The Presence of Benzene in Food: A Comprehensive Overview
Related Articles: The Presence of Benzene in Food: A Comprehensive Overview
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to The Presence of Benzene in Food: A Comprehensive Overview. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Presence of Benzene in Food: A Comprehensive Overview

Benzene, a colorless, flammable liquid with a sweet odor, is a ubiquitous chemical found naturally in crude oil and coal tar. While it plays a crucial role in various industrial processes, benzene is classified as a human carcinogen by the International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC). Its presence in food, even at low levels, raises concerns about potential health risks. This article aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of benzene in food, its sources, potential health implications, and regulatory measures in place to minimize exposure.
Sources of Benzene in Food:
Benzene contamination in food primarily stems from two main sources:
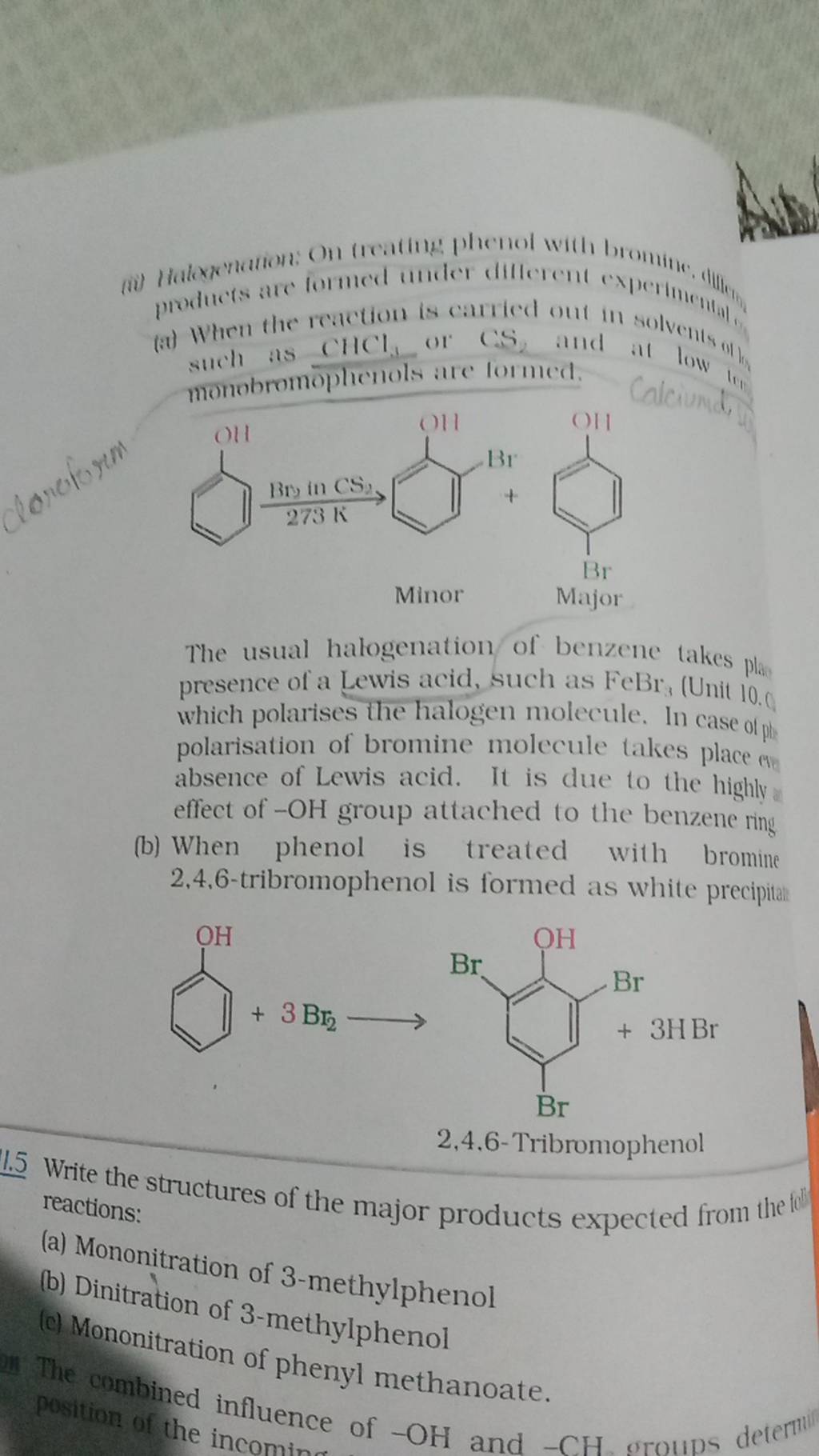
1. Packaging Materials:
- Polystyrene: Polystyrene, a widely used material for food packaging, can leach benzene into food, especially when exposed to heat, light, or prolonged storage. This is particularly relevant for food items like takeaway containers, disposable cups, and food trays.
- Other Plastics: While not as common as polystyrene, other plastic materials like polyethylene terephthalate (PET) and polyvinyl chloride (PVC) can also release small amounts of benzene into food, albeit at lower levels.
2. Food Processing and Storage:
- Smoking and Drying: Traditional methods of food preservation like smoking and drying can lead to benzene formation. The burning of wood or other materials during smoking releases benzene, which can be absorbed by the food.
- High-Temperature Cooking: Cooking food at high temperatures, especially when using oils or fats, can lead to the formation of benzene as a byproduct of chemical reactions.
- Irradiation: Food irradiation, a process used to extend shelf life and eliminate harmful bacteria, can also generate small amounts of benzene.
Health Implications of Benzene Exposure:
Benzene is a known human carcinogen, meaning it can cause cancer. Prolonged exposure to benzene, even at low levels, can increase the risk of developing various types of cancer, including leukemia, lymphoma, and multiple myeloma.
Furthermore, benzene can also have other adverse health effects:
- Damage to Bone Marrow: Benzene can suppress bone marrow function, leading to a decrease in blood cell production, potentially resulting in anemia and immune system deficiencies.
- Reproductive Effects: Exposure to benzene has been linked to reproductive issues, including infertility and birth defects.
- Cardiovascular Issues: Some studies suggest a possible association between benzene exposure and an increased risk of cardiovascular diseases.
Regulatory Measures and Monitoring:
Recognizing the potential health risks associated with benzene, several regulatory bodies worldwide have established maximum allowable limits for benzene in food and food packaging materials.
- The United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA): The FDA has set an action level for benzene in food, meaning that if levels exceed this limit, the agency will take action to reduce exposure.
- The European Food Safety Authority (EFSA): EFSA has established guidelines for benzene levels in food and packaging materials, providing recommendations for safe levels of exposure.
- Other International Organizations: Similar regulations and monitoring programs are implemented by other international organizations, including the World Health Organization (WHO) and the Codex Alimentarius Commission.
Minimizing Exposure to Benzene in Food:
While it’s impossible to completely eliminate benzene exposure, consumers can take certain steps to minimize their intake:
- Choose Alternatives to Polystyrene: Opt for food containers made from glass, ceramic, or stainless steel.
- Avoid Overheating Food in Plastic: Avoid using plastic containers for storing or heating food, especially at high temperatures.
- Limit Processed and Smoked Foods: Reduce consumption of heavily processed foods, smoked meats, and other products that may contain higher levels of benzene.
- Follow Storage Instructions: Store food according to manufacturer instructions to minimize the risk of benzene leaching from packaging materials.
FAQs about Benzene in Food:
Q: Is benzene present in all foods?
A: No, benzene is not present in all foods. It is primarily found in foods that have been processed, packaged, or stored in ways that can lead to benzene formation or contamination.
Q: How much benzene is safe to consume?
A: There is no safe level of benzene exposure, as any amount can potentially increase the risk of cancer. However, regulatory bodies set maximum allowable limits to minimize exposure and protect public health.
Q: Are there any symptoms of benzene poisoning?
A: Symptoms of acute benzene poisoning can include dizziness, headache, nausea, vomiting, and loss of consciousness. Chronic exposure can lead to more serious health issues like anemia, leukemia, and other cancers.
Q: How can I test my food for benzene?
A: Testing for benzene in food requires specialized equipment and laboratory analysis. Consumers typically rely on regulatory agencies to monitor and ensure safe levels of benzene in food products.
Q: Is it safe to eat food that has been stored in a polystyrene container?
A: While polystyrene can leach benzene into food, the levels are generally low. However, it’s best to avoid using polystyrene containers for storing or heating food, especially for extended periods.
Conclusion:
Benzene is a potentially harmful chemical that can be found in food, primarily due to packaging materials and certain food processing techniques. While regulatory measures are in place to limit exposure, consumers can play an active role in minimizing their intake by choosing alternative packaging materials, avoiding high-temperature cooking in plastic, and limiting consumption of processed and smoked foods. By understanding the sources and potential health risks associated with benzene, individuals can make informed choices to protect their health and well-being.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Presence of Benzene in Food: A Comprehensive Overview. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/household_income.aspfinal-dddb0f870b8e4195993e0a9fa2c2fa20.jpg)















.jpg)

















![3D Printer Materials Guide 2020 [Everything You Need To Know]](https://www.3dbeginners.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/05/3d-printing-materials.jpg)
















:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/frontgate-catalog-3d7aea2897c2498f9b26b79e3bb6b650.jpg)