Exploring the Alkaline Side: Common Household Bases and Their pH
Related Articles: Exploring the Alkaline Side: Common Household Bases and Their pH
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Exploring the Alkaline Side: Common Household Bases and Their pH. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Exploring the Alkaline Side: Common Household Bases and Their pH

The world around us is a delicate balance of acids and bases, each playing a crucial role in various chemical reactions. While acids are known for their sour taste and corrosive nature, bases, also known as alkalis, exhibit properties that are often less familiar. However, bases are equally important in our daily lives, contributing to a wide range of applications from cleaning and cooking to personal care and industrial processes.
This article delves into the world of common household bases, exploring their pH values, properties, and uses, highlighting their significance in our everyday lives.
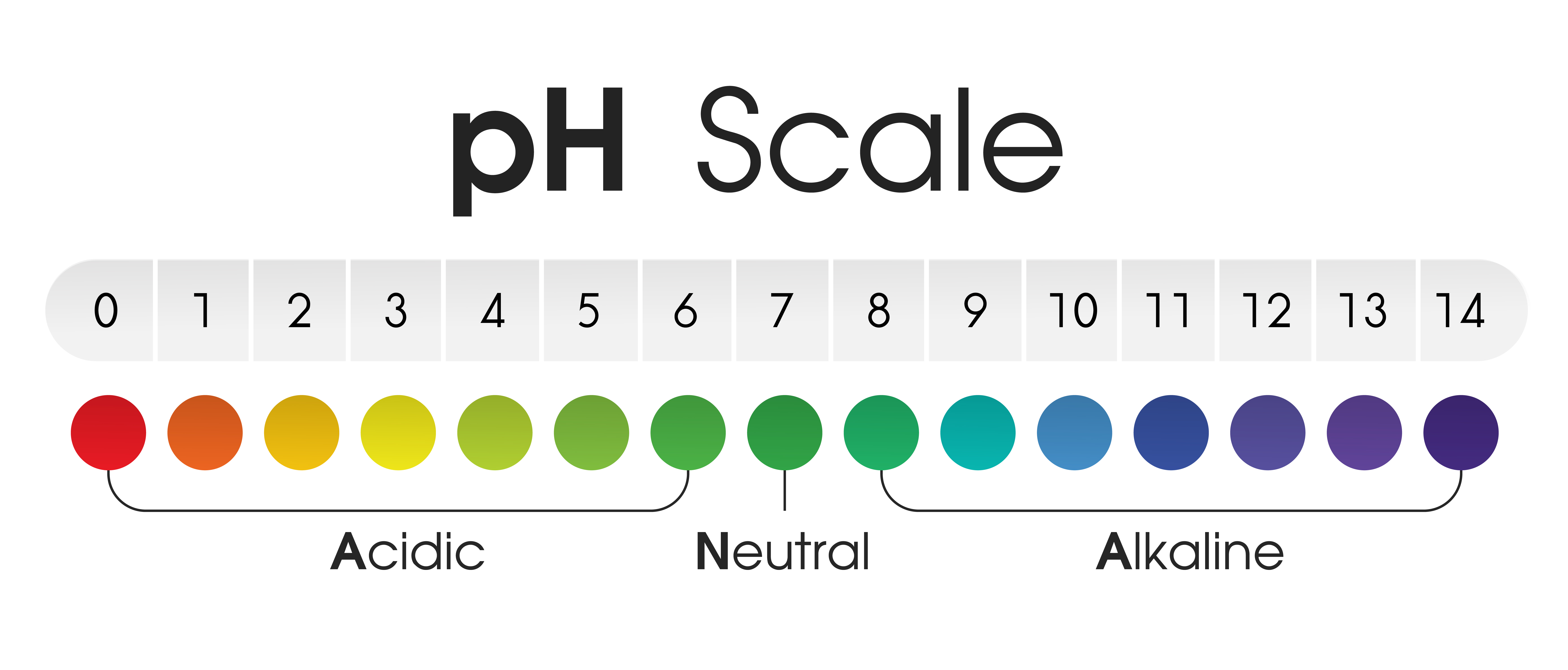
Understanding pH and the pH Scale
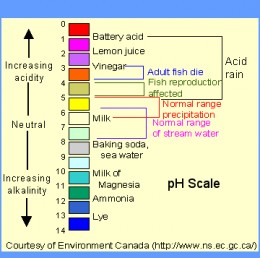
The pH scale is a numerical measure of the acidity or alkalinity of a solution. It ranges from 0 to 14, with 7 representing neutral. Solutions with a pH less than 7 are acidic, while those with a pH greater than 7 are basic or alkaline.
The pH scale is logarithmic, meaning that each whole number change in pH represents a tenfold change in acidity or alkalinity. For instance, a solution with a pH of 3 is ten times more acidic than a solution with a pH of 4, and a hundred times more acidic than a solution with a pH of 5.
Common Household Bases and Their pH Values
Several common household products contain bases, each with its own unique pH value and properties.
1. Baking Soda (Sodium Bicarbonate):
- pH: Approximately 8.3
- Properties: Mildly alkaline, commonly used as a leavening agent in baking, a cleaning agent, and a deodorizer.
- Uses: Baking, cleaning surfaces, deodorizing refrigerators, neutralizing acids (e.g., in insect bites or spills).
2. Washing Soda (Sodium Carbonate):
- pH: Approximately 11.5
- Properties: Highly alkaline, used in laundry detergents and cleaning agents.
- Uses: Laundry washing, cleaning hard water stains, removing grease and grime.
3. Ammonia (NH3):
- pH: Approximately 11.5
- Properties: Strong base, highly volatile, used in cleaning products and fertilizers.
- Uses: Cleaning surfaces, removing stains, loosening dirt, degreasing.
4. Borax (Sodium Borate):
- pH: Approximately 9.5
- Properties: Mildly alkaline, used in laundry detergents, cleaning products, and as an insecticide.
- Uses: Laundry washing, cleaning surfaces, controlling pests, creating slime.
5. Lye (Sodium Hydroxide):
- pH: Approximately 13.5
- Properties: Strong base, highly corrosive, used in drain cleaners and soap making.
- Uses: Drain cleaning, soap making, chemical processing.
6. Calcium Hydroxide (Lime):
- pH: Approximately 12.5
- Properties: Strong base, used in construction materials, agriculture, and water treatment.
- Uses: Mortar and cement production, soil pH adjustment, water purification.
7. Soap:
- pH: Varies depending on the type, generally between 9 and 11.
- Properties: Contains fatty acids and a base (typically sodium hydroxide or potassium hydroxide), used for cleaning and personal hygiene.
- Uses: Washing hands, bathing, cleaning dishes, laundering clothes.
8. Antacids:
- pH: Varies depending on the type, generally between 7 and 10.
- Properties: Contain bases that neutralize stomach acid, used to relieve heartburn and indigestion.
- Uses: Treating heartburn, indigestion, and acid reflux.
The Importance of pH in Household Bases
The pH of a base determines its strength and effectiveness. Higher pH values indicate stronger alkalinity, which can be beneficial for certain applications, but also pose potential risks.
- Cleaning: Strong bases, like lye, are effective for dissolving grease and grime, making them suitable for drain cleaning and heavy-duty cleaning tasks. However, their corrosive nature requires caution to prevent skin and surface damage.
- Laundry: Laundry detergents often contain bases like washing soda to remove dirt and stains, but excessive alkalinity can damage delicate fabrics.
- Personal Care: Soap and antacids utilize bases to clean and neutralize stomach acid, respectively. However, overuse of certain bases, like harsh soaps, can irritate skin and disrupt the natural pH balance.
FAQs about Common Household Bases
1. Can I mix different household bases together?
Mixing different bases can lead to unexpected reactions, potentially producing heat, toxic fumes, or corrosive substances. It is generally not recommended to mix bases without proper knowledge and precautions.
2. How can I safely handle household bases?
Always wear protective gloves and eye protection when handling bases. Avoid contact with skin and eyes, and work in a well-ventilated area. Store bases in their original containers and keep them out of reach of children and pets.
3. What happens if I accidentally ingest a base?
Ingestion of bases can cause serious burns to the mouth, throat, and digestive system. Immediately contact a poison control center or seek medical attention if you suspect ingestion of a base.
4. How can I neutralize a base spill?
Neutralize a base spill with a weak acid, such as vinegar or lemon juice. Always wear protective gear and work in a well-ventilated area. After neutralization, clean the spill thoroughly with water.
5. What are the benefits of using bases in the home?
Bases offer numerous benefits in the home, including cleaning, laundry, personal care, and food preparation. They can effectively remove dirt, grease, and stains, neutralize acids, and contribute to various chemical reactions.
Tips for Using Common Household Bases
- Read the label: Always read the label carefully and follow the instructions for use and safety precautions.
- Test in a small area: Before using a base on a large surface, test it in a small, inconspicuous area to ensure it does not damage the material.
- Use diluted solutions: For most household applications, it is safer and more effective to use diluted solutions of bases.
- Store properly: Store bases in their original containers, away from heat and moisture.
- Keep out of reach of children: Always store bases out of reach of children and pets.
Conclusion
Common household bases play an essential role in our daily lives, providing solutions for cleaning, laundry, personal care, and other essential tasks. Understanding the properties and uses of these bases, along with their potential risks, is crucial for safe and effective use. By following safety precautions and using them appropriately, we can harness the power of bases to enhance our lives and maintain a clean and healthy environment.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Exploring the Alkaline Side: Common Household Bases and Their pH. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!

























































![Top 11 Common Household Items Toxic to Dogs [2022] Felcana](https://cdn.shopify.com/s/files/1/0014/0915/5142/files/household-items-toxic-to-dogs.png?v=1608220288)














