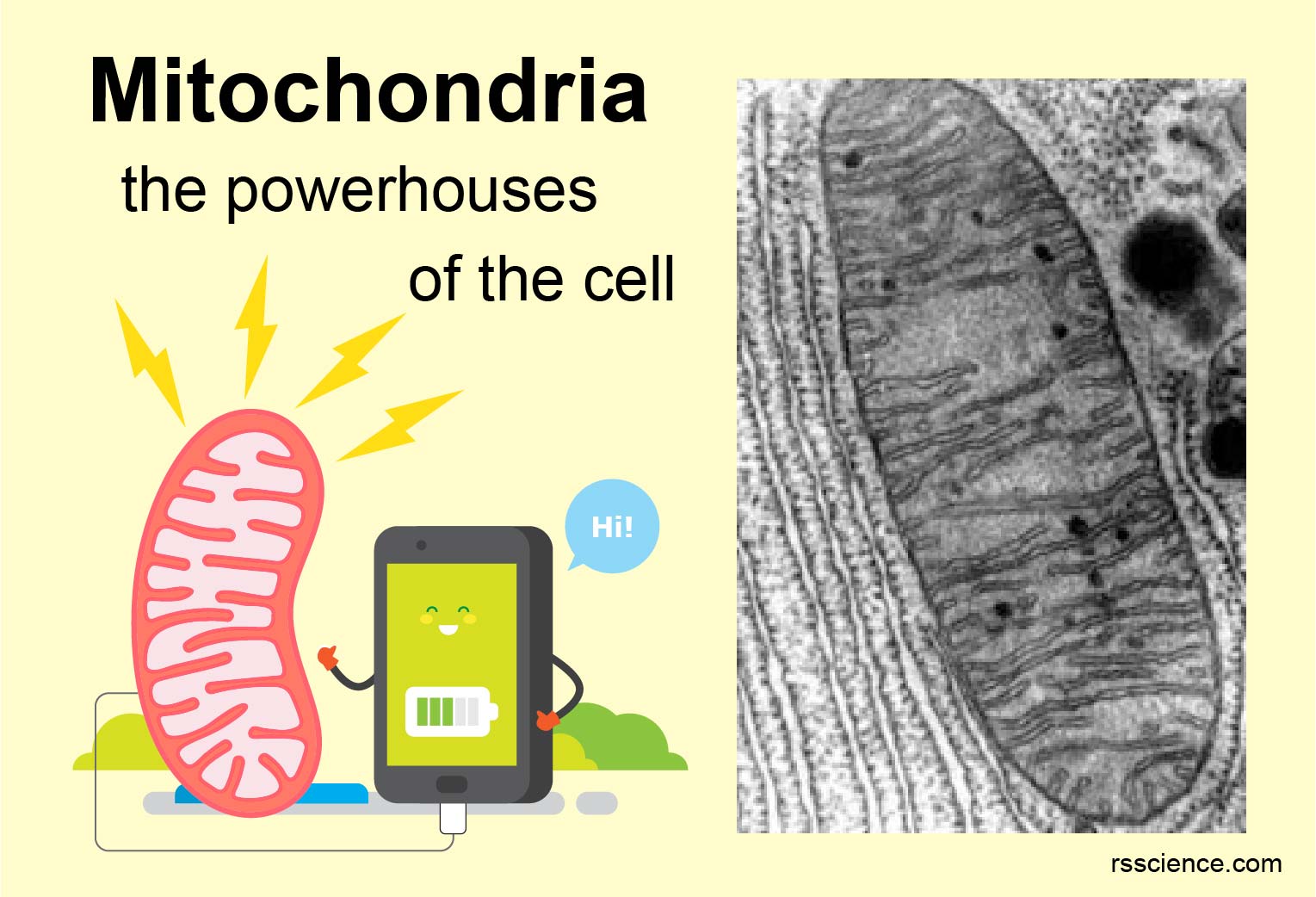
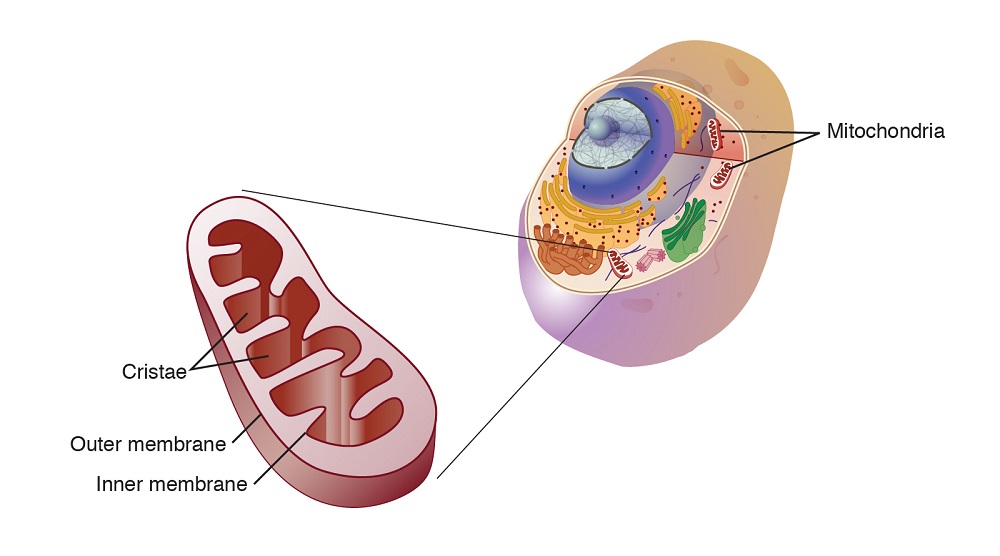
Mitochondria: The Energy Factories of the Cell
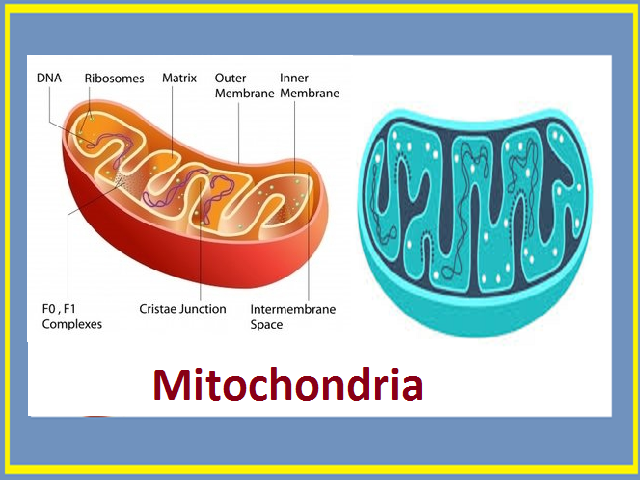
Mitochondria are often referred to as the "powerhouses of the cell" due to their primary function: ATP (adenosine triphosphate) production through cellular respiration. This process involves breaking down glucose and other nutrients to generate energy that fuels various cellular activities, including muscle contraction, protein synthesis, and nerve impulse transmission.
Cells with Abundant Mitochondria: A Specialized Workforce
Certain cell types require a significantly higher energy output to perform their specialized functions. These cells, therefore, contain a greater number of mitochondria to meet their elevated energy demands. Examples of such cells include:
- Muscle Cells: Muscles require a constant supply of energy for contraction and movement. Muscle cells, particularly those in skeletal and cardiac muscles, are packed with mitochondria to support their high energy needs.
- Nerve Cells: Neurons, the fundamental units of the nervous system, are highly active cells that transmit electrical signals throughout the body. The energy demands of neuronal activity are met by a large number of mitochondria within these cells.
- Liver Cells: The liver plays a crucial role in detoxification, metabolism, and energy storage. Liver cells contain a high concentration of mitochondria to support these diverse metabolic functions.
- Sperm Cells: Sperm cells require a substantial amount of energy to propel themselves towards the egg during fertilization. This energy is generated by a large number of mitochondria found within the sperm’s midpiece.
- Pancreatic Beta Cells: These cells produce and secrete insulin, a hormone essential for regulating blood sugar levels. Beta cells require a high energy output to synthesize and release insulin, which is facilitated by a dense population of mitochondria.
Benefits of Abundant Mitochondria
The presence of abundant mitochondria in specific cell types offers several advantages, including:
- Enhanced Energy Production: Cells with more mitochondria can generate greater amounts of ATP, providing them with the necessary energy to perform their functions efficiently. This is particularly important for cells with high energy demands, such as muscle cells and neurons.
- Increased Metabolic Efficiency: Mitochondria play a vital role in various metabolic processes, including glucose metabolism, fatty acid oxidation, and amino acid synthesis. Cells with abundant mitochondria exhibit enhanced metabolic efficiency, contributing to overall cellular health.
- Improved Oxidative Stress Management: Mitochondria are the primary source of reactive oxygen species (ROS), byproducts of energy production that can damage cellular components. Cells with abundant mitochondria often possess robust antioxidant defenses, mitigating oxidative stress and protecting against cellular damage.
- Enhanced Cell Signaling: Mitochondria are not only energy producers but also active participants in cell signaling pathways. Cells with abundant mitochondria may exhibit improved communication and coordination within the body.
- Enhanced Resistance to Stress: Cells with abundant mitochondria are often more resilient to various stressors, including environmental toxins, oxidative stress, and nutrient deprivation. This enhanced resilience contributes to overall cellular health and longevity.
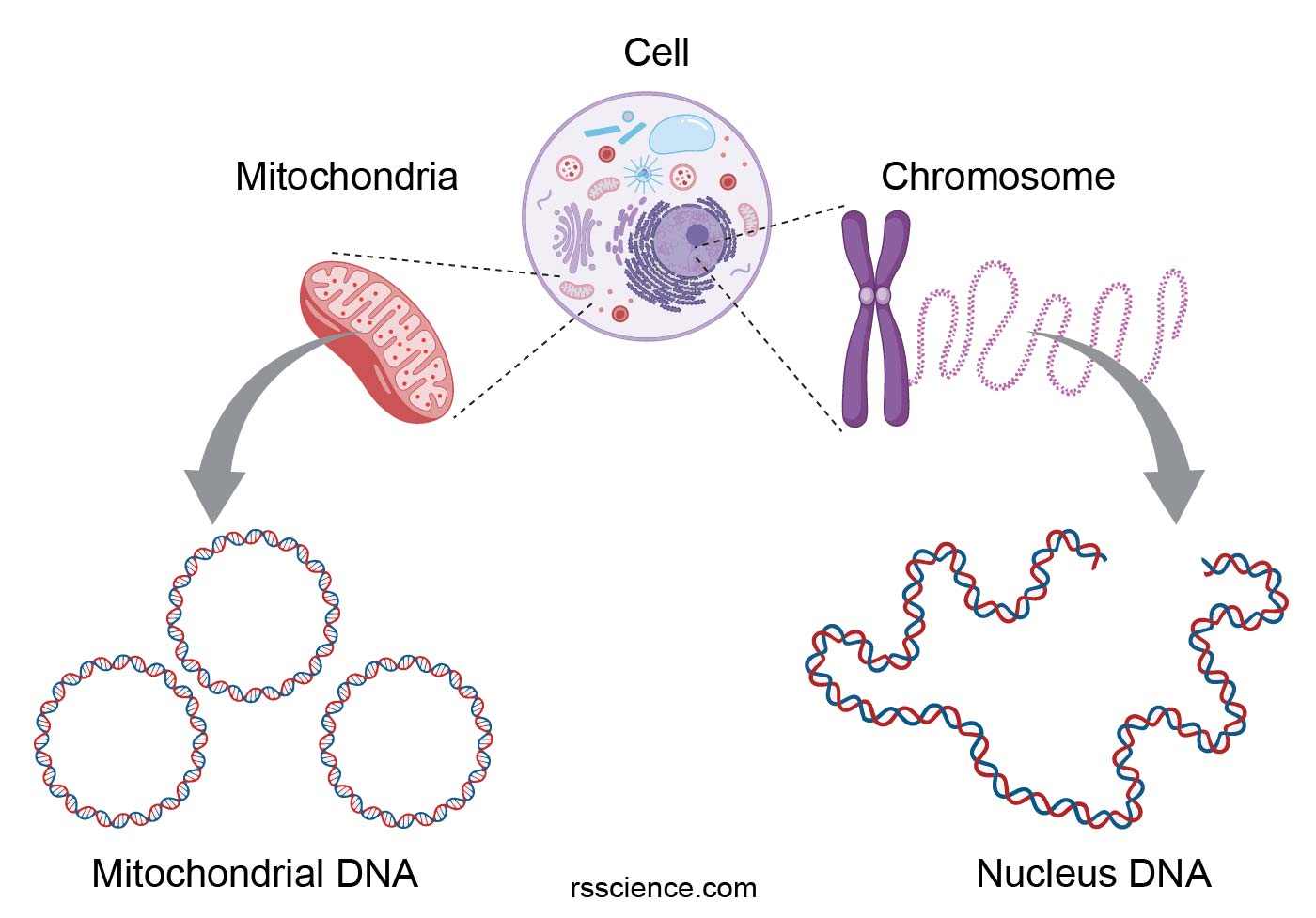
Mitochondrial Function and Health
The proper functioning of mitochondria is crucial for overall health. Dysfunctional mitochondria, often associated with aging and disease, can lead to:
- Reduced Energy Production: Impaired mitochondrial function can result in decreased ATP production, leading to fatigue, weakness, and reduced physical performance.
- Increased Oxidative Stress: Dysfunctional mitochondria produce excessive amounts of ROS, contributing to oxidative damage and cellular aging.
- Metabolic Disorders: Mitochondrial dysfunction is implicated in various metabolic disorders, including diabetes, obesity, and cardiovascular disease.
- Neurodegenerative Diseases: Impaired mitochondrial function is linked to neurodegenerative diseases, such as Alzheimer’s disease and Parkinson’s disease.
FAQs: Mitochondria and Cell Function
1. How do cells increase their mitochondrial content?
Cells can increase their mitochondrial content through a process called mitochondrial biogenesis. This process involves the synthesis of new mitochondria from existing ones, often triggered by increased energy demands or environmental stressors.
2. Can we manipulate mitochondrial content in cells?
Research is ongoing to explore methods for manipulating mitochondrial content in cells. Exercise, caloric restriction, and certain supplements have been shown to stimulate mitochondrial biogenesis, potentially enhancing cellular function and health.
3. What are the implications of mitochondrial dysfunction for disease?
Mitochondrial dysfunction is implicated in a wide range of diseases, including neurodegenerative diseases, metabolic disorders, and cardiovascular disease. Research is focused on developing therapies that target mitochondrial dysfunction to improve disease outcomes.
Tips for Maintaining Mitochondrial Health:
- Regular Exercise: Exercise stimulates mitochondrial biogenesis, leading to increased energy production and improved cellular function.
- Healthy Diet: A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains provides essential nutrients for optimal mitochondrial function.
- Caloric Restriction: Moderate caloric restriction has been shown to enhance mitochondrial function and extend lifespan in some studies.
- Supplementation: Certain supplements, such as CoQ10 and N-acetylcysteine, may support mitochondrial health, although further research is needed.
- Stress Management: Chronic stress can negatively impact mitochondrial function. Techniques for stress management, such as meditation and yoga, may help maintain mitochondrial health.
Conclusion
Cells with abundant mitochondria play a vital role in maintaining cellular function and overall health. These energy-rich cells contribute to diverse physiological processes, including muscle contraction, nerve impulse transmission, and metabolic regulation. Understanding the significance of these cells and promoting their health through lifestyle modifications and interventions is crucial for maintaining optimal well-being. Further research on mitochondrial function and its implications for disease will continue to advance our understanding of this essential organelle and its impact on human health.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Powerhouse Within: Exploring the Significance of Mitochondria-Rich Cells. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!