The Significance Of Average Cost: A Comprehensive Exploration
The Significance of Average Cost: A Comprehensive Exploration
Related Articles: The Significance of Average Cost: A Comprehensive Exploration
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to The Significance of Average Cost: A Comprehensive Exploration. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: The Significance of Average Cost: A Comprehensive Exploration
- 2 Introduction
- 3 The Significance of Average Cost: A Comprehensive Exploration
- 3.1 Defining Average Cost: A Foundation for Understanding
- 3.2 Unveiling the Importance of Average Cost
- 3.3 Exploring the Applications of Average Cost
- 3.4 Understanding the Limitations of Average Cost
- 3.5 Frequently Asked Questions about Average Cost
- 3.6 Tips for Utilizing Average Cost Effectively
- 3.7 Conclusion: The Enduring Importance of Average Cost
- 4 Closure
The Significance of Average Cost: A Comprehensive Exploration

The concept of average cost, while seemingly straightforward, plays a crucial role in various economic and business contexts. It serves as a valuable tool for understanding the overall cost of production, making informed pricing decisions, and analyzing the financial health of a business. This article delves into the intricacies of average cost, exploring its different forms, applications, and implications.
Defining Average Cost: A Foundation for Understanding
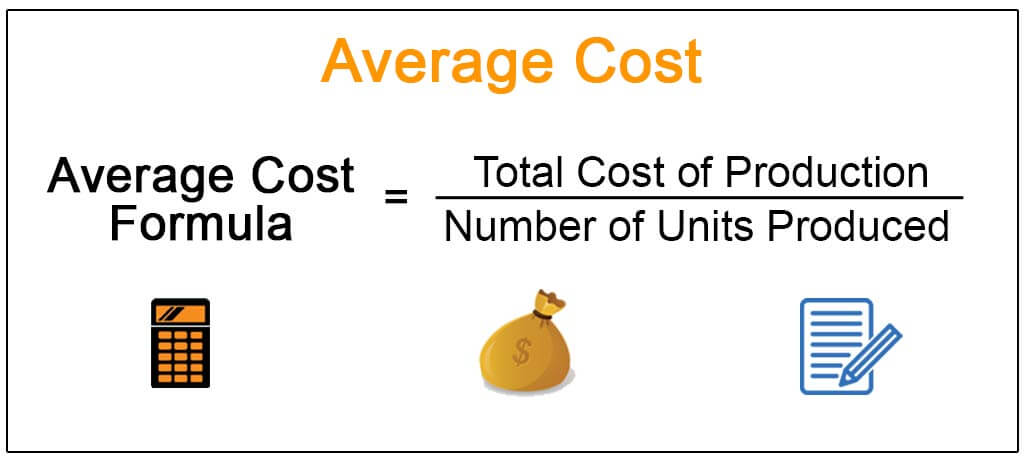
Average cost, in its simplest form, refers to the total cost of production divided by the total number of units produced. This metric offers a comprehensive view of the cost per unit, encompassing both fixed and variable costs. Fixed costs, such as rent and salaries, remain constant regardless of production volume, while variable costs, such as raw materials and utilities, fluctuate with production levels.
There are two primary types of average cost:
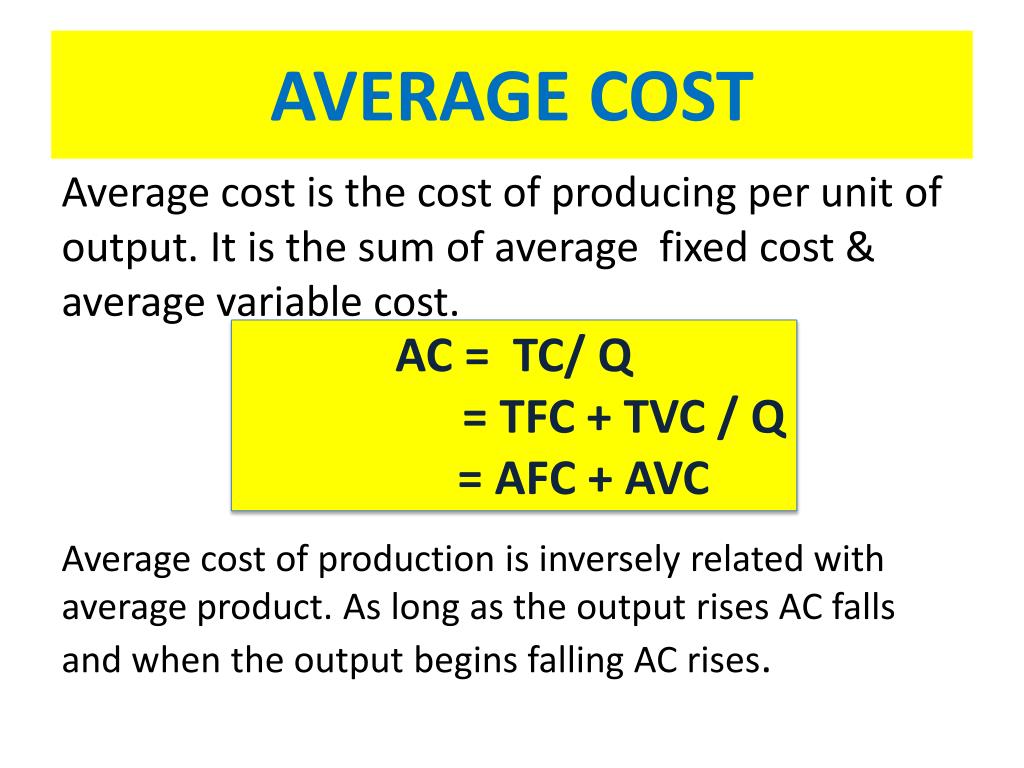
- Average Total Cost (ATC): This represents the total cost of production divided by the total quantity produced. It encapsulates both fixed and variable costs.
- Average Variable Cost (AVC): This reflects the variable cost of production divided by the total quantity produced. It focuses solely on costs that fluctuate with output.
Unveiling the Importance of Average Cost
The significance of average cost lies in its multifaceted applications:
- Pricing Strategies: Businesses leverage average cost to determine optimal pricing strategies. By understanding the cost per unit, companies can set prices that cover production expenses while ensuring profitability.
- Profitability Analysis: Average cost is instrumental in assessing a business’s profitability. Comparing average cost to the selling price per unit reveals the profit margin, providing insights into the financial health of the enterprise.
- Cost Control Measures: Tracking average cost over time helps businesses identify cost-saving opportunities. By analyzing trends and comparing costs across different production periods, companies can identify areas for optimization.
- Production Efficiency: Average cost serves as a benchmark for production efficiency. Decreases in average cost indicate improved efficiency, while increases suggest potential bottlenecks or inefficiencies.
- Investment Decisions: Businesses consider average cost when making investment decisions. A lower average cost might indicate a more efficient production process, making the business more attractive to investors.
Exploring the Applications of Average Cost
Average cost finds applications across diverse industries and sectors:
- Manufacturing: Manufacturers use average cost to calculate the cost of producing each unit of a product, facilitating pricing decisions and profit margin analysis.
- Retail: Retailers utilize average cost to determine the cost of goods sold, track inventory levels, and set competitive prices.
- Services: Service providers employ average cost to understand the cost of delivering each service, optimizing pricing strategies and identifying cost-saving opportunities.
- Agriculture: Farmers use average cost to calculate the cost of producing crops or livestock, factoring in factors like land, labor, and input costs.
- Healthcare: Healthcare providers utilize average cost to determine the cost of providing medical services, informing pricing decisions and budget planning.
Understanding the Limitations of Average Cost
While average cost provides valuable insights, it’s crucial to acknowledge its limitations:
- Oversimplification: Average cost assumes a uniform cost structure across all units produced, which may not always hold true. Production costs can fluctuate based on factors like economies of scale or changes in input prices.
- Lack of Time Sensitivity: Average cost is a static measure, failing to capture dynamic changes in costs over time. It doesn’t account for fluctuations in input prices, labor costs, or technological advancements.
- Limited Scope: Average cost focuses solely on production costs, neglecting other crucial factors like marketing expenses, research and development costs, and administrative overhead.
Frequently Asked Questions about Average Cost
Q: How is average cost calculated?
A: Average cost is calculated by dividing the total cost of production by the total number of units produced.
Q: What are the different types of average cost?
A: There are two main types: Average Total Cost (ATC) and Average Variable Cost (AVC). ATC includes both fixed and variable costs, while AVC only considers variable costs.
Q: What are some factors that can influence average cost?
A: Factors like input prices, labor costs, technology, production volume, and economies of scale can influence average cost.
Q: How can average cost be used to improve business efficiency?
A: By tracking average cost over time, businesses can identify cost-saving opportunities, streamline production processes, and optimize resource allocation.
Q: What are the limitations of using average cost?
A: Average cost can be an oversimplification, failing to capture dynamic cost fluctuations and neglecting other important business expenses.
Tips for Utilizing Average Cost Effectively
- Track Average Cost Consistently: Regularly calculate and analyze average cost to identify trends and potential areas for improvement.
- Consider Different Cost Components: Break down average cost into its constituent components (fixed and variable costs) for a more detailed understanding.
- Account for Time Sensitivity: Recognize that average cost is a static measure and adjust your analysis based on changing market conditions and input prices.
- Complement Average Cost with Other Metrics: Use average cost in conjunction with other financial metrics, such as profit margin, return on investment, and cash flow, for a comprehensive view of business performance.
Conclusion: The Enduring Importance of Average Cost
Average cost remains a fundamental concept in economics and business, providing a valuable tool for understanding production costs, making informed pricing decisions, and analyzing the financial health of an enterprise. While acknowledging its limitations, businesses can effectively leverage average cost by implementing consistent tracking, considering different cost components, and incorporating it into a broader financial analysis framework. By understanding and utilizing average cost effectively, organizations can optimize their operations, enhance profitability, and achieve sustainable growth.

:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/DDM_INV_average-cost-method_final-111522-05a9a63e95e8457682faa53e734352e8.jpg)


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Significance of Average Cost: A Comprehensive Exploration. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!