Understanding Amperage In Household Appliances: A Guide To Electrical Consumption
Understanding Amperage in Household Appliances: A Guide to Electrical Consumption
Related Articles: Understanding Amperage in Household Appliances: A Guide to Electrical Consumption
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Understanding Amperage in Household Appliances: A Guide to Electrical Consumption. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Understanding Amperage in Household Appliances: A Guide to Electrical Consumption
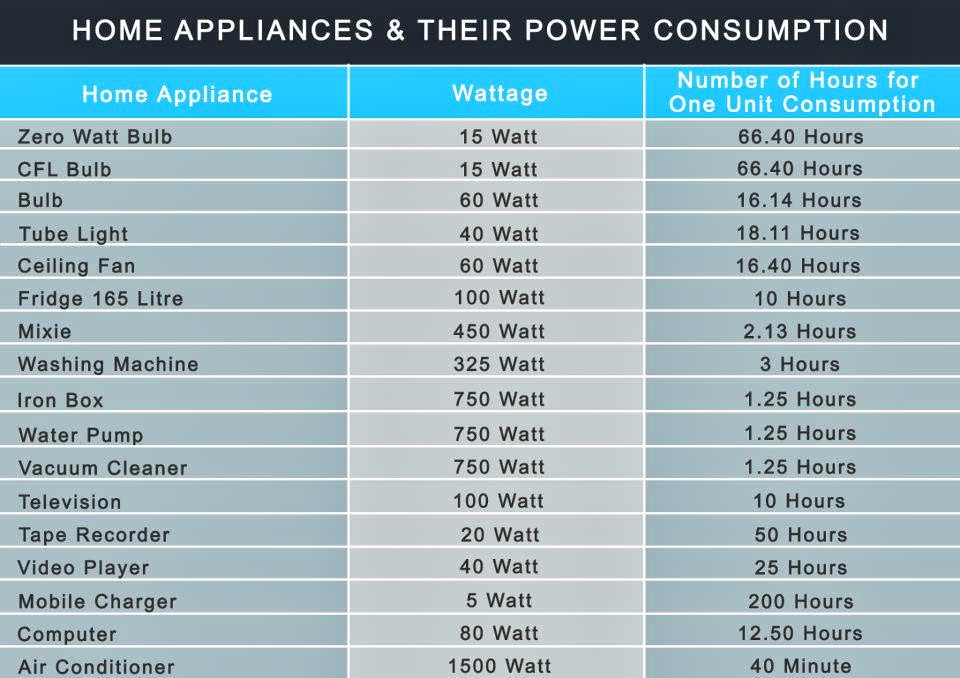
Amperage, often denoted as "amps," is a fundamental concept in electricity, representing the rate of electrical current flow. In the context of household appliances, understanding amperage is crucial for ensuring safe and efficient operation. This article delves into the amperage requirements of common household items, providing insights into their electrical consumption and the implications for your home’s electrical system.
Understanding the Basics: Voltage, Current, and Power
Before exploring specific appliances, it is essential to grasp the relationship between voltage, current, and power.
- Voltage (V): This represents the electrical potential difference, akin to pressure in a water system. In the United States, standard household voltage is 120 volts.
- Current (A): Measured in amperes (amps), this represents the flow of electrical charge. Higher amperage signifies a greater flow of electricity.
- Power (W): Measured in watts, power represents the rate at which electrical energy is consumed. It is calculated by multiplying voltage and current (Power = Voltage x Current).
Amperage Requirements of Common Household Appliances
The following table provides an overview of the typical amperage requirements for various household appliances:
| Appliance | Amperage (A) |
|---|---|
| Lighting | |
| Incandescent Bulb (60W) | 0.5 |
| LED Bulb (10W) | 0.1 |
| Kitchen Appliances | |
| Microwave Oven | 10-15 |
| Electric Stove | 15-20 |
| Refrigerator | 5-7 |
| Dishwasher | 10-12 |
| Garbage Disposal | 10-15 |
| Laundry Appliances | |
| Washing Machine | 10-15 |
| Clothes Dryer | 15-20 |
| Other Appliances | |
| Television | 1-2 |
| Computer | 1-2 |
| Vacuum Cleaner | 8-10 |
| Air Conditioner | 10-20 (depending on size) |
Factors Influencing Amperage
Several factors influence the amperage required by a particular appliance:
- Power Consumption: Appliances with higher power ratings generally require more amperage.
- Efficiency: Energy-efficient appliances typically consume less power and therefore require lower amperage.
- Usage Patterns: Appliances used for extended periods or at high power settings require higher amperage.
- Voltage: Higher voltage systems can accommodate higher amperage flows.
The Importance of Amperage and Electrical Safety
Understanding amperage is crucial for ensuring electrical safety in your home:
- Overloading Circuits: Using appliances with high amperage requirements on circuits designed for lower amperage can lead to overheating and potential fire hazards.
- Circuit Breaker Protection: Circuit breakers are safety devices that interrupt the flow of electricity when excessive amperage is detected, preventing damage to wiring and appliances.
- Proper Wiring: Electrical wiring must be appropriately sized to handle the amperage requirements of the appliances it serves.
FAQs on Amperage in Household Appliances
Q: What happens if I use an appliance with a higher amperage requirement than my circuit can handle?
A: Overloading the circuit can lead to overheating, potentially causing fires or damage to appliances and wiring. Circuit breakers are designed to protect against this by interrupting the flow of electricity when excessive amperage is detected.
Q: How can I determine the amperage requirements of my appliances?
A: The amperage rating is usually found on the appliance’s nameplate or in the owner’s manual. You can also consult the appliance’s energy label, which often provides information about power consumption.
Q: Should I be concerned about the amperage requirements of my appliances?
A: It’s essential to be aware of the amperage requirements of your appliances, especially when using multiple high-power appliances simultaneously. This knowledge allows you to prevent overloading circuits and ensure electrical safety.
Tips for Managing Amperage in Your Home
- Avoid overloading circuits: Distribute high-power appliances across multiple circuits to prevent overloading.
- Use power strips with surge protection: Power strips can provide additional outlets and surge protection, but avoid overloading them.
- Consider upgrading your electrical panel: If you frequently experience circuit breakers tripping, consider upgrading your electrical panel to accommodate increased amperage requirements.
- Use energy-efficient appliances: Energy-efficient appliances consume less power and require lower amperage, reducing your energy bill and electrical load.
Conclusion
Understanding amperage is vital for safe and efficient operation of household appliances. By being aware of the amperage requirements of your appliances and taking steps to manage electrical loads effectively, you can ensure a safe and reliable electrical system in your home. Remember to consult a qualified electrician for any concerns or questions regarding your home’s electrical system.
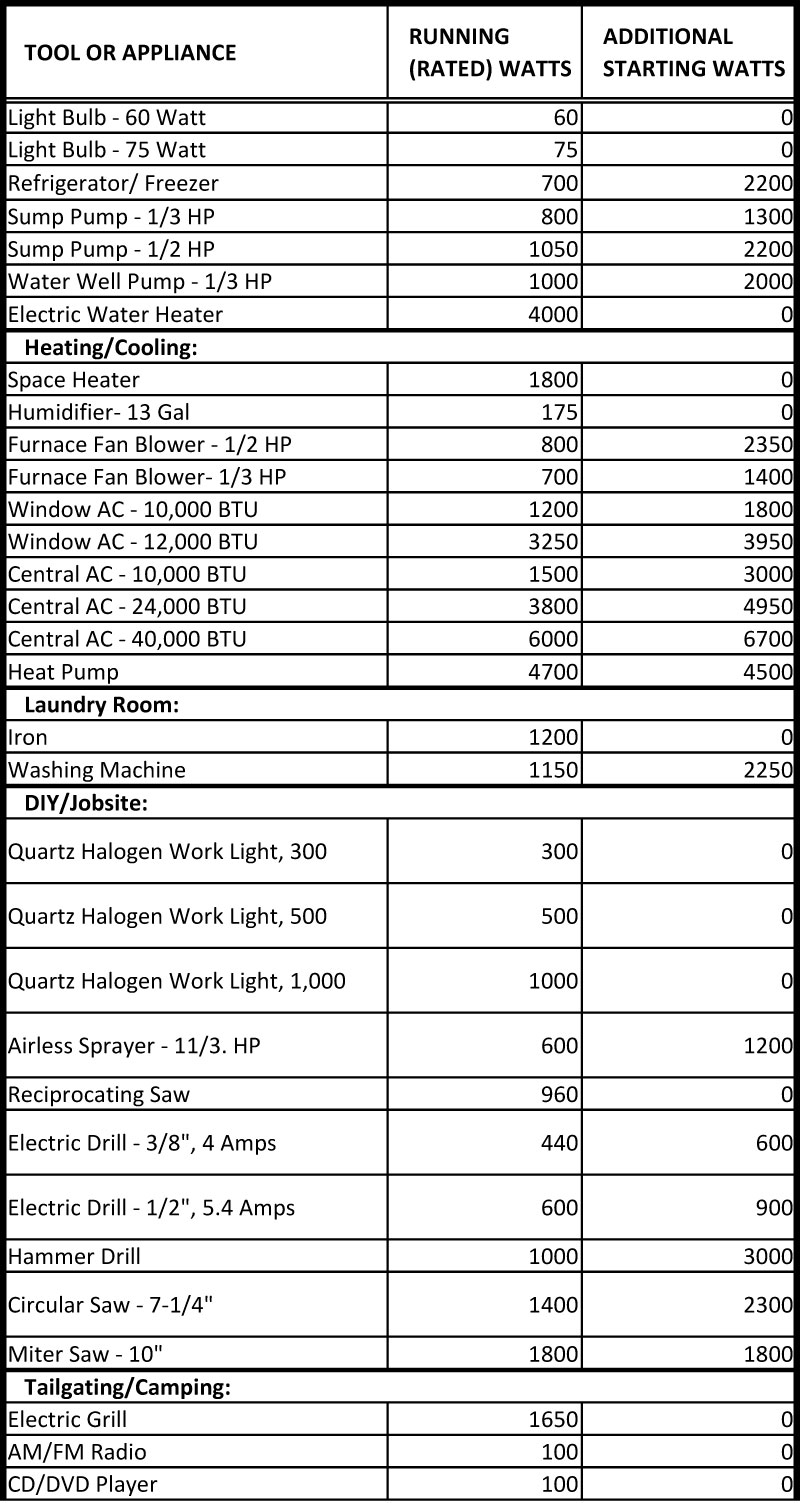


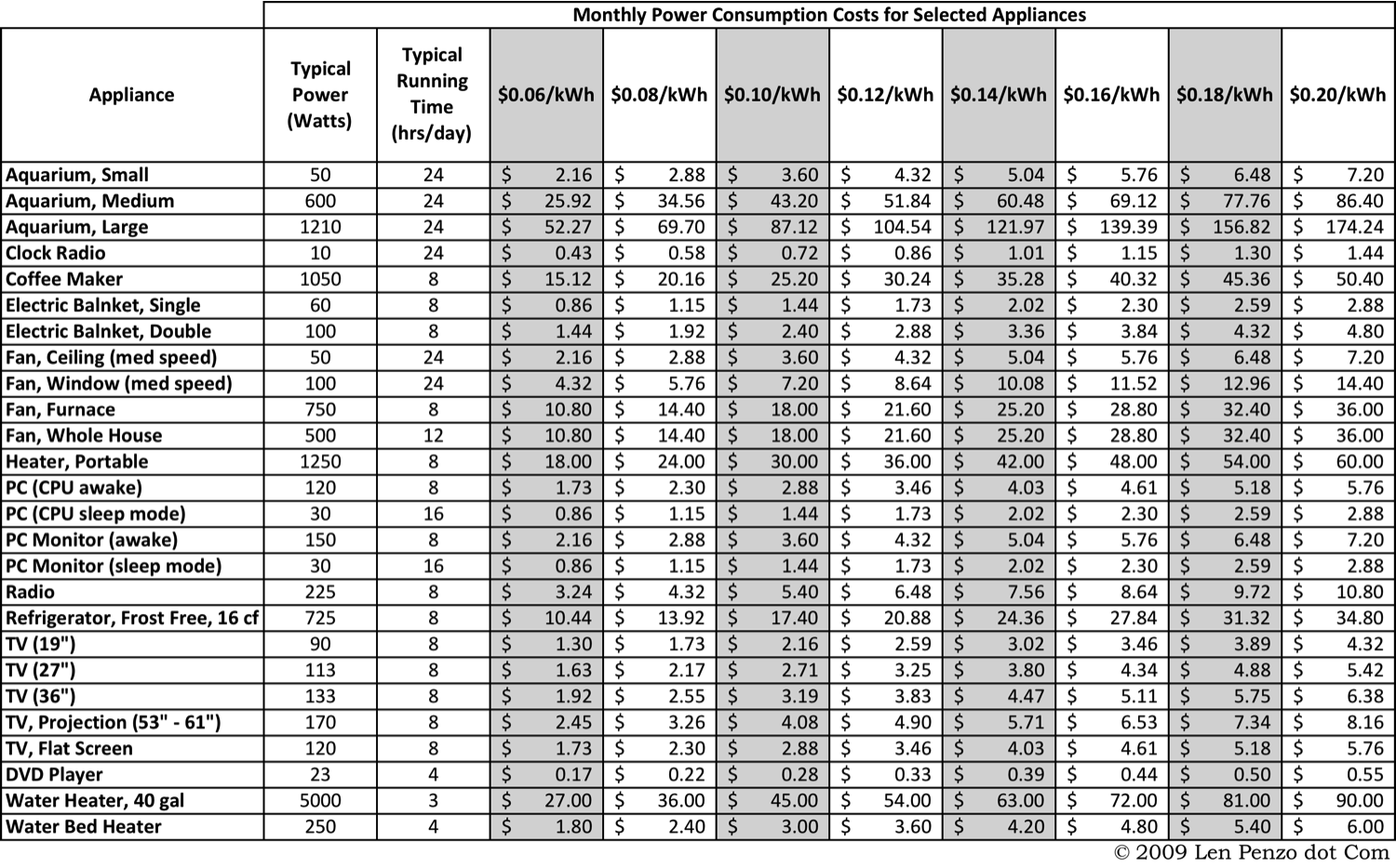
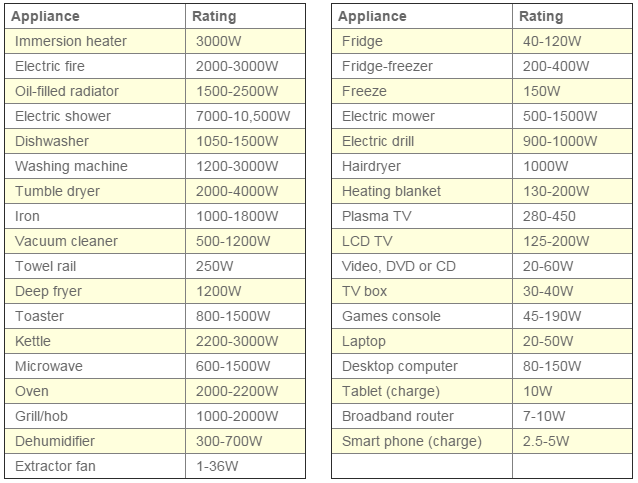


:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/calculate-electrical-circuit-load-capacity-1152739_final-5bd9c3a746e0fb002d327b0a.png)
Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Understanding Amperage in Household Appliances: A Guide to Electrical Consumption. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!