Understanding The Power Consumption Of Household Appliances: A Guide To Watts And Energy Efficiency
Understanding the Power Consumption of Household Appliances: A Guide to Watts and Energy Efficiency
Related Articles: Understanding the Power Consumption of Household Appliances: A Guide to Watts and Energy Efficiency
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Understanding the Power Consumption of Household Appliances: A Guide to Watts and Energy Efficiency. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Understanding the Power Consumption of Household Appliances: A Guide to Watts and Energy Efficiency
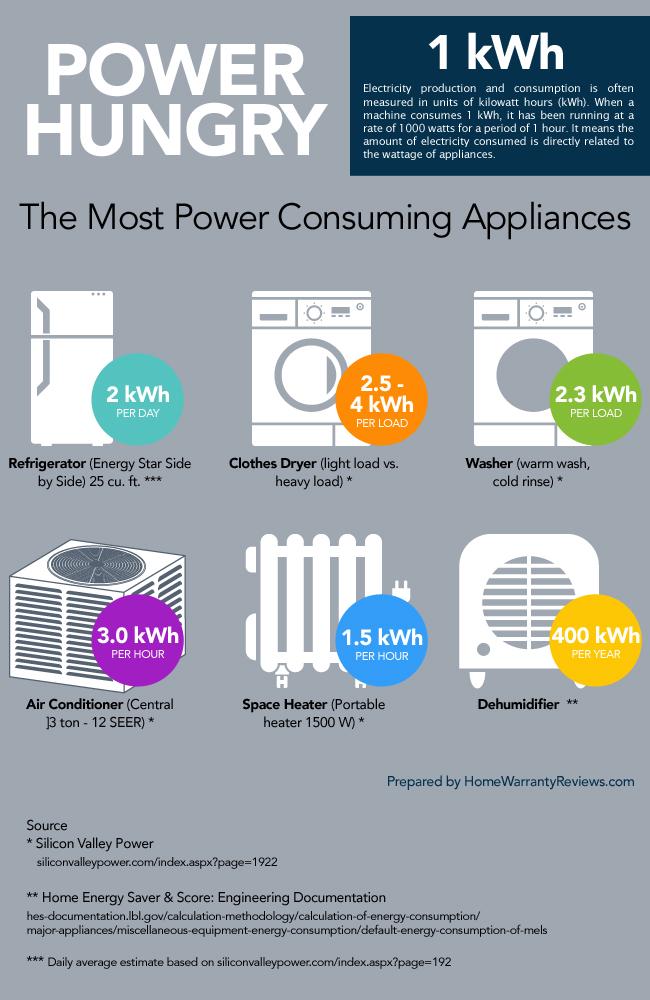
In the modern world, electricity powers our lives. From the lights that illuminate our homes to the appliances that simplify our daily routines, understanding the energy consumption of these devices is crucial for both financial and environmental sustainability. This article delves into the average wattage of common household appliances, offering insights into their energy usage and the potential for energy savings.
Wattage: A Measure of Power Consumption
Wattage, measured in watts (W), represents the rate at which an electrical device consumes energy. A higher wattage indicates greater power consumption and, consequently, higher energy costs. Understanding the wattage of different appliances allows consumers to make informed decisions about their energy usage and potentially reduce their electricity bills.
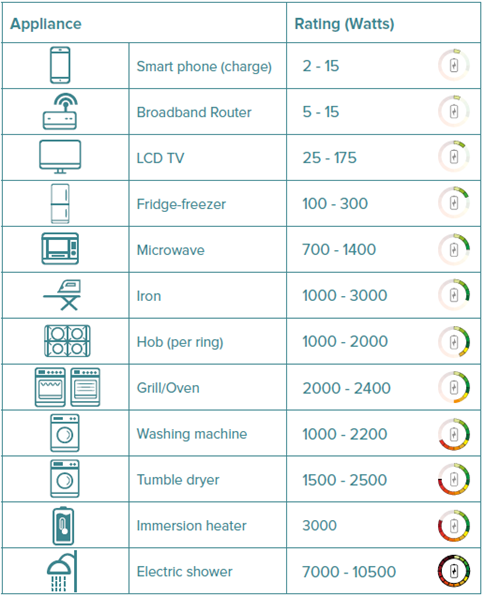
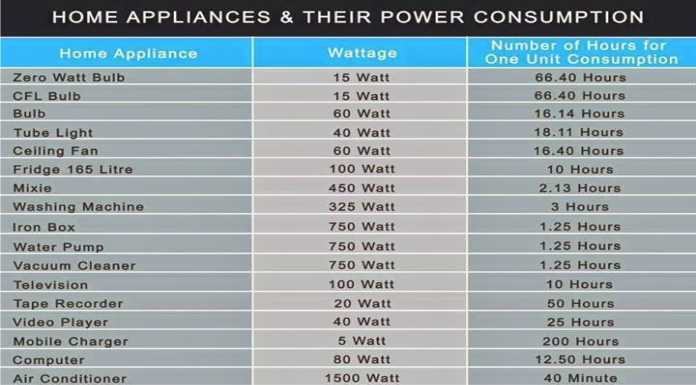
Average Wattage of Common Household Appliances
Lighting:
- Incandescent Light Bulbs: 40-100 W
- Compact Fluorescent Light Bulbs (CFLs): 5-15 W
- Light Emitting Diode (LED) Bulbs: 3-10 W
LED bulbs are significantly more energy-efficient than their incandescent counterparts, consuming significantly less power while providing comparable brightness.
Kitchen Appliances:
- Refrigerator: 100-200 W
- Freezer: 100-250 W
- Dishwasher: 1200-1800 W
- Microwave: 700-1200 W
- Oven: 2500-4000 W
- Stovetop (Electric): 1200-1800 W
- Coffee Maker: 600-1200 W
- Toaster: 800-1200 W
- Blender: 300-700 W
- Food Processor: 400-1000 W
Laundry Appliances:
- Washing Machine: 300-1000 W
- Clothes Dryer: 2000-4000 W
Entertainment and Electronics:
- Television: 50-200 W
- Computer: 100-300 W
- Laptop: 30-60 W
- Game Console: 100-200 W
Other Appliances:
- Hair Dryer: 1000-1800 W
- Vacuum Cleaner: 500-1200 W
- Iron: 1000-1500 W
Factors Influencing Wattage:
- Size and Capacity: Larger appliances generally consume more power. For example, a larger refrigerator will have a higher wattage than a smaller one.
- Features and Technology: Appliances with advanced features, such as energy-saving modes or variable speed settings, may consume less power.
- Usage Patterns: Frequent use of an appliance will result in higher energy consumption.
Benefits of Understanding Appliance Wattage
- Energy Savings: By choosing energy-efficient appliances with lower wattage ratings, consumers can significantly reduce their electricity bills.
- Environmental Impact: Lowering energy consumption contributes to a smaller carbon footprint, reducing greenhouse gas emissions.
- Informed Purchasing Decisions: Knowledge of wattage allows consumers to compare different models and make informed decisions based on their energy needs and budget.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) about Appliance Wattage
Q: How do I find the wattage of my appliances?
A: The wattage rating is typically listed on the appliance’s label or in its user manual.
Q: What is the relationship between wattage and electricity bills?
A: Higher wattage appliances consume more electricity, leading to higher energy bills.
Q: How can I reduce my electricity consumption?
A: Choose energy-efficient appliances with lower wattage ratings, avoid unnecessary use of appliances, and consider using energy-saving modes or features.
Q: Are there any government incentives for purchasing energy-efficient appliances?
A: Some governments offer rebates or tax credits for purchasing energy-efficient appliances. Check with your local energy provider or government agency for available programs.
Tips for Reducing Appliance Wattage and Energy Consumption
- Purchase Energy-Efficient Appliances: Look for appliances with the Energy Star label, which indicates that they meet energy-efficiency standards.
- Unplug Unused Appliances: Even when turned off, some appliances continue to consume a small amount of power. Unplugging them when not in use can save energy.
- Use Appliances Efficiently: Wash full loads of laundry and dishes, avoid preheating the oven unless necessary, and choose the appropriate cooking setting for your needs.
- Maintain Appliances Regularly: Clean filters and coils on appliances like refrigerators and washing machines to ensure optimal performance and energy efficiency.
- Consider Renewable Energy Sources: Explore options like solar panels or wind turbines to generate clean energy for your home.
Conclusion
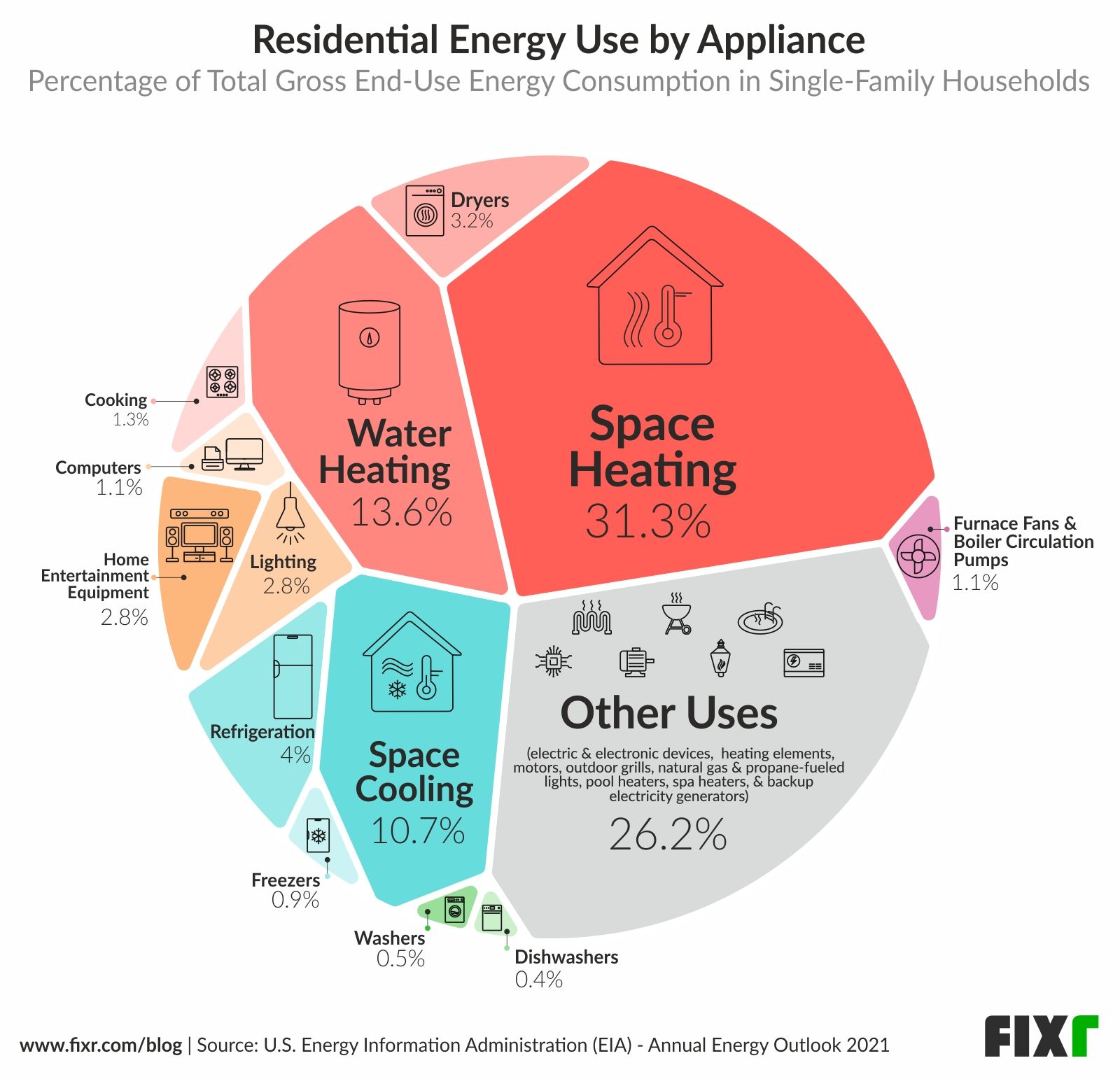
Understanding the average wattage of household appliances is crucial for making informed decisions about energy consumption. By choosing energy-efficient appliances, using them efficiently, and adopting sustainable practices, individuals can significantly reduce their electricity bills, minimize their environmental impact, and contribute to a more sustainable future. The information presented in this article serves as a guide for consumers to make conscious choices about their energy usage and embrace a more energy-conscious lifestyle.

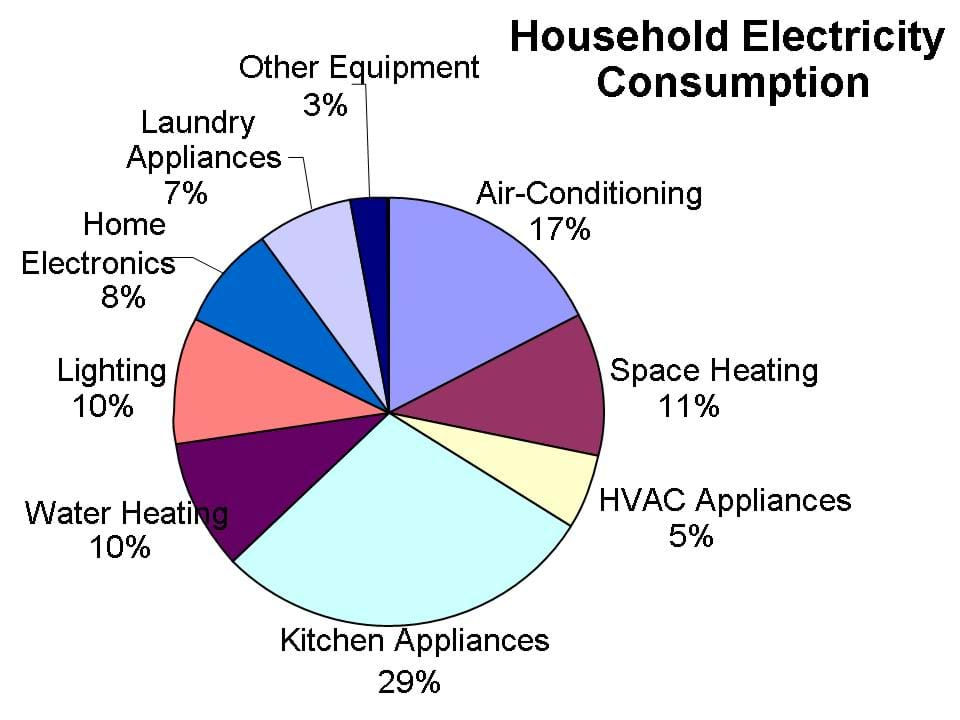

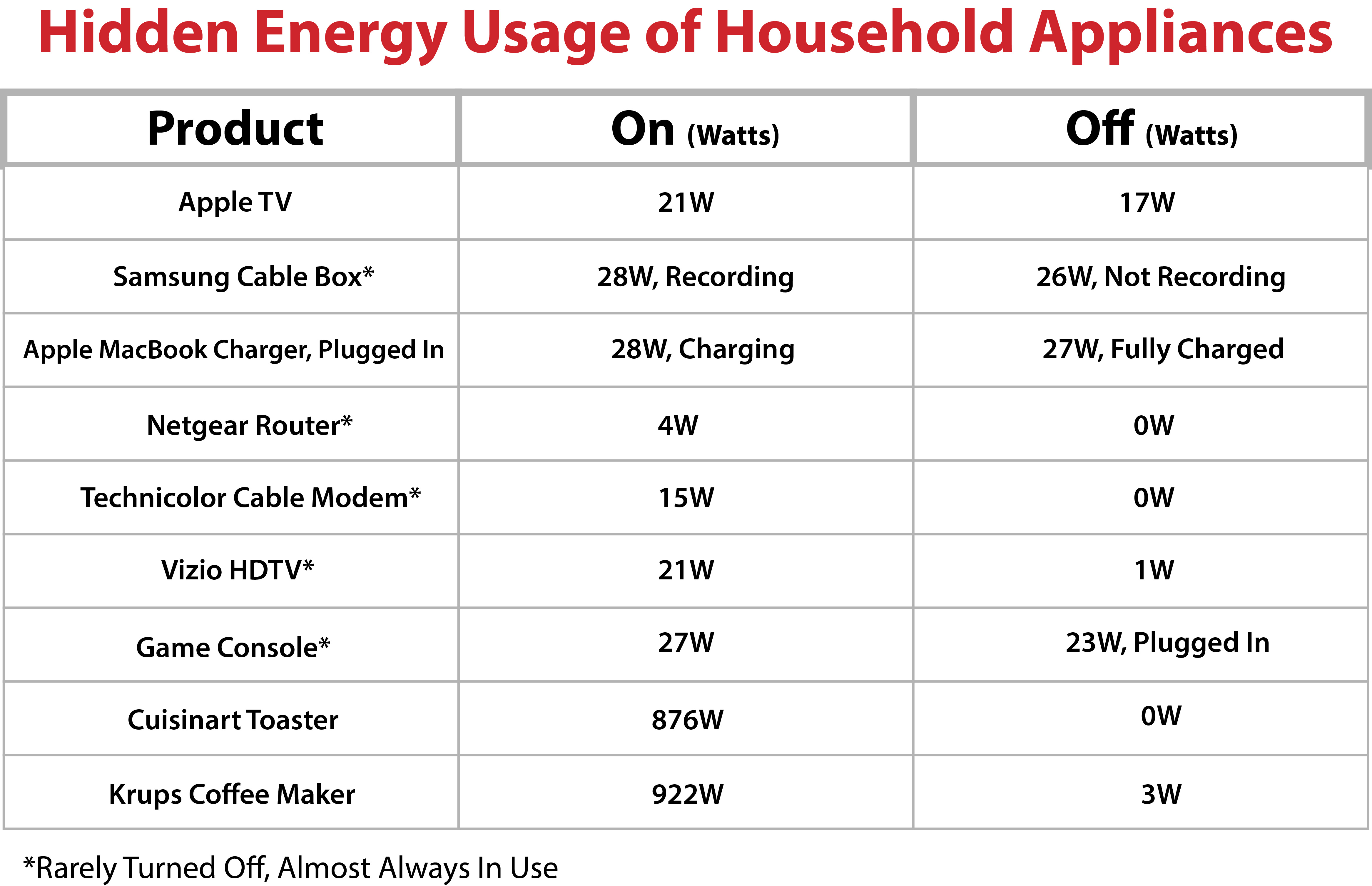
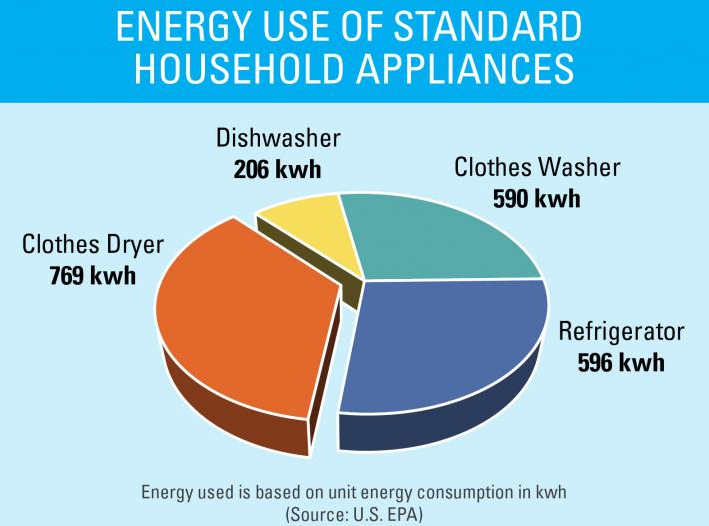
Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Understanding the Power Consumption of Household Appliances: A Guide to Watts and Energy Efficiency. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!