The Silent Killer: Understanding Carbon Monoxide In The Home
The Silent Killer: Understanding Carbon Monoxide in the Home
Related Articles: The Silent Killer: Understanding Carbon Monoxide in the Home
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to The Silent Killer: Understanding Carbon Monoxide in the Home. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Silent Killer: Understanding Carbon Monoxide in the Home

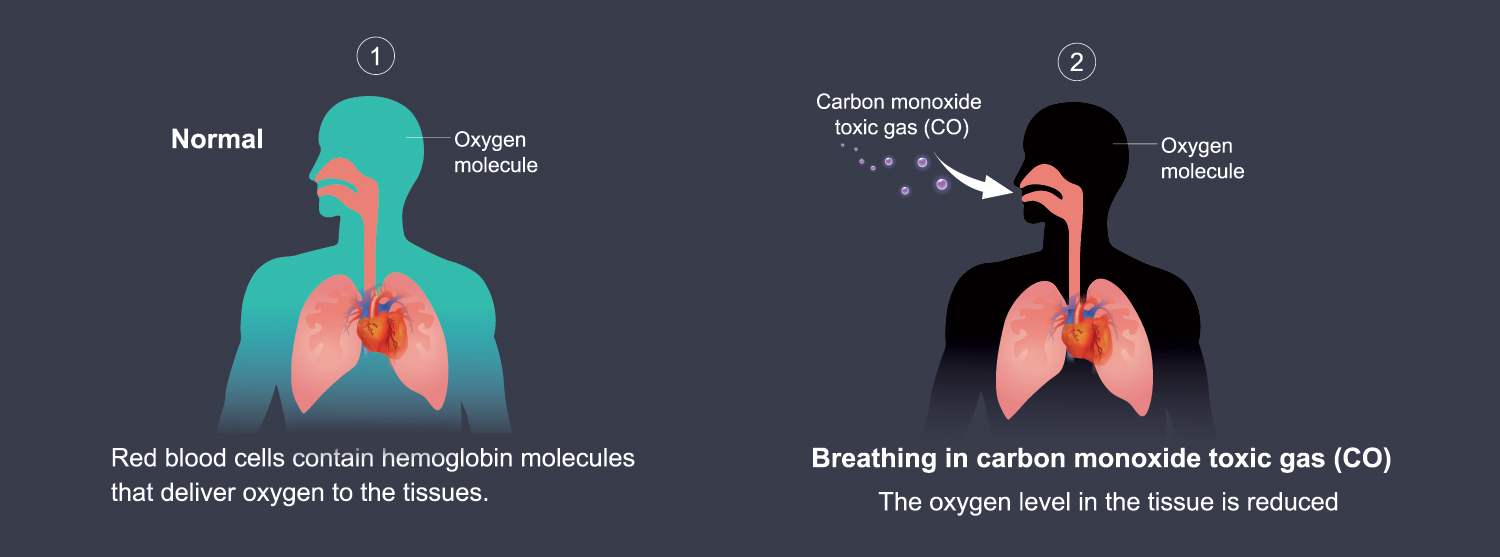
Carbon monoxide (CO), a colorless, odorless, and tasteless gas, poses a significant threat to human health. It is a byproduct of incomplete combustion and can accumulate in homes, leading to serious health consequences and even fatalities. Recognizing the potential sources of CO in the home is crucial for safeguarding the well-being of residents.
Common Sources of Carbon Monoxide in Homes
Understanding the potential sources of CO is essential for implementing preventive measures. Here are some of the most prevalent culprits:
1. Fuel-Burning Appliances:
- Gas Furnaces and Boilers: These appliances are a common source of CO if they are not properly maintained or are malfunctioning. Issues like cracked heat exchangers, blocked vents, or improper installation can lead to CO emissions.
- Gas Water Heaters: Similar to furnaces, gas water heaters require regular inspection and maintenance to ensure safe operation.
- Gas Stoves and Ovens: While generally safe, these appliances can release CO if not properly vented. Leaving food unattended or using a stovetop for extended periods without proper ventilation can increase the risk of CO accumulation.
- Gas Fireplaces: Open fireplaces, especially older models, can contribute to CO buildup if they are not equipped with a proper flue or chimney.
- Gas Logs: These decorative logs, often used in fireplaces, can emit CO if not installed or used correctly.
2. Combustion Engines:
- Gas-Powered Generators: These generators, commonly used during power outages, can release significant amounts of CO if operated in enclosed spaces or without proper ventilation.
- Cars and Trucks: Leaving vehicles running in garages or attached spaces can lead to dangerous CO levels.
3. Other Sources:
- Cigarette Smoke: Cigarette smoke contains CO, and prolonged exposure in poorly ventilated areas can elevate CO levels.
- Charcoal Grills: Using charcoal grills indoors or in poorly ventilated areas can result in dangerous CO accumulation.
- Propane and Kerosene Heaters: These heaters, if not properly vented, can also contribute to CO buildup.
- Gas-Powered Tools: Power tools that utilize gasoline engines, such as lawnmowers or generators, can emit CO if used in enclosed spaces.
Identifying Potential CO Risks
- Regular Inspections: Scheduling annual inspections of all fuel-burning appliances by a qualified technician is crucial.
- Proper Ventilation: Ensuring adequate ventilation in areas where fuel-burning appliances are present is essential.
- Carbon Monoxide Detectors: Installing CO detectors on every level of the home and near sleeping areas is vital.
- Following Manufacturer Instructions: Always adhere to manufacturer guidelines for operating and maintaining appliances.
- Maintaining Appliances: Regular cleaning and maintenance of appliances are essential for preventing malfunctions that can lead to CO emissions.
- Avoiding Using Appliances for Unintended Purposes: Using appliances for purposes other than those intended can increase the risk of CO production.
Symptoms of Carbon Monoxide Poisoning
Recognizing the symptoms of CO poisoning is essential for prompt action:
- Headache: A common symptom, often described as a dull ache.
- Dizziness and Fatigue: Feeling lightheaded, weak, or tired.
- Nausea and Vomiting: Feeling sick to the stomach.
- Shortness of Breath: Difficulty breathing or chest tightness.
- Confusion and Disorientation: Feeling confused or disoriented.
- Loss of Consciousness: In severe cases, CO poisoning can lead to unconsciousness.
Immediate Action in Case of Suspected CO Poisoning:
- Open Windows and Doors: Allow fresh air to circulate in the home.
- Turn Off Fuel-Burning Appliances: Disconnect any appliances that may be emitting CO.
- Evacuate the Home: Move everyone outside to fresh air immediately.
- Call Emergency Services: Dial 911 or your local emergency number.
- Seek Medical Attention: Even if symptoms appear mild, seek medical attention as CO poisoning can have long-term health effects.
FAQs about Carbon Monoxide in Homes
1. How can I tell if my home has a CO problem?
The only way to definitively know if your home has a CO problem is to use a CO detector. While symptoms of CO poisoning can be an indicator, they can also be caused by other factors.
2. Where should I install CO detectors?
Install CO detectors on every level of your home, including the basement and attic, and near sleeping areas.
3. How often should I test my CO detectors?
Test your CO detectors at least once a month and replace the batteries every six months or as recommended by the manufacturer.
4. What should I do if my CO detector alarms?
If your CO detector alarms, immediately evacuate your home, open windows and doors, and call emergency services.
5. How can I prevent CO poisoning?
Regularly inspect and maintain fuel-burning appliances, ensure proper ventilation, and install and maintain CO detectors.
Tips for Reducing CO Risks in Your Home
- Regularly inspect and maintain all fuel-burning appliances.
- Ensure proper ventilation in areas where fuel-burning appliances are located.
- Never use generators, charcoal grills, or gas-powered tools indoors or in attached spaces.
- Do not leave cars running in garages or attached spaces.
- Install and maintain CO detectors on every level of your home.
- Be aware of the symptoms of CO poisoning and seek medical attention immediately if you suspect CO poisoning.
Conclusion
Carbon monoxide poses a significant threat to human health. Recognizing potential sources of CO in the home, implementing preventive measures, and being aware of the symptoms of CO poisoning are crucial steps for protecting yourself and your family. By taking these precautions, you can significantly reduce the risk of CO poisoning and ensure a safe and healthy living environment.







Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Silent Killer: Understanding Carbon Monoxide in the Home. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!