Unveiling The Secrets Of Electromagnetic Waves: A Journey Of Exploration
Unveiling the Secrets of Electromagnetic Waves: A Journey of Exploration
Related Articles: Unveiling the Secrets of Electromagnetic Waves: A Journey of Exploration
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Secrets of Electromagnetic Waves: A Journey of Exploration. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling the Secrets of Electromagnetic Waves: A Journey of Exploration

Electromagnetic (EM) waves, ubiquitous in our modern world, are a fascinating phenomenon that underpins numerous technologies and influences our daily lives in profound ways. From the light we see to the radio waves that connect us, EM waves permeate our existence, carrying information and energy across vast distances. Understanding their nature and behavior is crucial for unlocking their potential and harnessing their power for advancements in various fields.
Exploring the Nature of Electromagnetic Waves
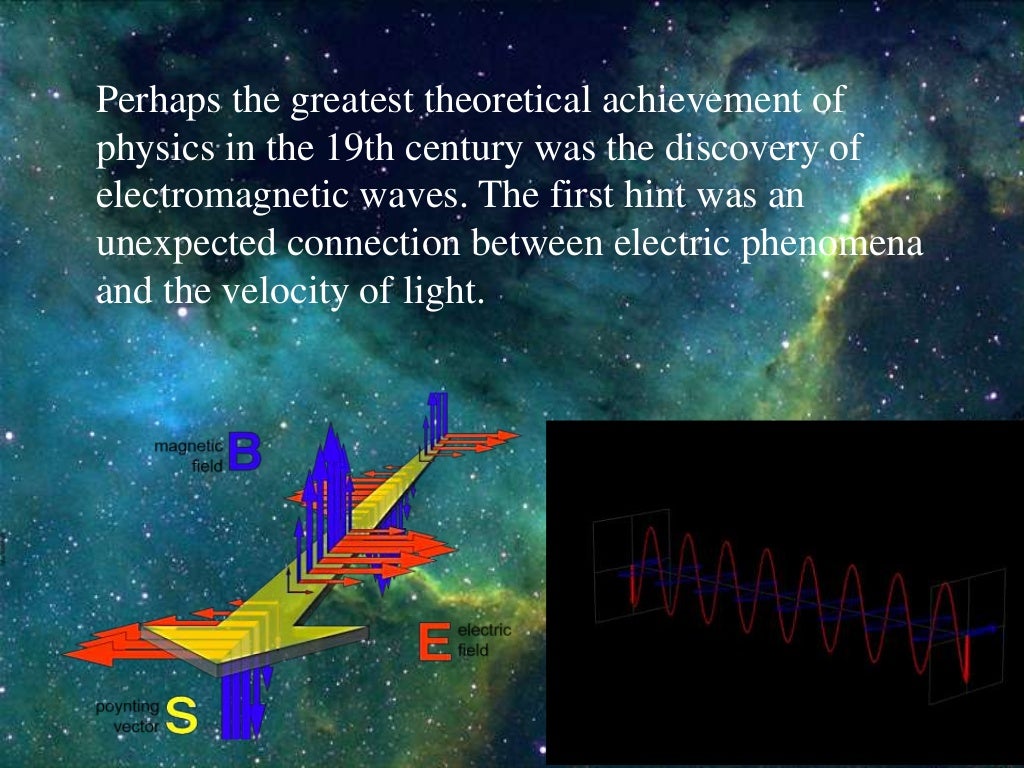
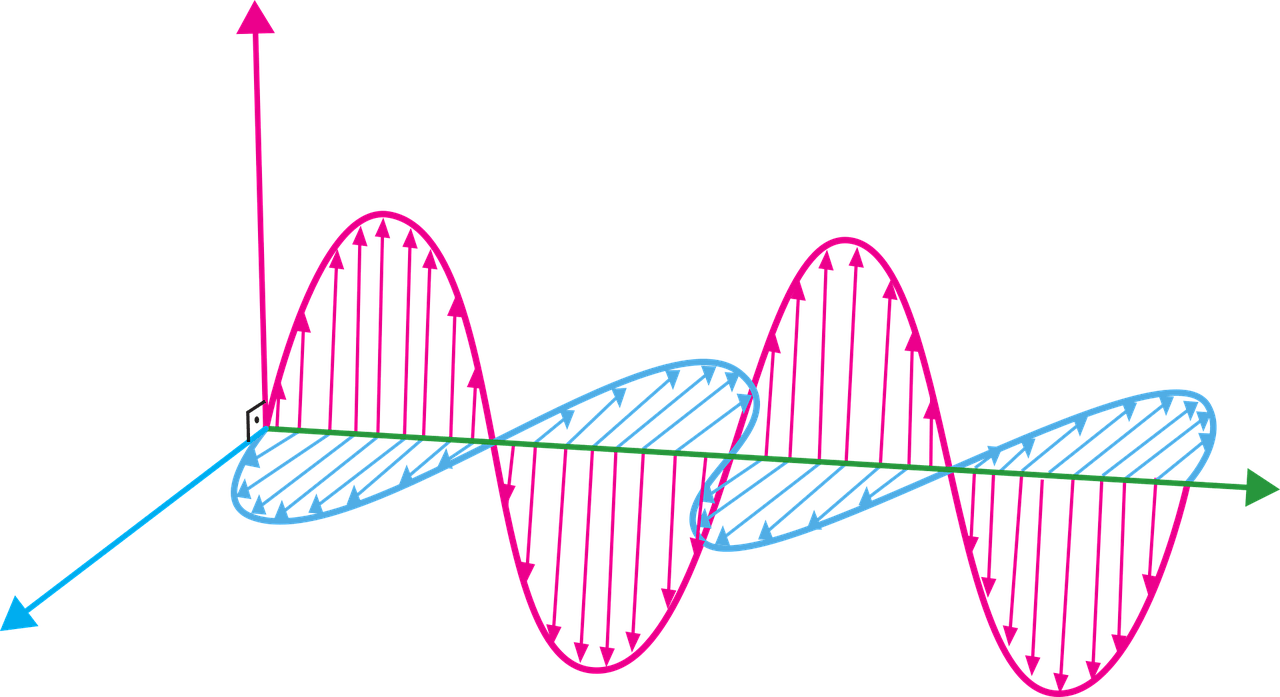
EM waves are a form of energy that propagates through space as oscillating electric and magnetic fields. These fields are perpendicular to each other and to the direction of wave propagation, forming a self-sustaining wave that travels at the speed of light. The frequency of the wave, which determines the energy it carries, dictates its classification within the electromagnetic spectrum.
The Electromagnetic Spectrum: A Diverse Range of Waves
The electromagnetic spectrum encompasses a vast range of frequencies, each with unique characteristics and applications. From the low-frequency radio waves used for communication to the high-energy gamma rays employed in medical imaging, the spectrum offers a diverse palette of tools for scientific exploration and technological innovation.
Radio Waves: The Backbone of Communication
Radio waves, the longest wavelength EM waves, are the foundation of wireless communication. They are used for broadcasting, mobile phone networks, satellite communication, and radar systems. Their long wavelengths allow them to travel long distances and penetrate obstacles, making them ideal for communication across vast areas.
Microwaves: Heating and Communication
Microwaves, with wavelengths ranging from millimeters to meters, are used for heating food in microwave ovens and for transmitting data in satellite communication and Wi-Fi networks. Their ability to penetrate food and heat water molecules makes them effective for cooking, while their high frequency allows for high bandwidth communication.
Infrared Radiation: Heat and Sensing
Infrared radiation, with wavelengths longer than visible light, is associated with heat. It is used in night vision devices, thermal imaging, and remote sensing applications. Infrared radiation is emitted by all objects with a temperature above absolute zero, making it a valuable tool for detecting and analyzing heat signatures.
Visible Light: The Spectrum of Colors
Visible light, the narrow band of the electromagnetic spectrum that our eyes can perceive, is responsible for our perception of color. It is crucial for photosynthesis, photography, and visual communication. The different colors within the visible spectrum correspond to different wavelengths, with red having the longest and violet the shortest.
Ultraviolet Radiation: Energy and Health
Ultraviolet (UV) radiation, with wavelengths shorter than visible light, carries more energy and can be harmful to living organisms. It is responsible for sunburns and skin cancer, but it also plays a role in vitamin D production and is used in sterilization and disinfection processes.
X-rays: Imaging and Medical Applications
X-rays, with even shorter wavelengths than UV radiation, have high penetrating power and are used in medical imaging, airport security, and industrial inspection. Their ability to pass through soft tissues but be absorbed by bones allows them to provide detailed images of internal structures.
Gamma Rays: High Energy and Medical Applications
Gamma rays, the highest energy EM waves, are produced by radioactive decay and nuclear reactions. They have the highest penetrating power and are used in medical treatment, sterilization, and industrial applications. Gamma rays are also used in astronomy to study distant objects and celestial events.
Activity: Exploring the Electromagnetic Spectrum
To gain a deeper understanding of the electromagnetic spectrum and the diverse applications of EM waves, engage in the following activity:
Materials:
- A radio
- A microwave oven
- A thermometer
- A flashlight
- A UV lamp (optional)
- A Geiger counter (optional)
Procedure:
- Radio Waves: Tune a radio to different stations and observe the varying frequencies and wavelengths of the radio waves used for broadcasting.
- Microwaves: Place a cup of water in a microwave oven and observe the heating effect of microwaves on water molecules.
- Infrared Radiation: Use a thermometer to measure the temperature of different objects, such as a light bulb, a computer, or a window.
- Visible Light: Shine a flashlight on different objects and observe the reflection and absorption of light.
- Ultraviolet Radiation: If available, use a UV lamp to observe the fluorescence of certain materials.
- X-rays: If available, use a Geiger counter to detect the presence of X-rays.
- Gamma Rays: If available, use a Geiger counter to detect the presence of gamma rays from a radioactive source.
Observations and Analysis:
- Note the different frequencies and wavelengths of the EM waves used in each activity.
- Observe the effects of the waves on different materials and objects.
- Research the applications of each type of EM wave in various fields.
- Discuss the potential benefits and risks associated with each type of EM wave.
Benefits and Importance of Understanding Electromagnetic Waves
Understanding the nature and behavior of EM waves is crucial for advancing technology, improving healthcare, and enhancing our understanding of the universe.
Technological Advancements:
- Communication: EM waves are the foundation of wireless communication, enabling us to connect with people and devices across the globe.
- Navigation: GPS systems rely on radio waves to pinpoint our location and guide us.
- Imaging: X-rays and MRI scans provide detailed images of internal structures, revolutionizing medical diagnosis and treatment.
- Remote Sensing: Satellites use various EM waves to monitor Earth’s environment, weather patterns, and natural resources.
Healthcare and Medicine:
- Medical Imaging: X-rays, CT scans, and MRI scans allow doctors to diagnose and treat diseases more effectively.
- Cancer Treatment: Radiation therapy uses gamma rays to target and destroy cancerous cells.
- Sterilization: UV radiation is used to sterilize medical equipment and prevent infections.
Scientific Exploration:
- Astronomy: EM waves from distant stars and galaxies provide valuable information about the universe’s composition, age, and evolution.
- Materials Science: EM waves are used to study the properties of materials at the atomic and molecular level.
FAQs about Electromagnetic Waves:
Q: Are electromagnetic waves dangerous?
A: Some types of EM waves, such as ultraviolet radiation and gamma rays, can be harmful to living organisms. However, the amount of exposure and the type of radiation determine the level of risk.
Q: How are electromagnetic waves used in everyday life?
A: EM waves are used in numerous everyday applications, including communication, heating, lighting, and medical imaging.
Q: What are the different types of electromagnetic waves?
A: The electromagnetic spectrum encompasses a wide range of waves, including radio waves, microwaves, infrared radiation, visible light, ultraviolet radiation, X-rays, and gamma rays.
Q: How do electromagnetic waves travel through space?
A: EM waves travel through space as oscillating electric and magnetic fields that are perpendicular to each other and to the direction of wave propagation.
Q: What is the speed of light?
A: The speed of light in a vacuum is approximately 299,792,458 meters per second.
Tips for Further Exploration:
- Research the history of electromagnetic wave discovery and the scientists who made significant contributions.
- Explore the applications of EM waves in different fields, such as telecommunications, astronomy, and medicine.
- Participate in workshops or science fairs that focus on electromagnetic waves and their applications.
- Build your own radio antenna or experiment with different types of EM waves using readily available materials.
Conclusion
Electromagnetic waves are a fundamental force in our universe, shaping our technology, influencing our health, and expanding our understanding of the cosmos. By delving into the fascinating world of EM waves, we unlock a wealth of knowledge and potential, paving the way for advancements in various fields and a deeper appreciation of the intricate workings of our world.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Secrets of Electromagnetic Waves: A Journey of Exploration. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!