Understanding Household Electricity Consumption: A Comprehensive Guide To Wattage
Understanding Household Electricity Consumption: A Comprehensive Guide to Wattage
Related Articles: Understanding Household Electricity Consumption: A Comprehensive Guide to Wattage
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Understanding Household Electricity Consumption: A Comprehensive Guide to Wattage. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Understanding Household Electricity Consumption: A Comprehensive Guide to Wattage
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Understanding Household Electricity Consumption: A Comprehensive Guide to Wattage
- 3.1 Factors Influencing Household Wattage Consumption
- 3.2 Average Wattage Consumption in Different Appliances
- 3.3 Calculating Household Electricity Consumption
- 3.4 Importance of Understanding Household Wattage Consumption
- 3.5 FAQs Regarding Household Wattage Consumption
- 3.6 Tips for Managing Household Wattage Consumption
- 3.7 Conclusion
- 4 Closure
Understanding Household Electricity Consumption: A Comprehensive Guide to Wattage

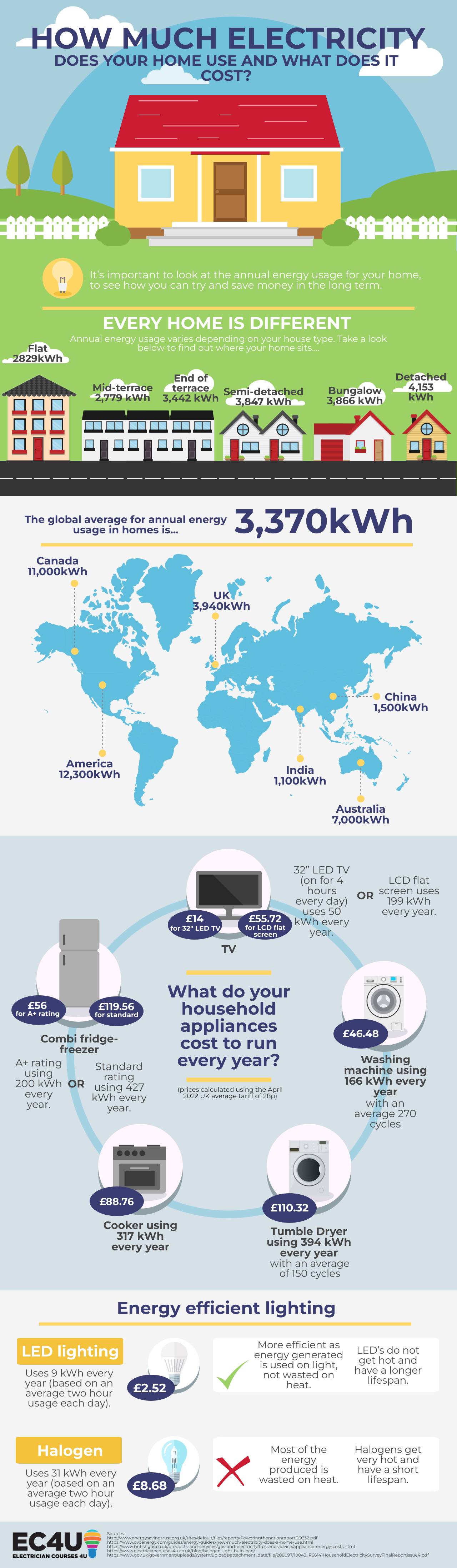
The average household consumes a considerable amount of electricity, powering everything from lighting and appliances to heating and cooling systems. This consumption, measured in watts (W) and kilowatt-hours (kWh), is a crucial factor in determining energy bills and understanding the environmental impact of household activities. This article delves into the complexities of household electricity consumption, providing insights into the factors influencing it, its implications, and strategies for efficient energy management.
Factors Influencing Household Wattage Consumption
The average wattage consumed by a household is not a fixed value. It varies significantly based on several factors, including:
- Household Size: Larger households generally consume more electricity due to increased appliance usage, lighting needs, and heating/cooling requirements.
- Climate: Homes in colder climates require more energy for heating, while those in warmer climates demand more for cooling.
- Appliance Usage: The type and frequency of appliance use significantly impact electricity consumption. Energy-intensive appliances like refrigerators, ovens, and air conditioners consume a substantial amount of power.
- Lifestyle: A household’s lifestyle choices, such as cooking habits, entertainment preferences, and laundry frequency, directly influence electricity consumption.
- Home Insulation: Well-insulated homes require less energy for heating and cooling, resulting in lower overall electricity consumption.
- Energy Efficiency of Appliances: Newer appliances with energy-efficient features consume less power compared to older models.
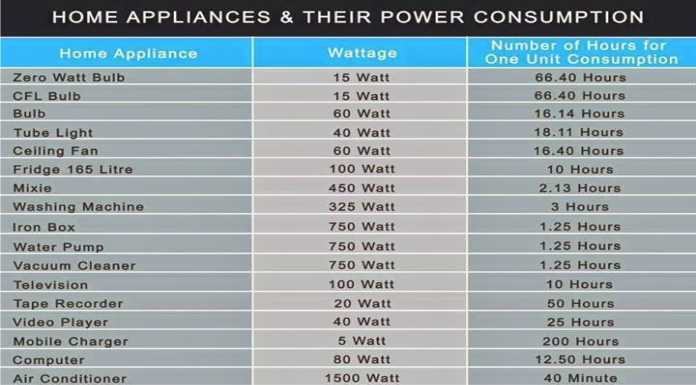
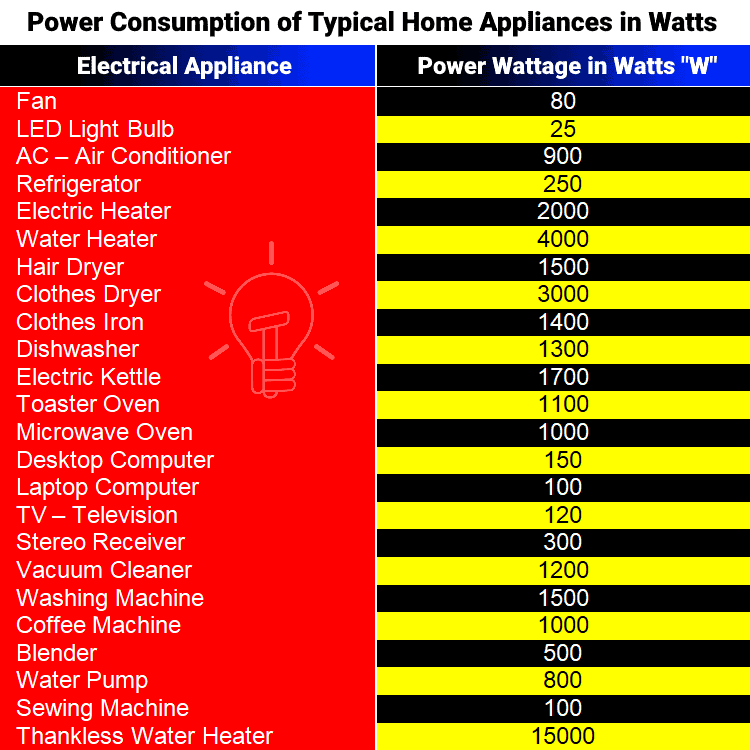
Average Wattage Consumption in Different Appliances
To understand the overall electricity consumption of a household, it is essential to analyze the wattage of individual appliances. The following table provides a general overview of the average wattage consumption of common household appliances:
| Appliance | Average Wattage |
|---|---|
| Refrigerator | 100-200 W |
| Oven | 1,500-3,000 W |
| Microwave | 700-1,200 W |
| Dishwasher | 1,200-1,800 W |
| Washing Machine | 500-1,000 W |
| Dryer | 2,000-4,000 W |
| Air Conditioner | 1,000-3,000 W |
| Television | 50-200 W |
| Computer | 100-300 W |
| Lighting (Incandescent) | 60-100 W |
| Lighting (LED) | 5-15 W |
It is important to note that these are average values, and actual wattage consumption can vary depending on the specific model and usage patterns.
Calculating Household Electricity Consumption
To determine the overall electricity consumption of a household, one needs to calculate the total kilowatt-hours (kWh) used over a specific period. This can be achieved using the following formula:
kWh = (Wattage x Hours of Use) / 1000
For example, if a refrigerator with a wattage of 150 W is used for 24 hours a day, its daily energy consumption would be:
kWh = (150 W x 24 hours) / 1000 = 3.6 kWh
By calculating the energy consumption of individual appliances and adding them up, one can estimate the total electricity consumption of a household.
Importance of Understanding Household Wattage Consumption
Understanding household wattage consumption is crucial for several reasons:
- Reducing Energy Bills: By identifying appliances and habits contributing to high electricity consumption, households can implement strategies to reduce their energy usage and save on energy bills.
- Environmental Sustainability: Reducing electricity consumption helps minimize carbon footprint and promote a more sustainable lifestyle.
- Energy Efficiency: Understanding appliance wattage allows for informed decisions when purchasing new appliances, ensuring energy-efficient options are chosen.
- Load Management: Knowing the wattage consumption of different appliances helps in managing electrical loads to avoid overloading circuits and potential safety hazards.
FAQs Regarding Household Wattage Consumption
Q: How can I reduce my household’s electricity consumption?
A: There are several strategies for reducing household electricity consumption, including:
- Using energy-efficient appliances: Opting for appliances with Energy Star certification can significantly reduce electricity consumption.
- Turning off lights and appliances when not in use: Simple habits like switching off lights when leaving a room and unplugging appliances when not in use can save a considerable amount of energy.
- Using natural light: Maximizing natural light during the day reduces the need for artificial lighting.
- Adjusting thermostat settings: Lowering thermostat settings in winter and raising them in summer can significantly reduce energy consumption for heating and cooling.
- Adopting energy-efficient practices: Using cold water for laundry, air-drying clothes instead of using a dryer, and avoiding using the oven during peak hours are some energy-saving practices.
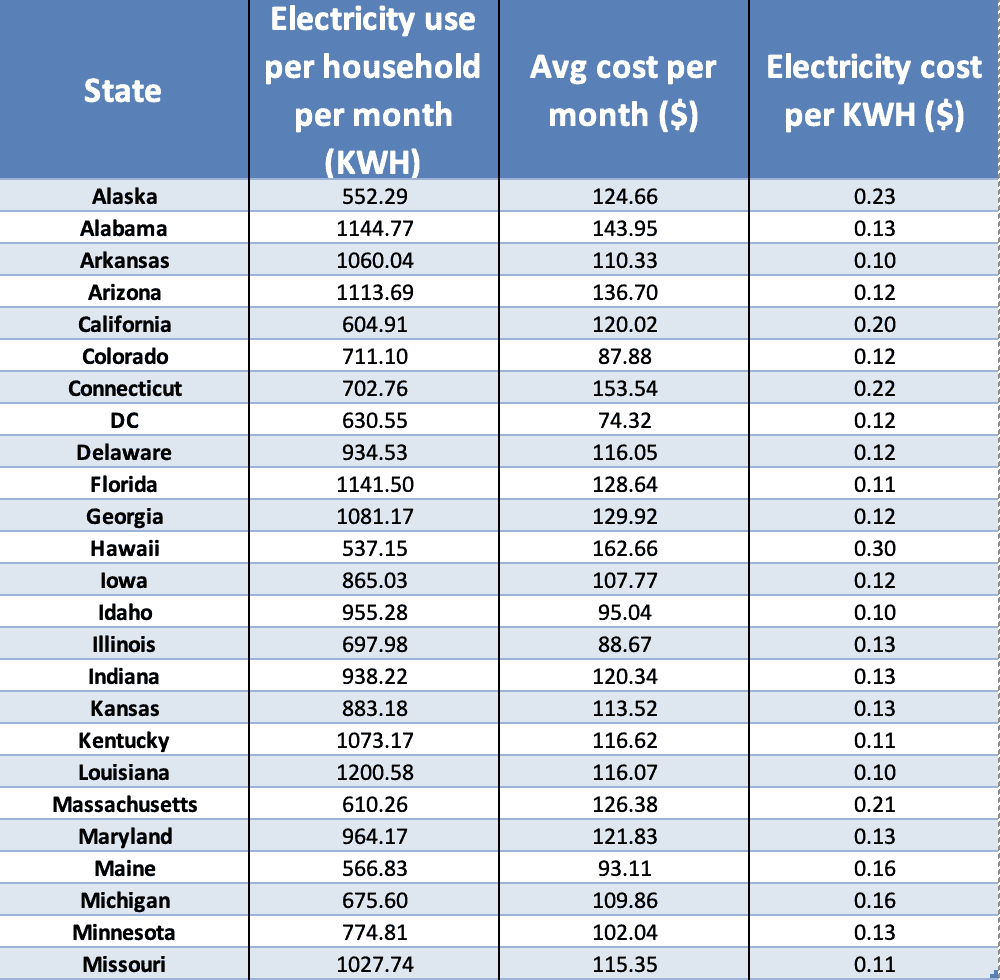
Q: What is the average electricity consumption of a household in the United States?
A: According to the U.S. Energy Information Administration, the average U.S. household consumes around 10,972 kWh of electricity per year. However, this figure can vary significantly based on factors like location, household size, and lifestyle.
Q: How can I monitor my household’s electricity consumption?
A: Several methods can be used to monitor household electricity consumption:
- Smart Meters: Many utility companies provide smart meters that allow for real-time monitoring of electricity consumption.
- Home Energy Monitors: These devices plug into an electrical outlet and track energy usage for different appliances.
- Energy Audit: A professional energy audit can identify areas of energy waste and provide recommendations for improvement.
Q: What are the benefits of reducing household electricity consumption?
A: Reducing household electricity consumption offers several benefits:
- Lower energy bills: Reduced electricity usage translates to lower energy bills, saving money.
- Environmental sustainability: Reducing reliance on fossil fuels for electricity generation contributes to a cleaner environment.
- Improved energy security: Decreased electricity consumption reduces dependence on external energy sources.
Tips for Managing Household Wattage Consumption
- Prioritize energy-efficient appliances: When purchasing new appliances, consider their energy efficiency rating.
- Use energy-saving light bulbs: Switch to LED bulbs, which consume significantly less energy than traditional incandescent bulbs.
- Unplug unused appliances: Unplug chargers, electronics, and appliances when not in use to avoid phantom load, which refers to energy consumption even when devices are turned off.
- Optimize heating and cooling systems: Ensure proper insulation and ventilation to minimize energy loss.
- Adopt energy-conscious habits: Make small changes like air-drying clothes, using cold water for laundry, and avoiding using the oven during peak hours.
- Utilize energy monitoring tools: Use smart meters or home energy monitors to track electricity consumption and identify areas for improvement.
Conclusion
Household wattage consumption is a critical aspect of energy management, impacting both financial well-being and environmental sustainability. Understanding the factors influencing electricity consumption, calculating energy usage, and implementing energy-efficient practices can significantly reduce energy bills, minimize environmental impact, and promote a more sustainable lifestyle. By adopting a proactive approach to managing household wattage consumption, individuals can contribute to a more energy-efficient and environmentally responsible future.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Understanding Household Electricity Consumption: A Comprehensive Guide to Wattage. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!