Unpacking The Power We Use: A Comprehensive Look At Average Household Energy Consumption
Unpacking the Power We Use: A Comprehensive Look at Average Household Energy Consumption
Related Articles: Unpacking the Power We Use: A Comprehensive Look at Average Household Energy Consumption
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Unpacking the Power We Use: A Comprehensive Look at Average Household Energy Consumption. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unpacking the Power We Use: A Comprehensive Look at Average Household Energy Consumption
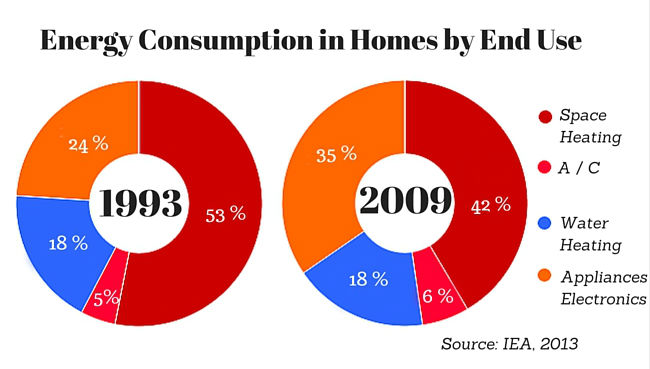
The modern world runs on electricity. From powering our appliances and lighting our homes to fueling our transportation and entertainment, electricity is the lifeblood of contemporary living. Understanding how much energy we consume as individuals and as a collective is crucial for managing resources, minimizing environmental impact, and navigating the complexities of the energy landscape. This article delves into the intricacies of average household power use, exploring its components, factors influencing consumption, and the implications for our energy future.
Defining Average Household Power Use: A Complex Calculation
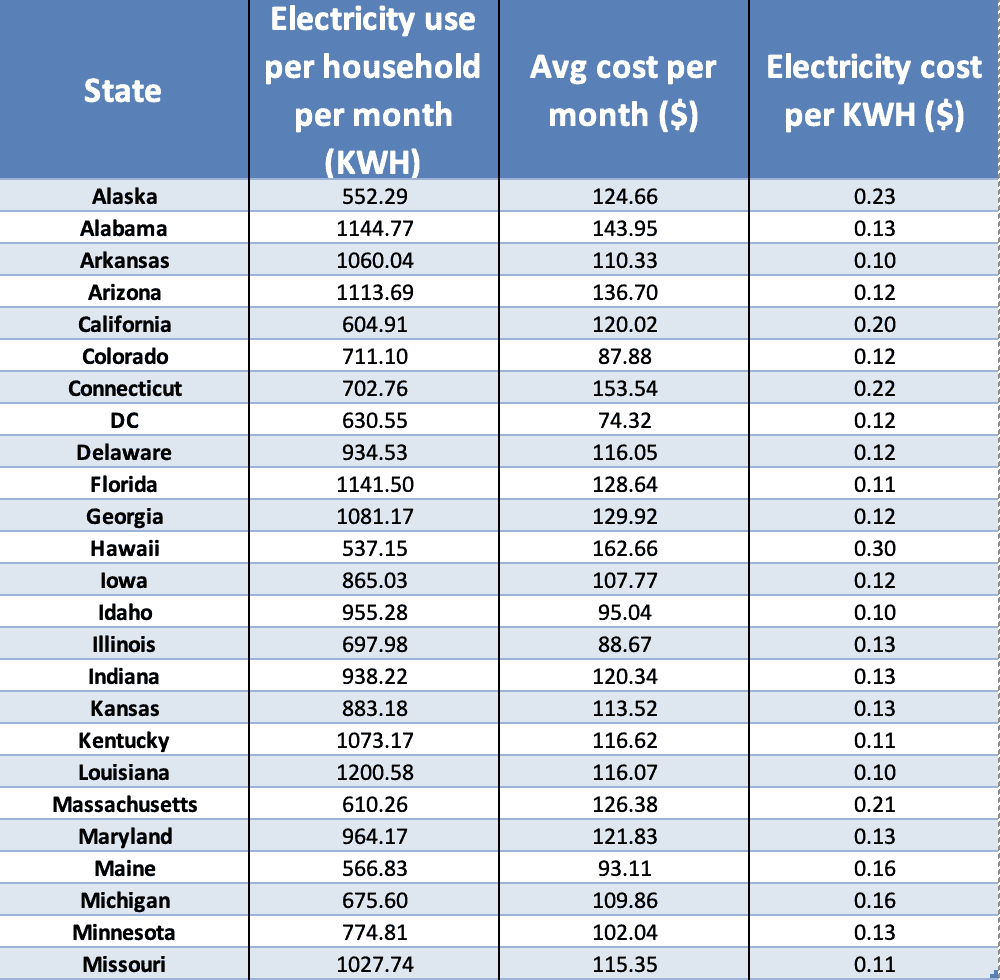
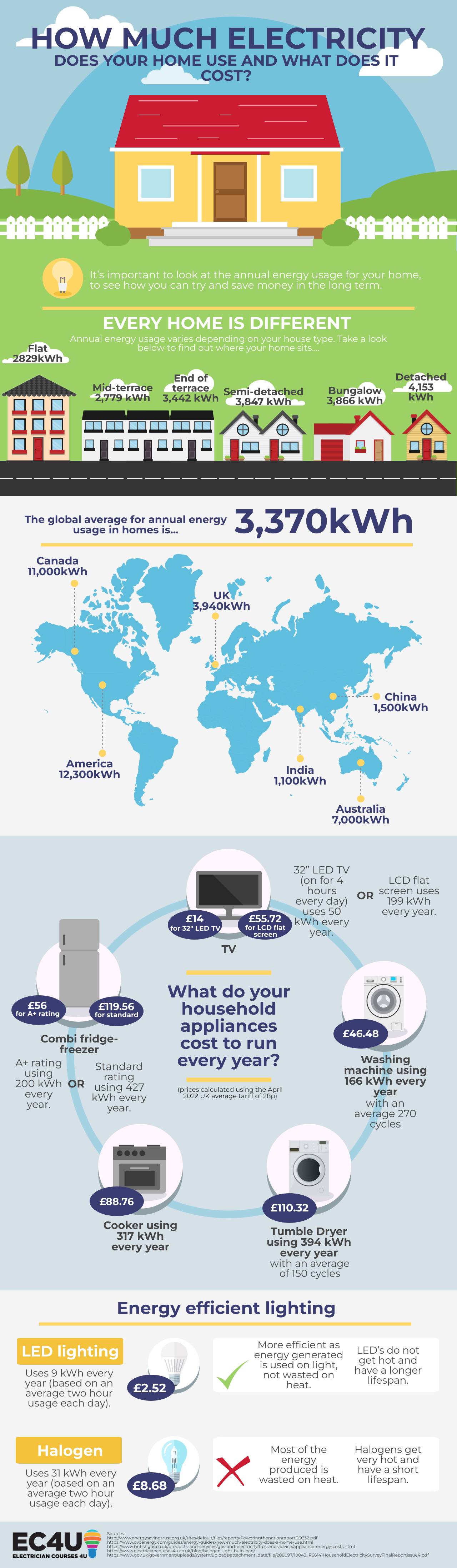
"Average household power use" is a multifaceted concept, encompassing the total amount of electricity consumed by a typical household within a specific timeframe. This average is derived from data collected across various households, considering factors like geographic location, household size, appliance usage patterns, and energy efficiency measures.
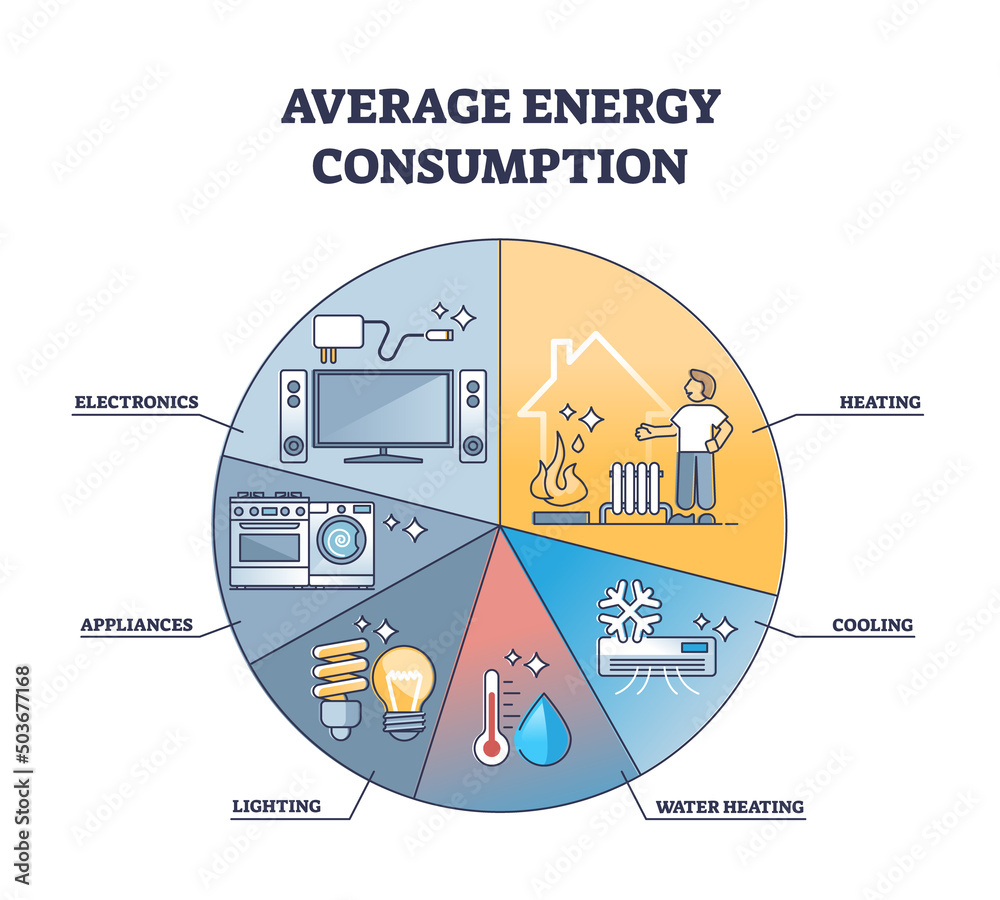
Unveiling the Components: A Breakdown of Energy Consumption
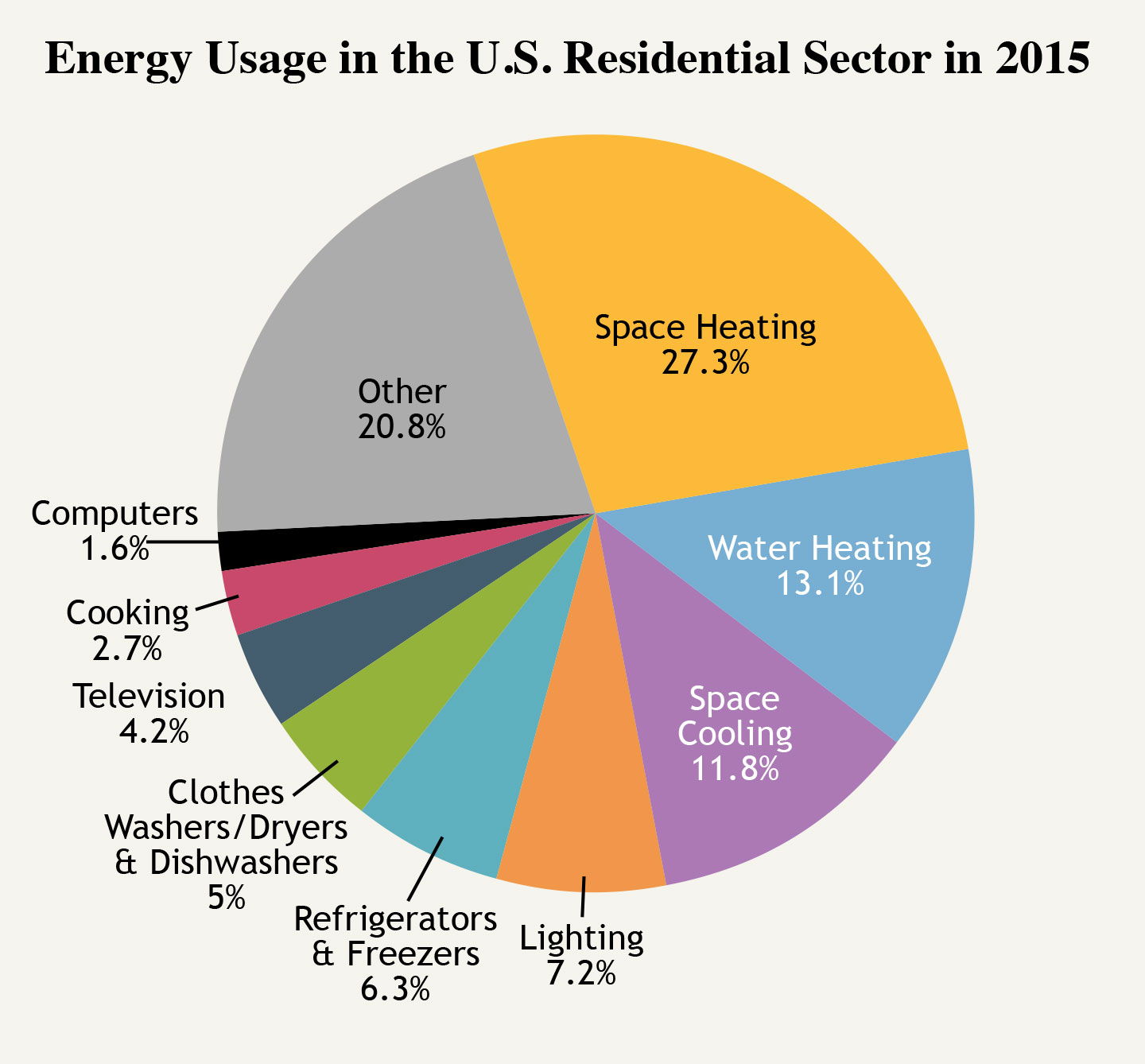
The average household power use is a composite figure representing the energy consumed by a multitude of appliances and systems. Here is a breakdown of the major contributors:
1. Heating and Cooling: Climate, home insulation, and heating/cooling system efficiency are key drivers of energy consumption in this category. Heating, especially in colder regions, can account for a significant portion of a household’s energy usage.
2. Water Heating: Hot water is essential for daily tasks like showering, dishwashing, and laundry. The efficiency of water heaters, along with water usage habits, significantly impacts energy consumption.
3. Appliances: Refrigerators, freezers, ovens, dishwashers, washing machines, dryers, and other appliances consume varying amounts of energy depending on their efficiency rating and usage patterns.
4. Lighting: While modern LED bulbs are significantly more energy-efficient than older incandescent bulbs, lighting still contributes to overall energy consumption.
5. Electronics: Computers, televisions, gaming consoles, and other electronic devices consume energy even when not actively in use. The amount of energy consumed varies depending on the device’s power consumption and usage patterns.
6. Other Uses: Energy consumption also includes contributions from miscellaneous sources like outdoor lighting, garage door openers, and electric vehicle charging.
Factors Influencing Average Household Power Use: A Multifaceted Picture
The average household power use is not a static figure. It is influenced by a range of factors, including:
1. Climate and Location: The climate significantly impacts energy consumption, particularly for heating and cooling. Households in colder regions generally use more energy for heating, while those in warmer regions utilize more energy for cooling.
2. Household Size and Demographics: Larger households naturally consume more energy due to increased appliance usage, heating/cooling needs, and overall activity.
3. Housing Structure and Insulation: Well-insulated homes with energy-efficient windows and doors lose less heat in winter and gain less heat in summer, reducing the need for heating and cooling.
4. Appliance Efficiency: The efficiency of appliances like refrigerators, washing machines, and dishwashers directly impacts energy consumption. Older, less efficient appliances consume more energy than newer, energy-efficient models.
5. Usage Patterns: Individual habits and choices significantly influence energy consumption. For example, leaving lights on in empty rooms, running appliances on high settings, and taking long showers all contribute to increased energy use.
6. Energy Prices and Incentives: Fluctuations in energy prices and the availability of incentives like rebates for energy-efficient appliances can influence consumer behavior and energy consumption patterns.
The Importance of Understanding Average Household Power Use
Understanding average household power use is crucial for several reasons:
1. Individual Energy Management: By understanding how much energy they consume, individuals can make informed decisions about their energy usage and identify areas for potential savings.
2. Environmental Sustainability: Reducing energy consumption helps to minimize greenhouse gas emissions and promote a more sustainable future.
3. Financial Savings: Lower energy consumption translates to lower energy bills, saving money for households.
4. Energy Policy and Infrastructure: Data on average household power use provides valuable insights for policymakers and energy companies to develop effective energy policies and infrastructure.
5. Technological Advancements: Understanding energy consumption patterns drives innovation in energy efficiency technologies and renewable energy solutions.
FAQs about Average Household Power Use
1. How much energy does the average household use?
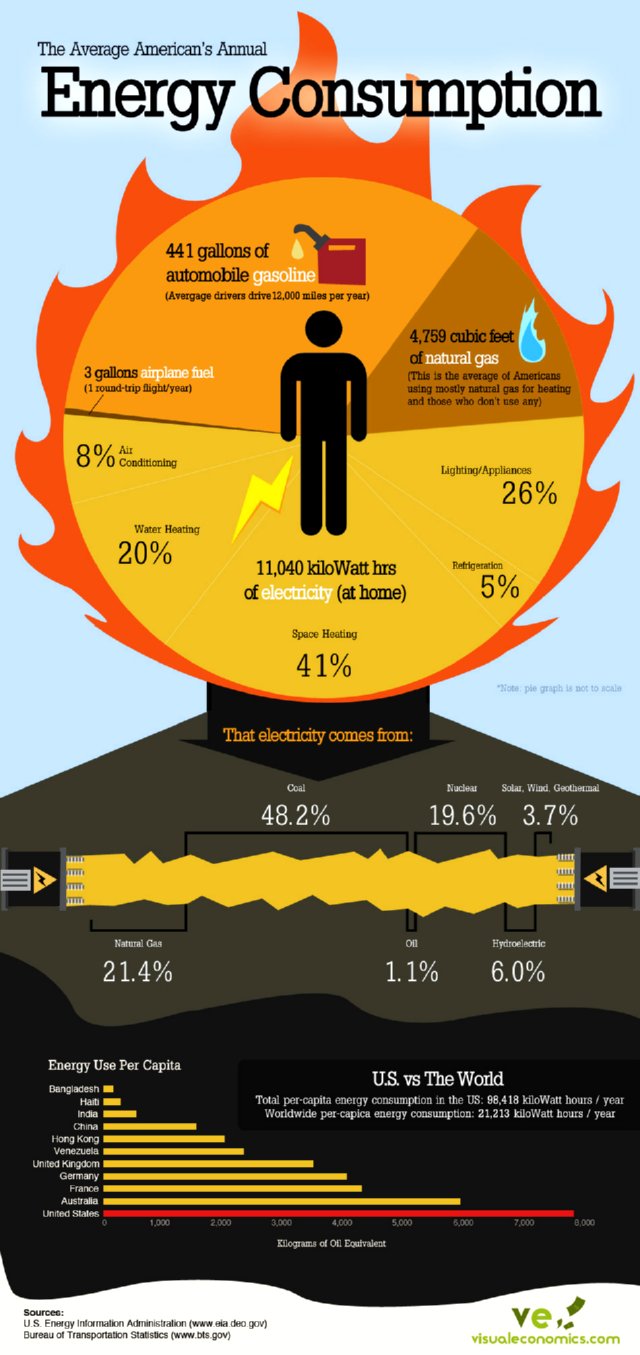
The average household power use in the United States is approximately 10,715 kilowatt-hours (kWh) per year. However, this figure can vary significantly depending on the factors mentioned earlier.
2. What are the most energy-intensive appliances in a household?
Heating and cooling systems, water heaters, refrigerators, and ovens are generally the most energy-intensive appliances in a household.
3. How can I reduce my household energy consumption?
There are several ways to reduce household energy consumption, including:
- Improving insulation: Proper insulation can significantly reduce heating and cooling costs.
- Using energy-efficient appliances: Replacing older appliances with newer, energy-efficient models can save energy and money.
- Adjusting thermostat settings: Lowering the thermostat in winter and raising it in summer can reduce energy consumption.
- Conserving water: Taking shorter showers, fixing leaks, and using water-efficient appliances can reduce the energy required for water heating.
- Unplugging electronics: Unplugging electronics when not in use can reduce phantom energy consumption.
4. What are the benefits of using renewable energy sources?
Renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind power, offer several benefits:
- Environmental sustainability: They produce clean energy without emitting greenhouse gases.
- Reduced reliance on fossil fuels: They contribute to energy independence and reduce dependence on fossil fuels.
- Economic benefits: They create jobs in the renewable energy sector and can lower energy costs for consumers.
5. What are some future trends in household energy consumption?
Future trends in household energy consumption are likely to be influenced by:
- Growing adoption of electric vehicles: As electric vehicles become more prevalent, household energy consumption is expected to increase due to charging needs.
- Increased use of smart home technologies: Smart home technologies can optimize energy consumption by controlling appliances and systems based on real-time data.
- Continued development of renewable energy sources: Advancements in renewable energy technologies are expected to lead to greater adoption and reduced reliance on fossil fuels.
Tips for Reducing Average Household Power Use
1. Conduct an Energy Audit: An energy audit can identify areas for improvement in your home’s energy efficiency.
2. Optimize Heating and Cooling Systems: Ensure your heating and cooling systems are properly sized and maintained for optimal efficiency.
3. Upgrade Appliances: Consider replacing older, less efficient appliances with newer, energy-efficient models.
4. Adopt Energy-Saving Habits: Turn off lights when leaving a room, unplug electronics when not in use, and take shorter showers to reduce energy consumption.
5. Utilize Natural Light: Maximize natural light in your home by opening curtains and blinds during the day to reduce reliance on artificial lighting.
6. Install a Programmable Thermostat: A programmable thermostat can automatically adjust temperatures based on your schedule, reducing energy consumption.
7. Explore Renewable Energy Options: Consider installing solar panels or wind turbines to generate clean energy for your home.
8. Participate in Energy Efficiency Programs: Many utilities offer programs and incentives to encourage energy efficiency, such as rebates for energy-efficient appliances.
Conclusion
Average household power use is a critical indicator of our energy consumption habits and the impact we have on the environment. By understanding the factors that influence energy consumption and adopting energy-efficient practices, we can reduce our environmental footprint, save money, and contribute to a more sustainable energy future. The journey towards a more efficient and sustainable energy landscape requires continuous effort and innovation, both at the individual and societal levels. By making informed choices and embracing new technologies, we can collectively reduce our energy consumption and pave the way for a greener and more prosperous future.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unpacking the Power We Use: A Comprehensive Look at Average Household Energy Consumption. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!